Tungsten-Oxide-Based Material Applications
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 26 February 2022 22:44
A research team from the Taiwan University of Science and Technology has published a paper in Frontiers in Materials on the progress of tungsten-oxide-based material applications. Tungsten-oxide-based material has received great attention due to its ability to absorb near-infrared (NIR) light and its efficient photothermal conversion properties.
In recent years, the NIR absorption properties of various nanomaterials, noble metal nanomaterials, carbon-based materials, conducting polymers, and semiconductor nanoparticles have been investigated.

In addition, WO3-based materials with unusual oxygen defect structures and strong localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) provide strong light absorption in a wide range of wavelengths in the near-infrared region. In the past, some light-absorbing nanomaterials, such as precious metals, polymers, and other inorganic nanomaterials, have attracted attention for their use in photothermal therapy for cancer treatment.
In the team's study, they review the synthesis, properties, and applications of tungsten-oxide-based nanomaterials as a novel photothermal material. The team also discusses the basic ideas for the development of photothermal nanomaterials and the factors that influence their structural design.
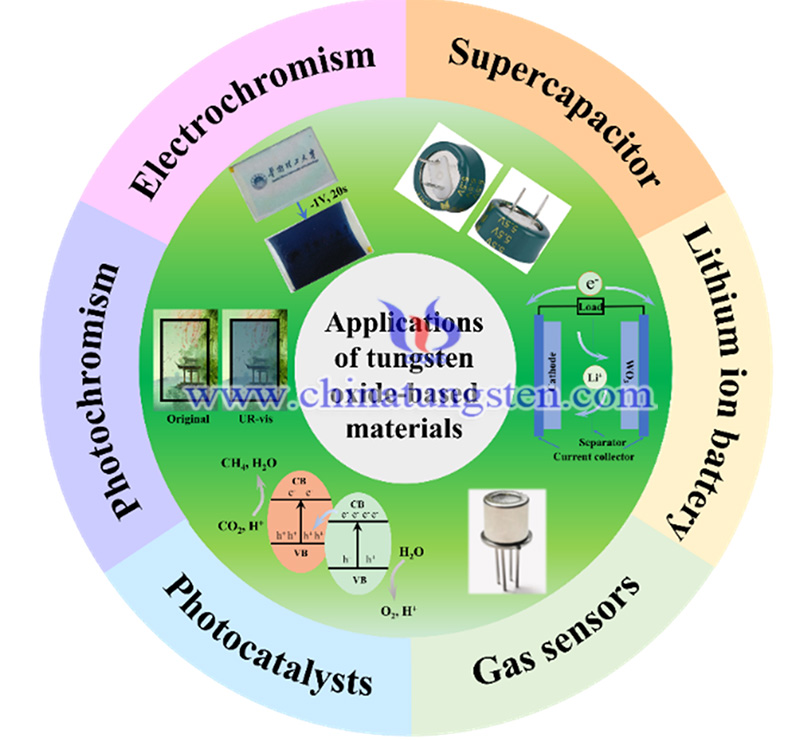
In addition, recent advances in WO3-x- and MxWO3-based nanomaterials (including their hybrids) in various fields such as near-infrared light shielding, pyroelectricity, water evaporation, photocatalysis, gas sensors, and energy-related applications are highlighted. Finally, the study provides promising insights into this rapidly developing field, indicating that it may stimulate additional research leading to practical applications.
Near-infrared (NIR) irradiation has a wide range of wavelengths in the 780-2,500 nm range. Essentially, nearly half of the energy available at the Earth's surface consists of sunlight in the near-infrared (i.e., greater than 780 nm). Maximizing the use of near-infrared light for human use has been a topic that has attracted active discussion and research among scientists.
Photothermal materials (PTMs) with near-infrared absorption have stimulated the research interest of scientists due to their photothermal behavior. Photothermal conversion is a process in which light energy at specific wavelengths is absorbed and converted directly into heat.
In this study, the team summarizes the overall progress made in the last few years in the application of tungsten oxide-based materials. WO3-x, MxWO3, and their hybrids serve as interesting research topics, especially in terms of morphology control and composite structures to enhance optical absorption, charge separation, redox capability, and electrical conductivity.
The well-studied liquid-phase technique, i.e., sol-gel thermal treatment, is the most used method along with hydrothermal treatment as a simple and cost-effective way to produce tungsten oxide with different nano-morphologies. The morphology can be fine-tuned by controlling variables such as time, precursor concentration, and temperature.
A key difficulty is to increase the tungsten-oxide-based material utilization efficiency by extending the solar spectral response from the ultraviolet to the near-infrared region. To meet these requirements, a mixture of WO2.72 and MxWO3 is important due to its strong light absorption and interval charge properties. A major advantage of this material is the LSPR effect, which allows researchers to focus not only on the properties of new applications, but the study offers the opportunities to improve the efficiency of the application.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com