Application of Tungsten Wire in Automobile Defogger Glass
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 15:21
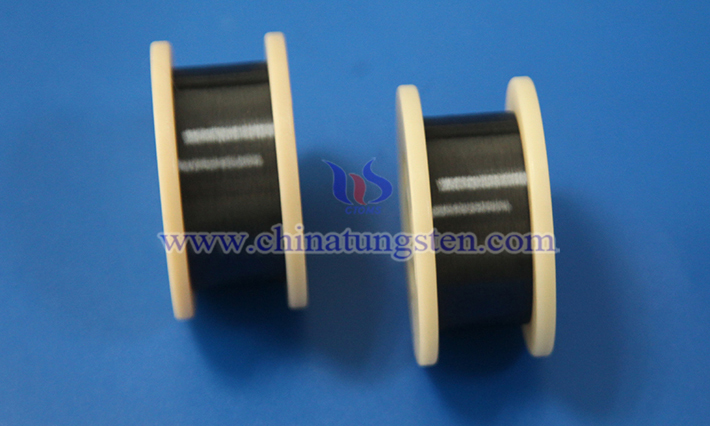

The application of tungsten wire in automobile defogger glass is mainly reflected in the defogger heating system of rearview mirror and rear windshield, which achieves rapid heating defoggering through its high resistance and high heat resistance, improving driving safety.
Application of High-Density Tungsten Alloy Counterweights in the Shipping Industry
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 14:52

Across the vast and boundless ocean, ships and marine engineering structures are like drifting "islands," constantly facing the challenges of a complex and ever-changing marine environment. The relentless pounding of waves, the fierce blowing of sea winds, the periodic rise and fall of tides, and the continuous impact of ocean currents all place extremely high demands on the stability of marine engineering structures and ships. A slight misstep could cause a ship to lose balance, leading to cargo damage or threats to personnel safety. Similarly, stability issues in marine engineering structures could disrupt operations, result in significant economic losses, and cause severe environmental damage.
Ammonium Tungsten Bronze
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 10:20
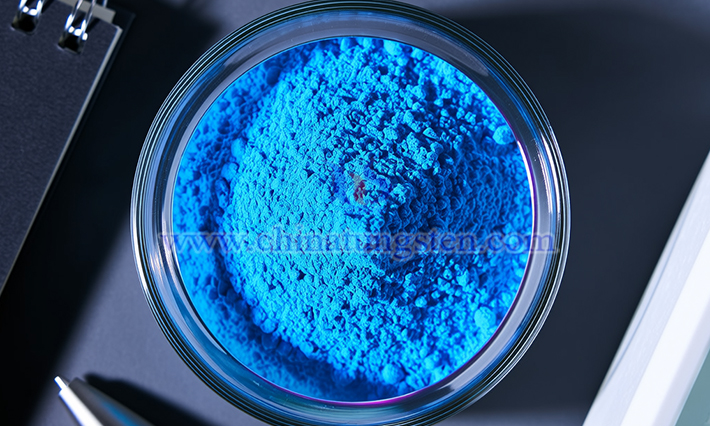

Like sodium tungsten bronze (NaₓWO₃) and potassium tungsten bronze (KₓWO₃), ammonium tungsten bronze ((NH₄)ₓWO₃) is also a type of tungsten bronze. Although NaₓWO₃, KₓWO₃, and (NH₄)ₓWO₃ share similar crystal structures, such as cubic or tetragonal forms, their physicochemical properties and applications differ slightly due to the varying elements added.
Tungsten Wire
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 10:15
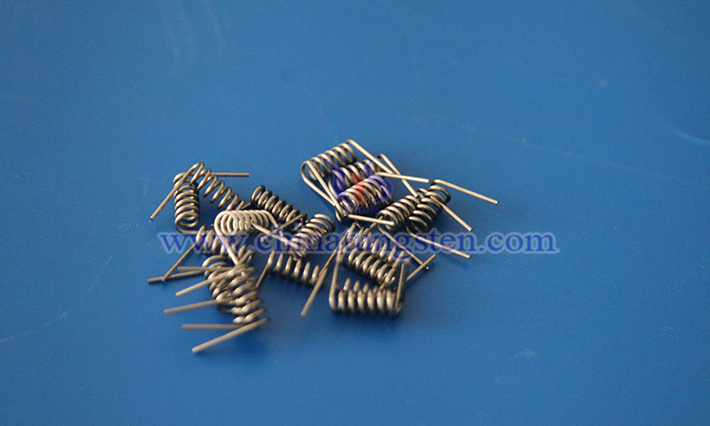

As a typical tungsten product, tungsten wire is a fine filament made by forging and drawing tungsten rods, known in English as tungsten wire, with a tungsten content generally exceeding 99.95%. However, due to the high hardness and brittleness of metallic tungsten, which makes processing difficult, small amounts of potassium oxide, silicon oxide, and aluminum oxide are often added during production. The resulting modified tungsten wire is commonly referred to as doped tungsten wire, 218 tungsten wire, or non-sagging tungsten wire, offering superior overall performance compared to pure tungsten wire.
Cerium-Tungsten Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 10:11
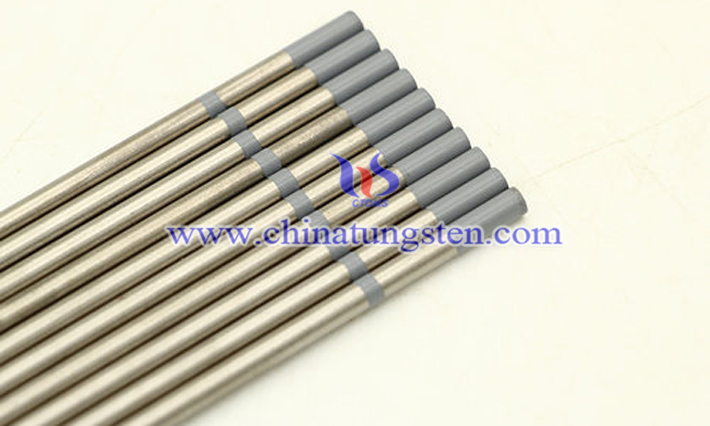

As a typical representative of rare earth tungsten electrodes, the cerium-tungsten electrode is an electrode product with an appropriate amount of cerium oxide added to a tungsten base. It is a non-radioactive, refractory, or non-consumable metal electrode material, serving as the preferred substitute for thorium-tungsten electrodes. Known in English as the cerium tungsten electrode, it features a gray color-coded tip. The cerium oxide content is generally 2%, with electrode diameters ranging from 0.5 mm to 12.0 mm and lengths of 150 mm or 175 mm.
Tungsten–Titanium–Cobalt Hard Alloy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 10:06
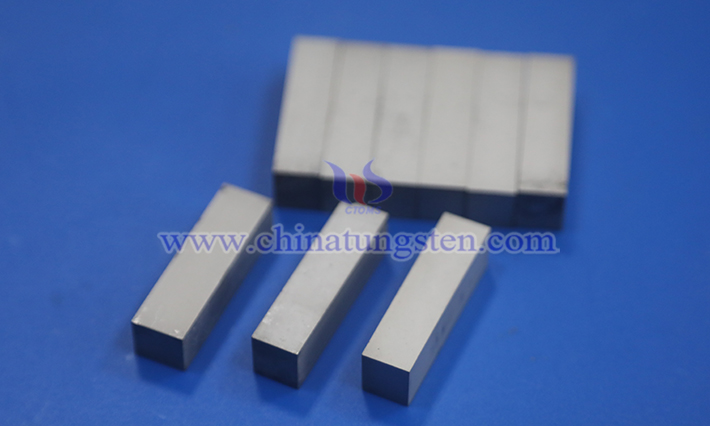

Based on differences in chemical composition and structural components, common hard alloys can be categorized into steel-bonded hard alloys, tungsten-cobalt alloys, tungsten-titanium-tantalum-cobalt alloys, and Tungsten-Titanium-cobalt alloys, with their physicochemical properties and applications being largely similar.
Lanthanum-Tungsten Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 July 2025 10:03
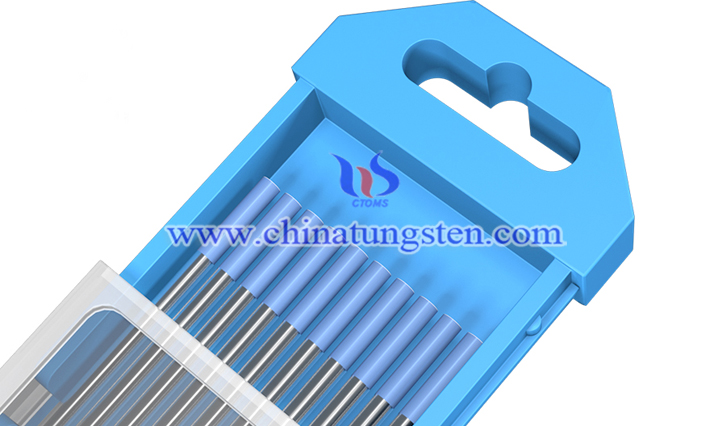
Composite tungsten electrode materials can be categorized into thorium-tungsten electrodes, cerium-tungsten electrodes, yttrium-tungsten electrodes, zirconium-tungsten electrodes, and lanthanum-tungsten electrodes, depending on the additives used. Although all these tungsten electrodes are primarily made from the refractory metal tungsten, their physical and chemical properties and applications vary slightly due to differences in modifiers.
Impact of Phosphorus Element on Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy Performance
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 10 July 2025 11:34
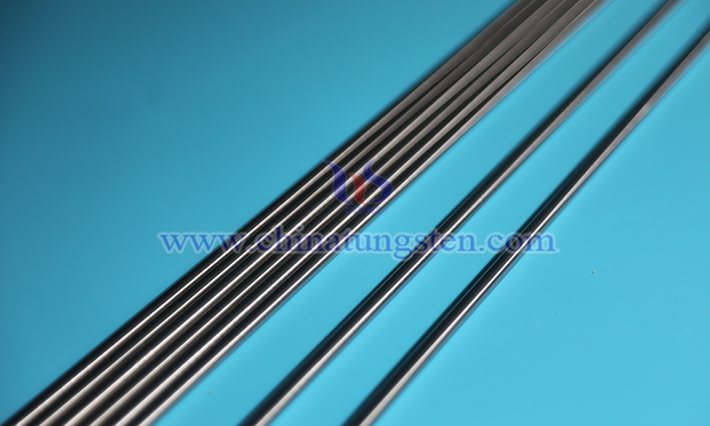
Phosphorus element, as a typical harmful impurity in tungsten-nickel-iron alloy, is typically controlled to below 0.01%. Even in trace amounts, it influences the alloy’s mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and processing stability through grain boundary segregation and compound precipitation.
Methods to Reduce Sulfur Content in Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 10 July 2025 11:30
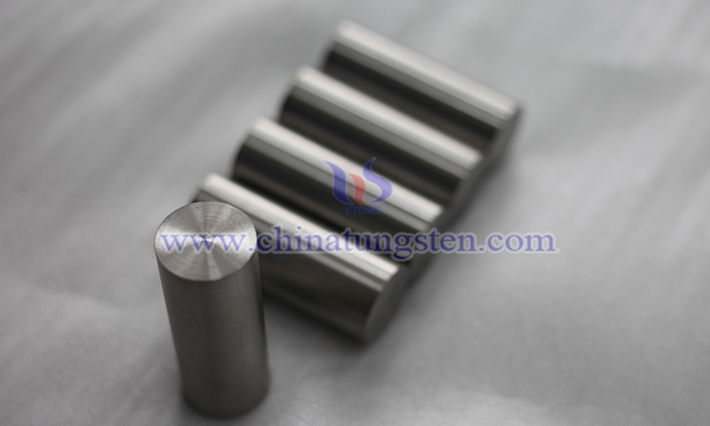
Sulfur element predominantly exerts harmful effects on tungsten-nickel-iron alloy performance: its impact is minimal at low levels, but excessive sulfur content leads to the formation of low-melting-point sulfides and grain boundary weakening, resulting in a sharp decline in impact toughness, deterioration of strength and plasticity, reduced corrosion resistance, and hindered processability.
Impact of Sulfur Element on Tungsten-Nickel-Iron Alloy Performance
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 10 July 2025 11:26
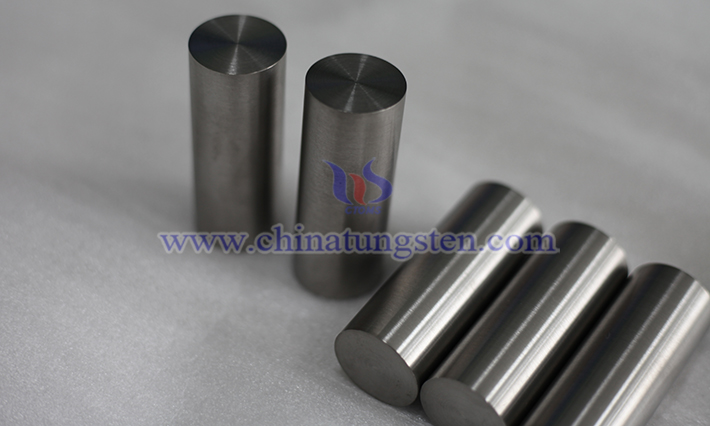

Sulfur element, as a typical impurity element in tungsten-nickel-iron alloy (typically introduced via raw materials or mixed in during smelting), exists in low concentrations but significantly affects the alloy’s mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and processability. This influence is primarily realized through sulfur’s forms of existence (sulfide precipitation, grain boundary segregation) and its interaction with the matrix, exhibiting systematic variations based on sulfur content, precipitate type, and service environment.



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com