Application Advantages of Tungsten Alloy Collimators in Medical Field
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 14 October 2025 14:50
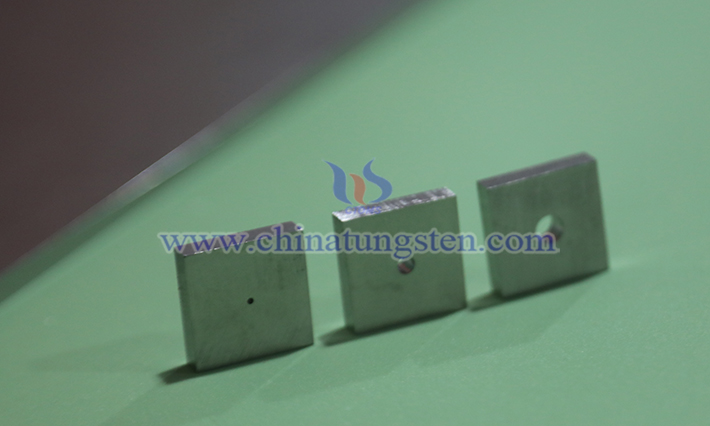

Tungsten alloy collimators, primarily composed of tungsten with nickel, iron, and other elements, exhibit density characteristics surpassing those of collimators made from other materials, giving them a significant advantage in radiation shielding and wide application in the medical field. The application advantages of tungsten alloy collimators include strong radiation shielding capability, excellent radiation durability, environmental friendliness, and superior chemical stability.
What Is Tungsten Alloy Collimator?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 14 October 2025 14:44
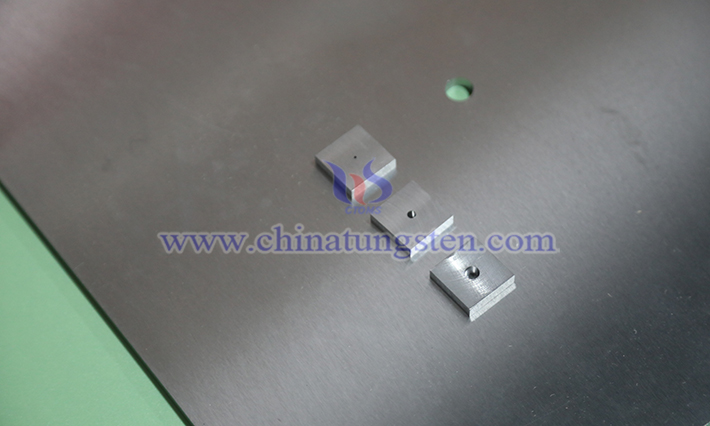

Tungsten alloy collimator is a radiation control device designed using high-density tungsten alloy materials, with its core function being to limit the direction and range of radiation propagation through physical structures. It is widely used in medical, industrial, and scientific fields.
What Impact Does the Tungsten Prices Surge Have on the Industrial Chain?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 19:07

The rise in tungsten prices has an uneven impact on various segments of the industrial chain, presenting a "smile curve":
How Much Influence Do Capital and Funding Have on Tungsten Price?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 19:04
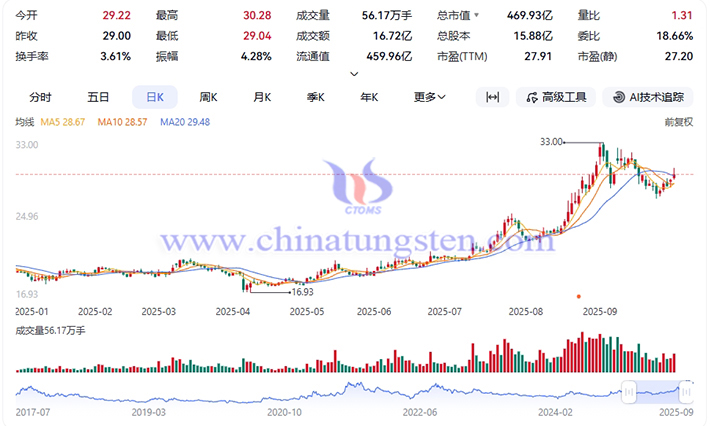
Capital and market sentiment have played a significant role in amplifying fluctuations in this round of price increases. Market data shows that capital has played a significant role in driving tungsten price increases. Price updates are quickly reflected within hours through share price fluctuations of related concept stocks in the secondary market.
What Are the International Market Factors Behind the Tungsten Price Surge?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 19:00

China accounts for approximately 83% of global tungsten concentrate production (according to 2025 USGS data), with deep processing accounting for an even higher proportion, exceeding 90%, giving it a dominant position in the global tungsten supply chain. The export controls implemented on February 4, 2025, and the tightening supply, forced the global supply chain to reassess its reliance on China's supply chain. As of September 30, 2025, European APT prices had risen to USD 580-650/mtu (RMB 366,000-410,000/ton), an 86.4% year-to-date increase. Due to the extended export approval period and uncertainty in China, overseas purchasing has been disrupted, resulting in a significant reduction in inventories and further exacerbating global market tensions. Although overseas tungsten mine development projects (such as Sangdong in South Korea and Mactung in Canada) are progressing, production is limited and far from sufficient to offset the impact of reduced Chinese supply.
How Do National Policies Affect Tungsten Prices?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 18:57
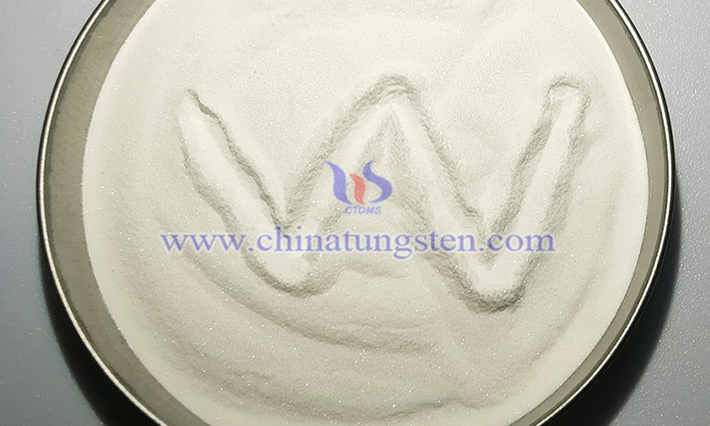

National policies, combining "domestic mining control and foreign export regulation," have significantly impacted the supply and demand structure of the tungsten market.
What Supply Side Factors are Behind the Surge in Tungsten Prices?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 18:55
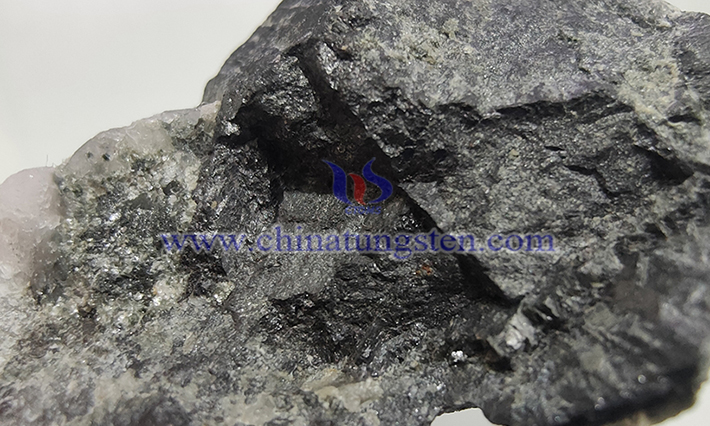

In 2025, the tungsten supply side saw a significant tightening, primarily driven by policy-driven quota controls and multiple external factors.
Why Did Tungsten Prices Suddenly Rise in 2025?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 18:47
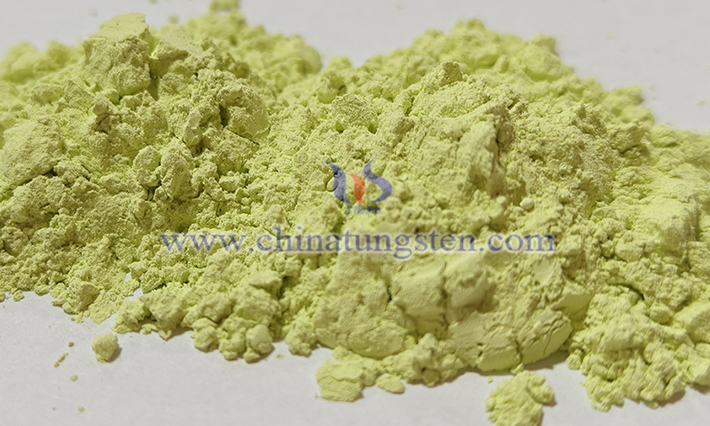

Since March 2025, China's tungsten prices have continued to rise, with a temporary surge in August, reaching a historical peak in early September, and doubling the price of major tungsten products this year.
What Are the Main Applications of Tungsten?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 18:41
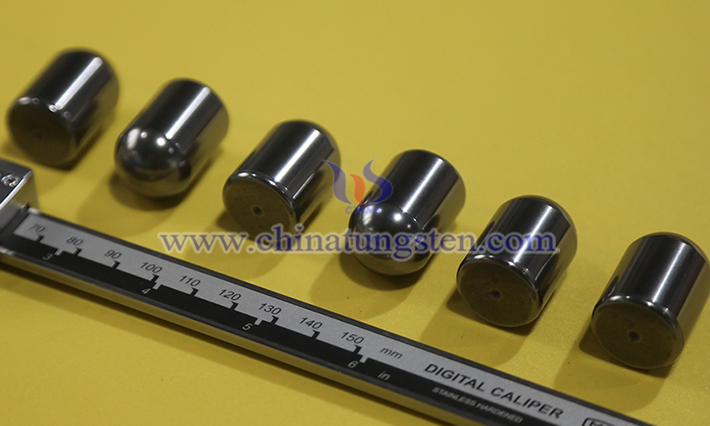

Tungsten is widely used in a variety of fields due to its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high density. Tungsten's uses include:
What Is Tungsten?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 13 October 2025 18:38
Tungsten is a silvery-gray transition metal with the element symbol W and atomic number 74. It has a high melting point (3422°C), high density (19.35 g/cm³), high hardness, and excellent high-temperature resistance. It is widely used in aerospace, defense, electronics, electric light sources, and cemented carbide.



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com