Tungsten Carbide Preparation-Carbon Aerogel Composite by Microwave Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 31 May 2019 17:59
Since Levy and Boudart first disclosed the similarity of catalytic properties between tungsten carbide and platinum in 1973, the catalytic properties of tungsten carbide have aroused great interest in the scientific community. So far, the application of tungsten carbide as a catalyst has been extensively studied experimentally and theoretically. The results show that tungsten carbide has good catalytic performance in a series of noble metal catalytic reactions.
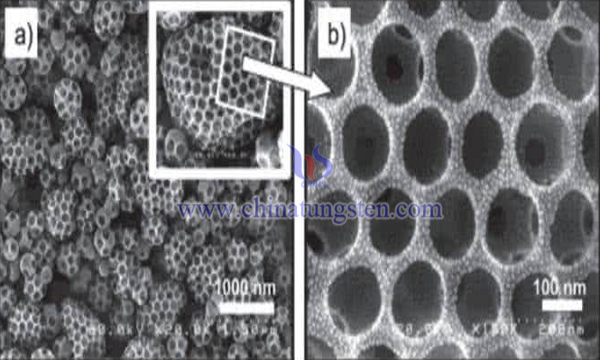
In the field of fuel cell catalysis, because precious metals are rare and expensive, and the source metal of carbides is abundant, it is meaningful to replace precious metals with carbides effectively.
The traditional preparation process of tungsten carbide is inherited from metallurgical industry. It is a direct reaction of metal, metal hydride or metal oxide with a certain proportion of carbon in a reducing atmosphere. The reaction temperature is usually higher than 1200 ℃. The product obtained is of great proportion and fineness. This kind of industrial material has a very low specific surface area and is not suitable for use as catalyst or carrier.
It is found that carbon aerogel is a new lightweight nano porous amorphous carbon material with large specific surface area, wide aperture and good conductivity. Compared with activated carbon, carbon aerogels have high electrical conductivity (about 25 ~ 100S/cm), and remain basically unchanged in a wide temperature range (50 to 300K). The porosity is 80% to 98%, and the typical pore size is less than 50nm. The size of colloidal particles in the network ranges from 3 to 20 nm. As the only aerogel with conductive properties, it has been widely applied in the field of electrochemical energy storage and conversion in fuel cells, electrochemical supercapacitors and lithium ion batteries.
Therefore, the microwave heating method is used to prepare tungsten carbide carbon aerogel composites. It includes the following steps:
Sodium tungstate with 0.42 grams of quality and two phenol in 1.1 grams was dissolved in 20ml water. Then 15ml formaldehyde was added to the water bath at 40 degrees centigrade, then 0.01 grams of sodium carbonate was added. Then placed in a sealed container, the reaction was 24h in 60 degree oven and red brown gel was obtained. After the gel was naturally dried, crushed and ground into a microwave oven with a power of 1000W and a frequency of 2.45GHz, the 20min was heated by alternating microwave heating (35 seconds heating and 5 second intermittently) in a microwave carbon bath, and then the tungsten carbide carbon aerogel composite powder was obtained after cooling.
The results show that the microwave heating process has the advantages of high heating speed, short carbonization time, simple operation, and in situ reaction of tungsten carbide and carbon aerogels. The composites have their own advantages, and enhance the mass transfer effect of the three-phase interface under the condition of good catalytic performance. It has broad application prospects.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com