Nano Tungsten Disulfide Medical Application
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 14 May 2019 17:17
With the increasing complexity of living environment, cancer is becoming the most serious serious disease endangering human health. Basic research and effective treatment are considered as the key link and effective means to cure cancer. Compared with traditional radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgical treatment, targeted drug carriers with high selectivity and low toxicity to cancer cells and little toxicity to normal cells in the course of treatment are considered to be one of the most effective methods to combat cancer.
Teo et al. studied the toxicity of tungsten disulfide nanotablets on human alveolar epithelial cells (A549) by WST-8 and MTT methods. The results showed that A549 cells maintained a survival rate of more than 80% after incubation for 24 hours at a maximum concentration of 400 ug/mL. It was confirmed that monolayer tungsten disulfide still exhibited low cytotoxicity to A549 cells at high concentration. Importantly, nano-tungsten disulfide has a large specific surface area, combined with good dispersion in aqueous solution and low cytotoxicity, it has a good medical application prospect in high-efficiency drug carriers.
The advantages of high efficiency and low toxicity of nano tungsten disulfide can also be demonstrated by another example. In the Advanced Materials journal, a leading international journal in Materials Science in 2014, a team led by Professor Liu Zhuang, Institute of Functional Nano-materials and Soft Substances, Suzhou University, also confirmed this view. Scientists have successfully developed photothermal treatment of nano-tungsten disulfide tablets. The reagent was successfully applied to the optical treatment of tumors.
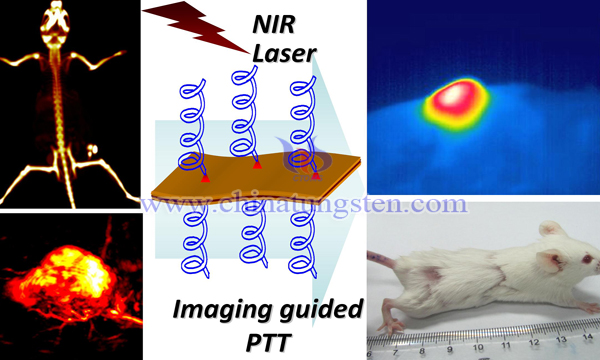
It has been reported that tungsten disulfide nanosheets with uniform size were obtained by lithium ion intercalation, and then polyethylene glycol polymer was modified on the surface of the nanosheets to make them more water-soluble and biocompatible, and tungsten disulfide nanomaterials have good optical absorption properties in the near infrared region.
Sulfide nanotablets were injected into mice via tail vein and enriched in the tumor site through the high permeability and retention effect (EPR effect). Because tungsten can absorb X-rays, it is the first time that good CT imaging of tumors has been achieved in animal models. At the same time, based on the near infrared absorption properties of tungsten sulfide nanomaterials, it can also be used for photoacoustic imaging of tumors. And under the near infrared laser irradiation, all the tumors were completely destroyed to achieve the goal of complete cure. Systematic toxicity studies showed that no obvious toxicity was observed in the injection dose, suggesting that transitional tungsten disulfide may be widely used in clinical photothermal therapy of tumors.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com