What Are the Uses of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:24
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 17
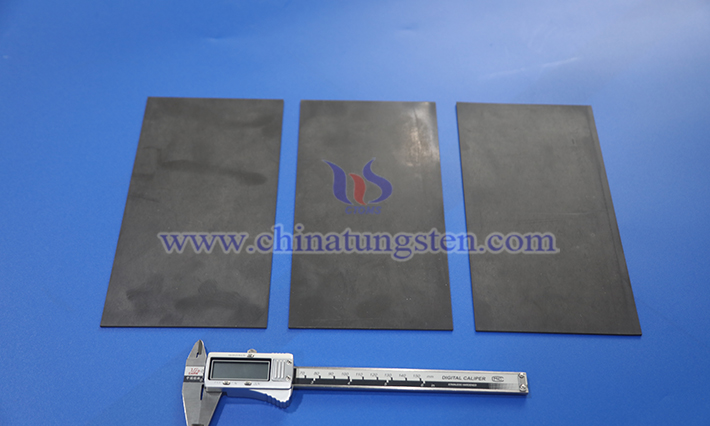
Tungsten resin, leveraging its high density, non-toxicity, radiation shielding capability, and processing flexibility, finds wide-ranging uses in medical, defense, industrial, civilian, and emerging technology fields.
What Are the Characteristics of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:22
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 19
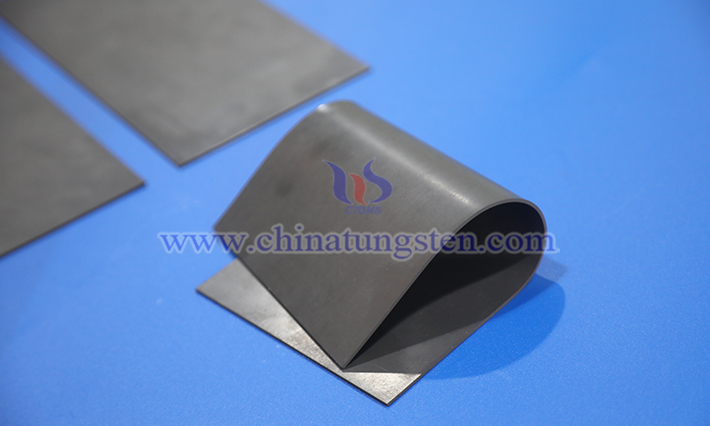
Tungsten resin is a composite material made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or polyethylene). It is widely used in defense, medical, industrial, and environmental fields, thanks to its unique physical, chemical, and processing characteristics.
Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:55
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 50
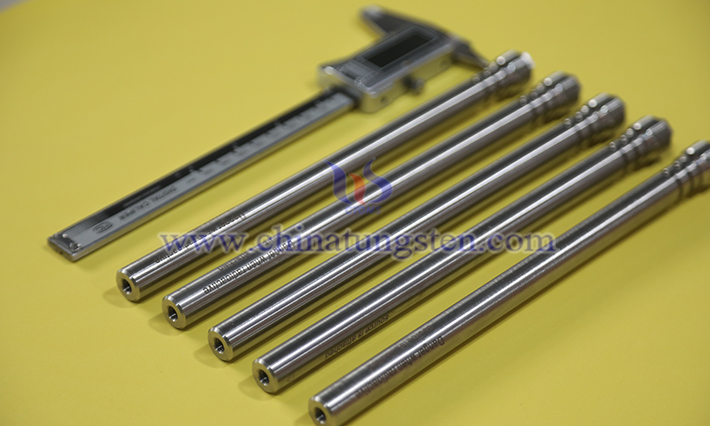

In contemporary industrial connection systems, tungsten alloy fasteners serve as high-performance connecting elements, playing a pivotal role and regarded as core components in materials engineering. Their exceptional performance stems from the inherent properties of tungsten and the optimization of other metal elements. Firstly, their high density ensures efficient weight distribution and connection stability within a limited volume.
What Is Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:20
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 20
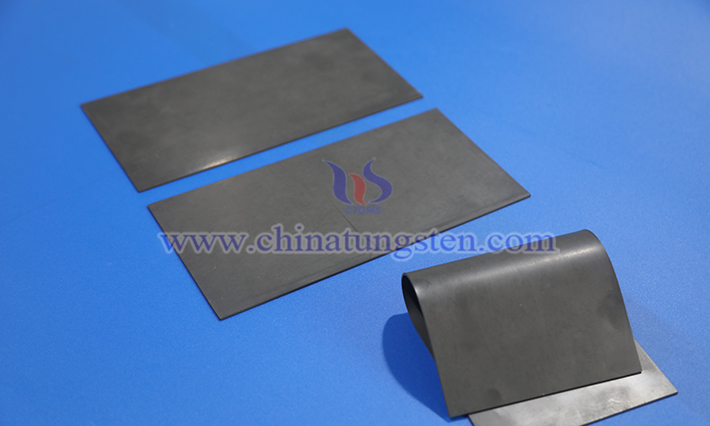
Tungsten resin, also known as tungsten polymer composite material or tungsten-filled resin, is a novel polymer composite material. It is primarily made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or thermoplastic resins) in specific ratios and through specialized processes. This material combines the unique physical properties of tungsten (such as high density and radiation resistance) with the processing flexibility of resins, resulting in a non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and easily moldable material.
Classification of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners (Part Three)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:49
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 49
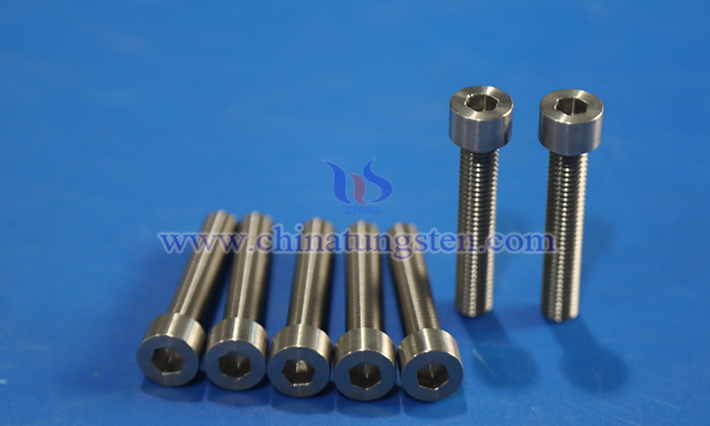

Tungsten alloy fasteners, with their high strength, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, play a crucial role in high-demand fields such as aerospace, nuclear industry, and precision machinery.
Read more: Classification of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners (Part Three)





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com