Graphene-Silver Tungstate Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 22:30

Photocatalysis is a new science. It uses semiconductor photocatalytic materials to obtain cheap and sustainable solar energy from nature, reduce the cost of hydrogen production and decompose various organic pollutants. It has a good application prospect in solving energy crisis and environmental pollution control.
Large Size Tungsten Copper Alloy Preparation by Powder Coating Thermal Deformation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 22:25

Tungsten copper alloys have been widely used in large capacity vacuum circuit breakers and microelectronics due to their excellent properties. Tungsten and copper are mainly used in electrical materials, including electrical contact materials and electrode materials. Tungsten copper alloy sheet has been used in power electronic devices as a new type of electronic packaging material due to its small expansion coefficient and good conductivity and thermal conductivity.
Terbium Doped Zinc Tungstate Long Afterglow Nanomaterials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 22:19

Long afterglow materials refer to materials that can absorb and store energy irradiated by external light, and then release these energy slowly in the form of visible light at room temperature. Long afterglow material is a new type of functional material which meets the development requirements of the 21st century. It has the characteristics of high efficiency, energy saving, green and environmental protection. Its application range has also expanded from lighting, decoration to communication, display and storage.
Tungsten Reinforced Aluminum Composites
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 17:56

Aluminum matrix composites have the advantages of low density, high tensile strength, high modulus of elasticity and high wear resistance. Therefore, aluminium matrix composites have great application potential in aviation and aeronautics.
Porous Tungsten Trioxide Nano Materials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 17:33

Tungsten trioxide is a semiconductor nanomaterial with indirect band gap transition. It has good photoelectric and gas sensing properties. In order to make full use of the photoelectric properties of tungsten trioxide, porous tungsten trioxide nanomaterials with regular morphology and high specific surface area need to be prepared.
Mechanically Alloyed Heat Treatment to Prepare The Tungsten Silicide Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 13:12

Tungsten silicide (W5Si3) is also known as a tetragonal silicon, which is a kind of tetragonal crystal. It is a very promising high-temperature structural material and electrode material.
Synthesis of Calcium Tungstate Spherical Material by Microwave Irradiation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 03 June 2019 12:46

As an important part of metal tungstate nanomaterials, calcium tungstate nanomaterials have unique crystal structure and remarkable nano-effects, so they have important application value in the field of catalytic oxidation and photochromism.
Tungsten Carbide Preparation-Carbon Aerogel Composite by Microwave Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 31 May 2019 17:59
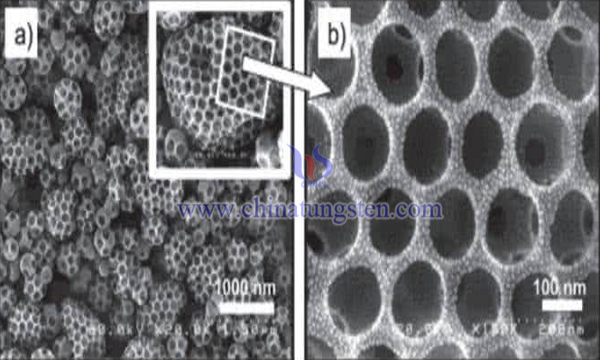
Since Levy and Boudart first disclosed the similarity of catalytic properties between tungsten carbide and platinum in 1973, the catalytic properties of tungsten carbide have aroused great interest in the scientific community. So far, the application of tungsten carbide as a catalyst has been extensively studied experimentally and theoretically. The results show that tungsten carbide has good catalytic performance in a series of noble metal catalytic reactions.
Cadmium Selenide-Bismuth Tungstate Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 31 May 2019 17:51

Cadmium selenide nanocrystals are the most widely studied and promising class of II-VI semiconductor nanocrystals. They have attracted worldwide attention due to their important non-linear optical properties, luminescent properties and other physical and chemical properties.
Nano Zirconium Tungstate Powder Preparation by Coprecipitation Method
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 31 May 2019 17:44

In recent years, in the application of automobile, energy and other fields, materials need to have the properties of corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, heat conduction and so on. Special ceramics are needed to meet the development of its application. Zirconium tungstate material has negative expansion. It has strong isotropic negative thermal expansion effect in the temperature range of 0.3-1050K. Its negative thermal expansion coefficient (NTE) is -9*10-6K-1, which is one of the hotspots in the research of negative expansion materials.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com