Tool Material for Machining Cobalt Alloys and CoCrMo Alloys
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 19 October 2022 16:40
The cutting tool material is the most important aspect of the cutting process in machining operations, especially when machining difficult-to-cut materials such as titanium, cobalt alloys, and CoCrMo alloys, where high heat and mechanical stresses caused at the tool edge are major problems.
To overcome this, cutting tools are required to have these characteristics; high toughness, thermal hardness at high temperatures, chemical and thermal stability, and good resistance to thermal shock. In the early development of cutting tools, it was difficult to find a suitable cutting tool that met all of these characteristics. Often, coatings were chosen as the best solution to provide uncoated tools with higher hardness, toughness, and stability at high temperatures. Tool wear becomes a important factor when cutting at high speeds.
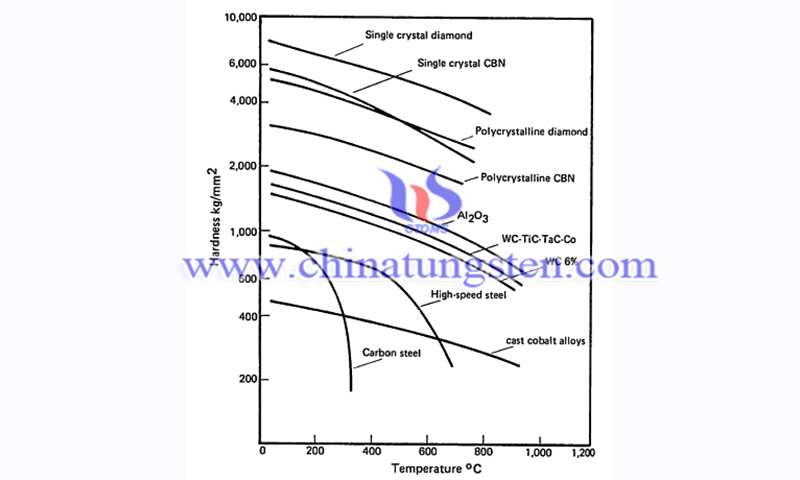
Therefore, cutting tools should not only maintain the above characteristics but also have a high resistance to wear. High temperatures in the cutting zone cause most of the tools to lose their thermal hardness, which shortens the tool’s life and also increases the wear rate. Therefore, the material to be machined, tool material, cutting conditions, tool wear, and cooling media are the influencing factors that affect the level of temperature generated in the cutting zone. In machining difficult-to-cut materials such as cobalt-chromium alloys, always leads to difficulties in selecting the right cutting tool.
Failure to select the correct tool material may reduce tool performance due to rapid flank wear, notch wear, edge chipping, crater wear, plastic deformation, and tool failure. Several cutting tool materials have been used by previous researchers in machining a family of cobalt superalloy materials. These materials include uncoated carbide tools, PVD-coated tools such as TiN/TiCN/Ti, TiN, TiCN/TiAN, TiN/TiCN, AlTiN, TiAlN, TiSiC, and CVD-coated tools.
Cobalt alloys and CoCrMo alloys are becoming increasingly popular in the aerospace and medical fields due to their excellent mechanical properties, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, high creep resistance, high hardness, heat resistance, and excellent biocompatibility.
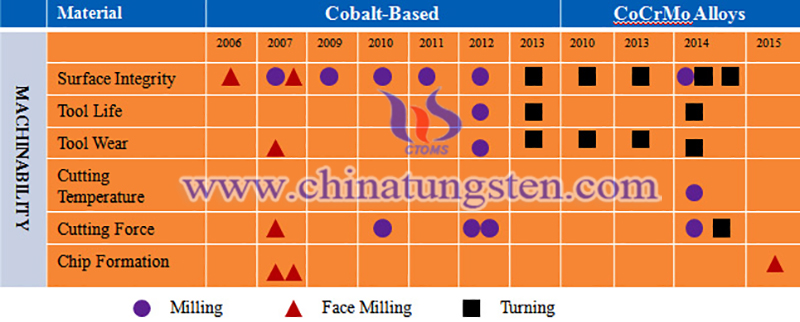
The machining of these materials faces many challenges and troubles, mainly due to their high strength, high toughness, high wear resistance, and low thermal conductivity. Based on the great applications of cobalt-based and CoCrMo alloys, more research is needed, especially in conventional machining processes, to overcome the poor machinability problems of these materials.
Cemented carbide tools are still the most popular tool material that many researchers compare to other tool materials such as HSS, ceramics, and CBN. New coolant strategies, such as low temperature, cold air, high-pressure coolants, and MQL with nanoparticles, are among the potential research topics for the future machining of these alloys. Research on cutting temperatures, chip formation, surface integrity, residual stresses, and wear mechanisms is still lacking and offers great opportunities for future research, especially when using high-speed machining.
Cited paper: Zaman H A, Sharif S, Kim D W, et al. Machinability of cobalt-based and cobalt chromium molybdenum alloys-a review[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017, 11: 563-570.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com