Sensitivity and Selectivity Effects of Tungsten Oxide Nanostructures on Pollution Gases
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 29 March 2022 15:24
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1434
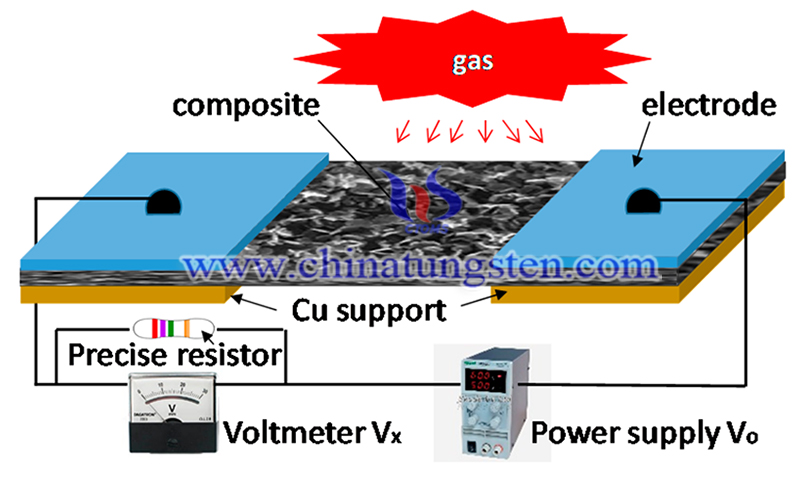
Recently, researchers from Jiujiang University and the University of Puerto Rico, USA, conducted a study on the sensitivity and selective effect of tungsten oxide nanostructures on pollution gases. The study titled “Effect of Tungsten Oxide Nanostructures on Sensitivity and Selectivity of Pollution Gases” has been published in the journal Sensors on 26 Aug. 2020. The study was carried out by Fenghui et al.
Read more: Sensitivity and Selectivity Effects of Tungsten Oxide Nanostructures on Pollution Gases
Oxidation and Reduction of Tungsten and Its Oxides
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 28 March 2022 19:15
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1864
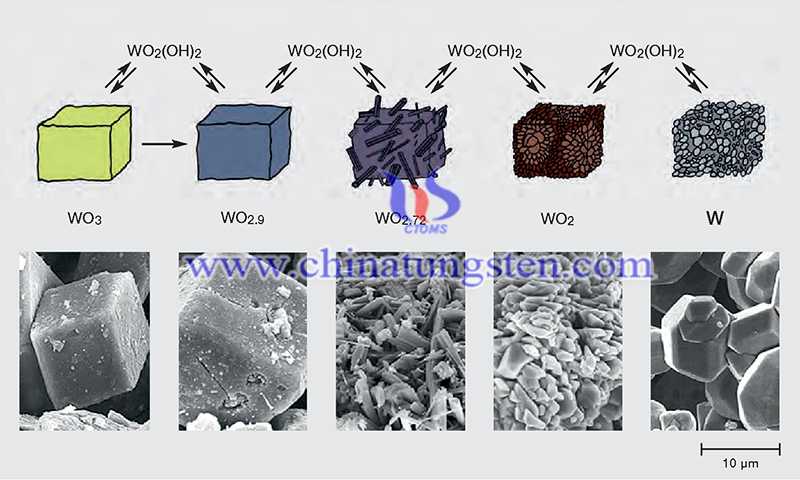

Tungsten (W) is mainly in the W+6 oxidation state in most W oxides, with six oxygen atoms surrounding each W atom in an octahedral configuration. In oxidized tungsten (WO3), these octahedra are arranged in a split-angle configuration. In reduced oxides (WOj, 2 < x < 3), complex combinations of WO6 octahedra in split-angle, split-edge, and split-face arrangements are frequently found. The WO4 tetrahedra and WO7 pentagonal dihedra, which are frequently found in fully oxidized and partially reduced compounds, respectively, add to the complexity of the crystal geography of these compounds.
Read more: Oxidation and Reduction of Tungsten and Its Oxides
Pulmonary Toxicity, Genotoxicity and Carcinogenicity Evaluation of Molybdenum, Lithium, and Tungsten
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 27 March 2022 17:16
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1335

Recently, researchers from the Danish National Research Centre for the Working Environment clarified the doses of molybdenum (Mo), lithium, and tungsten (W) for inhalation toxicity and evaluated the genotoxicity and carcinogenic potential of these three elements.
Six Applications of Molybdenum
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 28 March 2022 19:11
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1265

Molybdenum (Mo) is a refractory metal with a melting point of 2620°C. It hosts a small coefficient of expansion, high electrical conductivity, and good thermal conductivity. It does not react with hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and alkaline solutions at room temperature, and is only soluble in nitric acid, aqua regia, or concentrated sulfuric acid. Therefore, Mo and its alloys have a wide range of applications and good prospects. In this article, we will describe 6 uses of Mo.
Synthesis of Tungsten Carbide by Electrical Explosion of Wire
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 26 March 2022 18:52
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1536

Recently, a research team from the Russian Academy of Sciences has successfully prepared tungsten carbide (WC) powder in this study by synthesizing bimodal tungsten powder by electrical explosion of wire (EEW) method and investigated the carburization process of EEW bimodal tungsten powder.
Read more: Synthesis of Tungsten Carbide by Electrical Explosion of Wire





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com