A New Type of Tungsten Concentrates Dryer
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 June 2018 10:20

The traditional tungsten concentrates bake converter is heating through the drying oven. The main fuel of the oven is coal or dry wood. This drying method shows the following shortcomings in the production practice: first, it causes environmental pollution and consumes a lot of wood; Second, it is that both coal and dry wood need a larger fuel yard, and the effect is affected.
Recycling Ammonium Tungstate from Ammonium Tungsten Compound Tail Gas
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 June 2018 10:06

The calcined ammonium tungsten compound is the source of tungsten powder metallurgy raw material. The tail gas of calcined ammonium tungsten compound contains a large amount of water vapor, ammonia and ammonia slag. Recycling ammonium tungstate from the tail gas of the calcined ammonium tungsten compound usually requires the recycled tail gas, the treatment of the recycled liquid, the separation of solid and the filtration of the slag.
Smooth Thin Tungsten Sheet Manufacturing in Chinese Style
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 June 2018 09:41

Tungsten materials have excellent thermal stability, high temperature performance and X-ray absorptive capacity. Tungsten sheet with thickness less than 0.3mm is called thin tungsten sheet. Thin tungsten sheet has excellent thermal stability, high temperature performance and X-ray absorption capacity. It has been widely applied in the fields of electrical vacuum technology and medical diagnostic equipment.
How to Use Scheelite to Obtain Ferrotungsten
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 17:48

Ferrotungsten is an iron alloy series (containing tungsten, 70%-80%), an alloy of tungsten and iron. It is used as an alloy additive for steelmaking. The commonly used tungsten iron contains 70% and 80% tungsten types. With the depletion of wolframite resources, how to make full use of scheelite resources that occupy the majority of reserves has become particularly important.
Liquid Form Synthesis Tungsten Carbide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 17:40

Tungsten carbide is the main raw material for the production of hard alloy. The basic process of producing alloy powder in tungsten production and processing enterprises is that the tungsten carbide powder and cobalt powder are mixed through mechanical mixing. The uniformity of the alloy powder is not ideal, and it has a great influence on the subsequent hard alloy pressing. Some scholars try to pre allot alloy powder in liquid state, and then to reduce the alloy powder:
Bismuth Tungstate Plasma and Photocatalytic Plasticizer
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 17:25
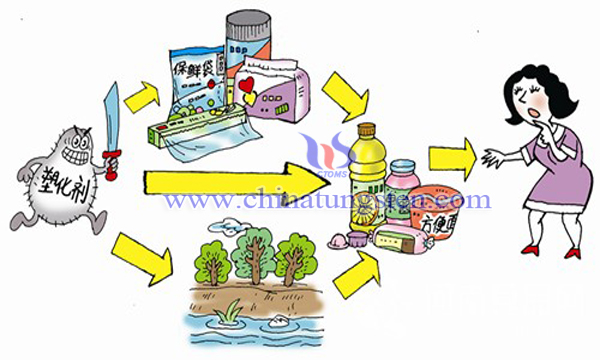
Phthalic acid ester (PAEs) is mainly used as a modified additive for plastics to increase plasticity and strength of plastics; it can also be used in the production and processing of pesticides, coatings, printing and dyeing, cosmetics and spices. The PAEs has estrogen effect, which can interfere with the endocrine and reproductive systems of animals and human beings and damage reproduction and development.
Bismuth Tungstate / Expanded Graphite Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 17:13
The light response of bismuth tungstate is good, but in practice, it usually needs modification. Some researchers have used graphite loaded bismuth tungstate to make composite materials. The preparation process is as follows:
Bismuth Tungstate / Boron Nitride Composite Photocatalyst (Part Two)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 16:56

Bismuth tungstate is a layered structure, and bismuth tungstate has a photocatalytic performance under visible light. It can photolysis and photodegradation of organic pollutants in visible light. Therefore, bismuth tungstate has a good application prospect in many related fields.
Boron Nitride / Bismuth Tungstate Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 16:42

Photocatalysis is a technology that uses the energy of natural light to convert into chemical reaction and produces catalytic technology to decompose organic substances which are harmful to the human body and the environment, and will not cause the waste of resources and the formation of additional pollution. Bismuth tungstate is a typical representative of new photocatalysis. The research is focused on the development of a new type of Bi2WO6 based composite photocatalyst. Modification are the effective means to improve the photocatalytic level of bismuth tungstate.
Tungsten Radiation Protective Clothing
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 June 2018 16:22

How to reduce all kinds of radiation intensity, effectively protect the environment and protect human health has been urgently mentioned on the agenda. Chinese researchers have developed a new type of tungsten radiation protective clothing, which reduces the cost through technology. The implementation of the process is as follows:


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com