Preparation of Graphene Supported MoS2 Cathode Material
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Monday, 28 December 2020 20:48
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) with a two-dimensional layered structure can effectively inhibit the shuttle effect of lithium-sulfur batteries. It contains metal-sulfur bonds and combines with polysulfides through electrostatic bonds or chemical bonds. To solve inherent problems in lithium-sulfur batteries, it’s important to prepare graphene supported MoS2 composite lithium-sulfur battery cathode materials.
Elemental sulfur is a very promising cathode material. It owns the advantages of high theoretical specific capacity, abundant storage capacity, low price, and environmental friendliness. However, there are still some problems that seriously restrict the practical progress of sulfur cathodes, such as the insulation of sulfur, the dissolution of intermediate polysulfides in the electrolyte, which leads to the loss of active materials, and the volume change of sulfur during charging and discharging. Preparing graphene supported molybdenum disulfide composite lithium-sulfur battery cathode materials could help to solve these issues.
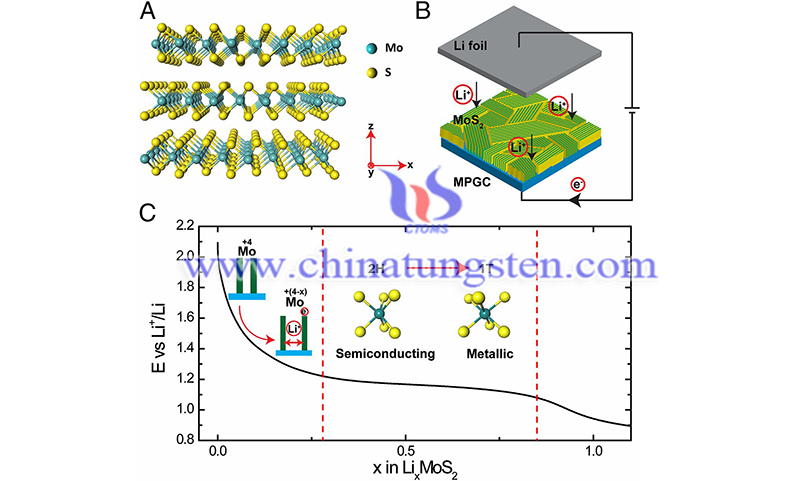
The structure and properties of MoS2 are briefly introduced, and the research progress on the design, preparation, structure and properties of MoS2 as a cathode material for Li-S batteries in recent years is reviewed. The effects of molybdenum disulfide structure and its composition with carbon materials or metallic oxides on the performance of the electrode materials are analyzed. Finally, the existing problems and possible future research directions are pointed out.
Prepare reduced graphene oxide (GO) supported molybdenum disulfide composite, add (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O and thiourea to GO dispersion by hydrothermal method, dissolve it thoroughly and mix uniformly by ultrasound. The liquid is transferred to a hydrothermal kettle for hydrothermal reaction to obtain brown-black aerogel, that is, reduced GO supported molybdenum disulfide composite. The obtained product is washed and then freeze-dried.
Using the sublimation method to cut the prepared reduced GO supported molybdenum disulfide composite into powder, and grind the obtained powder with sublimated sulfur powder until they are uniformly mixed. Then heat the mixture to 150-160℃ under the protection of argon and keep it for 10-15 hours. After it is naturally cooled to room temperature, take out the gray-black powder, which is the cathode material of the reduced GO supported molybdenum disulfide composite lithium-sulfur battery.
There are some precautions for the preparation method. The concentration of the graphene oxide dispersion is 1-3mg/ml, and the volume is 20-30ml. The molar ratio of (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O and thiourea is 1:(30-14). The quality ratio of (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O to reduced graphene oxide is 1:(0.5-2).
The positive MoS2 electrode material prepared by this method possesses the characteristics of multi-level pore structure, good conductivity and large specific surface, which could enhance the conductivity and ion transport capacity of the sulfur positive electrode, improve the utilization rate of sulfur, and alleviate the problem of sulfur volume expansion during charging and discharging. At the same time, the existence of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets forms chemical bonds with polysulfides, which play a chemical restriction on them, and can effectively promote and enhance the charge and discharge process.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com