Tungsten and Molybdenum Separation Strategy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 01 July 2018 17:33

In order to solve the problem of tungsten and molybdenum separation, some scholars have provided a complex amine hydroxamic extractant extraction method for tungsten molybdenum separation in tungsten molybdate solution, to solve the problem of deep separation of tungsten molybdenum with tungstate solution, to prepare a high purity sodium molybdate solution. The purpose of this study is to remove the tungsten in molybdate solution by using solvent extraction, such as hydrogen peroxide oxidation, vulcanizing agent vulcanization and EDTA complexation without adding other steps to prepare high purity molybdate.
Recycle Sodium Hydroxide from Sodium Tungstate Solution
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 22:25

In the existing technology, high alkali pressure cooking technology is commonly used in the smelting of scheelite concentrate and middle ore, and the amount of alkali is generally 2.8 ~ 4 times of the theoretical amount. The mass ratio of excess NaOH and WO3 in the crude sodium tungstate solution after the alkali pressing filter is 0.7 ~ 1.2. If it is not recycled, it has a negative effect on the subsequent process.
Low Grade Tungsten Molybdenum Ore High Efficiency Utilization
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 22:11

After a long time of mining, the quality of China's tungsten and molybdenum have been exhausted, and the effective separation of high requirements on the treatment process, if the preparation of high value-added utilization of low-grade refractory molybdenum mixed concentrate directly of high purity tungsten and molybdenum alloy products, simplify the process, but also can realize the efficient use of difficult to use tungsten and molybdenum resources.
ITER First Wall Protective Coating Material
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 22:02

Pure tungsten material not only has the common properties of general metals, such as conductivity, thermal conductivity, plasticity and metallic luster, but also has high density, high melting point, high thermal conductivity, low vapor pressure, low thermal expansion coefficient, strong absorption ray ability and sputtering threshold, good corrosion resistance and so on. Therefore, the ITER nuclear polymerization is very good. For variable device parts, it is an important material for plasma first wall protective coating.
Scheelite Concentrate Extraction from Tungsten Iron Ore
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 21:43

The existing technology of non-standard materials with low tungsten content is treated by traditional reverberatory furnace or rotary kiln sodium roasting. But roasting has the disadvantages of large consumption of roasting agent, low degree of automation, high energy consumption, low efficiency, high cost, large dust, low recovery rate and great influence on the environment. In the increasingly stringent environmental protection requirements, the development of tungsten iron ore seems to have no future.
Preparation for Tungsten Tubes by Rare Earth Lanthanum Doping
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 21:32

Tungsten tube is a kind of product of many tungsten products. At present, the methods of making tungsten tubes are mostly made of powder metallurgy or chemical vapor deposition. The tungsten tubes obtained by powder metallurgy are easy to crack and have high brittleness when they are installed and used at room temperature. While the chemical vapor deposition process needs to use or produce harmful gas in the process of production, and the environmental protection performance is low.
High Purity Tungsten Material Preparation Improvement
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 21:23

In the microelectronics industry, chips are developing towards high integration, high frequency and ultra I/O terminals. It is urgent to increase the packaging density. The three-dimensional wiring technology of large-scale integrated circuits arises at the historic moment. Tungsten is widely used in gate materials and wiring materials in integrated circuits with good electrical conductivity, escape work, close to silicon, and excellent thermal stability, and good bonding with silicon.
Large Size Thorium Tungsten Strip Manufacturing
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 29 June 2018 21:10
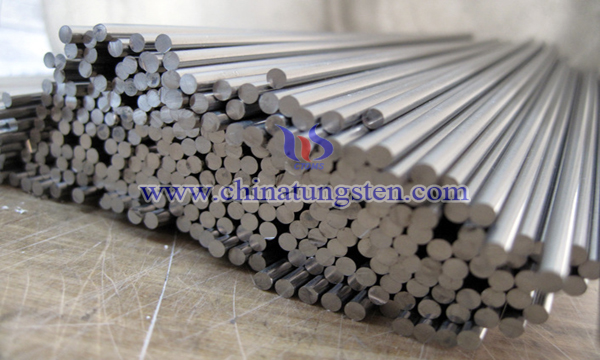
The thorium tungsten electrode is the earliest rare earth tungsten electrode, and it is also the best tungsten electrode with the best welding performance so far. The existing methods for making tungsten strip are: tungsten powder, pressing, presintering and two vertical melt tungsten strips. However, this old technology is only suitable for the manufacture of small size bars. In the process of sintering and sintering of large size thorium tungsten bars, it is easy to cause the problem of the central sporadic large crystals of thorium and tungsten bars and the hidden danger of ThO2 high temperature burning. It is difficult to ensure the uniform distribution of the weight of ThO2 particles in the tungsten base.
Calcium Content Determination in Tungsten Products
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 27 June 2018 22:58

Calcium is one of the harmful elements in tungsten products and must be strictly controlled. The calcium content of tungsten products is generally very low, which is 0.000x% grade. The atomic absorption spectrometry (plane grating spectrography) is used to determine the tungsten content, and the upper limit is 0.020%.
Nanometer Rare Earth Tungsten Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 27 June 2018 21:48

In addition to the addition of rare earth elements, the physical and chemical properties of tungsten powder itself are also very important. The particle size of tungsten powder is micrometer. Because of the large size of the tungsten powder, the powder is small, the distribution of active components in the powder is uneven, the surface active layer is thinner, the active material has a poor migration and diffusion at high temperature, which leads to the tungsten. Electrode zero field emission current density is low, high temperature resistance is low, thermal reflection performance is poor, tungsten electrode burning rate is difficult to adapt to the requirements of modern finishing.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com