Mesoporous Carbon-supported Tungsten Oxide Preparation Process
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 February 2019 23:06
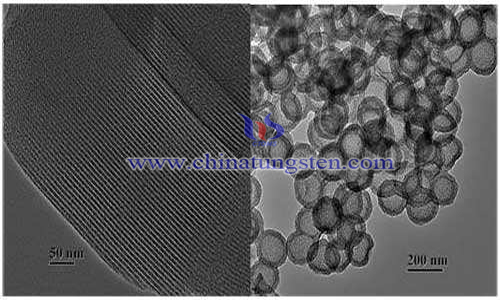
At present, tungsten functionalization of mesoporous carbon is mainly achieved by post-treatment (such as impregnation) of finished mesoporous carbon. The stability of Mesoporous Tungsten oxide/tungsten carbide obtained by this method is poor, and the loss is serious in the reaction process. Moreover, the tungsten species obtained by this method are poorly dispersed and the size distribution of tungsten particles is large, so a new process is needed to improve its shortcomings.
How to Prepare Porous Silicon / Multidimensional Tungsten Oxide Composites
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 February 2019 22:57
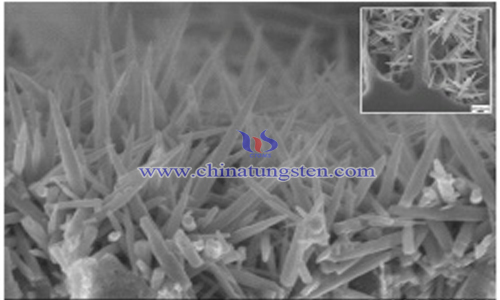
Tungsten oxide, as a semiconductor sensitive material with great research and application prospects, has been widely used to detect various toxic and dangerous gases (such as NO2, NH3, etc.). However, the working temperature of tungsten oxide is relatively high (150 ~250 ℃), so scientists and technicians have been devoting themselves to the research of reducing the working temperature of tungsten oxide.
Supported Bismuth Tungstate Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 February 2019 22:43

Bismuth tungstate (Bi2WO6) photocatalyst is considered as a potential excellent visible light photocatalytic material because of its unique electronic structure, excellent visible light absorption ability and high organic degradation ability.
Nano Silver / Tungsten Trioxide Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 21:52

Tungsten trioxide (WO3) is an important photocatalytic semiconductor material, which is widely used in the field of semiconductor heterogeneous photocatalytic technology to solve industrial wastewater and domestic wastewater pollution treatment.
Tungsten Carbide / Composite Photocatalyst
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 21:37

With the rapid development of global economy and the increasing demand for energy and resources, people pay more attention to and invest in the search for renewable and clean energy. Hydrogen energy, as a clean renewable energy, has the advantages of high combustion value, pollution-free, convenient storage and transportation. The photocatalytic decomposition of water to produce hydrogen using solar energy, which has huge reserves and no pollution, provides an ideal method to solve this problem, and has become a hot spot of scientific research.
Nano Tungsten Carbide Perfect Carbonization
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 21:27

Nano-cemented carbide not only has high hardness, good wear resistance, but also has high strength and toughness, and has good comprehensive properties. Its application field is expanding constantly. It has been widely used in manufacturing micro-drills, precision tooling and difficult cutting fields. As the basic raw material of nano-cemented carbide production, nano tungsten carbide has been prepared and its properties for the production of nano-cemented carbide. It has a great influence and has almost become the bottleneck in the production of nano-cemented carbide. For this reason, many enterprises and research institutes in many countries have carried out a lot of research.
Aluminum-Tungsten Composite Super Synthesis Process
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 21:03
Tungsten has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, high strength, high hardness and low thermal expansion coefficient. It is an irreplaceable key material in many fields, especially in the field of national defense, military industry and aerospace. However, its high density (too heavy) limits its application, so it is necessary to develop new lightweight materials with better comprehensive properties than tungsten.
Two-dimensional Nano-tungsten Disulfide Fabricated By PECVD
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 20:48

Among the two-dimensional transition metal sulfides, single-layer nano-tungsten disulfide is a typical sandwich layered structure. Because of its relatively weak van der Waals force between layers, it can also be peeled into single or few layers of nanosheets. It is considered to be another important two-dimensional nanosheet material besides graphene, which has unique physical, chemical and electrical properties.
Tungsten Steel Self-Defense Ring, The Secret Weapon Of Women's Life
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 08:54

The case of the girl in Yueqing, Zhejiang Province, who was killed by the drip and the wind, has aroused the attention of people from all walks of life. The occurrence of this case also reminded people of the Zhengzhou flight attendant’s car murder case three months ago. For a time, the voice of the question about the Drip Trip platform on the Internet was soaring. This also sounded the alarm of self-protection for the majority of female friends! We should still learn how to protect ourselves. Not only do we need to pay attention when we take a taxi, but we should also improve our vigilance at any time. After all, danger is everywhere, and it is impossible to prevent it! In order to be in distress, not only fear, Sun Tzu’s art of war tells us that it is necessary to have a plan to prepare for it! Below, mainly from three points to talk about how girls should defend themselves.
Tungsten Hexafluoride High Purity Method
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 01 February 2019 00:12

Tungsten hexafluoride, a chemical formula of WF6, is a colorless gas. When condensed, it is a pale yellow liquid with a molar mass of 297.83 g/mol, which is one of the most dense gases. Among tungsten tungsten fluorides, tungsten hexafluoride is the only stable and industrially produced variety.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com