Cemented Carbide Blades Wear Characteristics In Drilling LimestoneⅤ
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 08 September 2015 10:36
- Written by zhihua
- Hits: 301
3.2. Effect of the nozzle diameter on the wear rates of the cemented carbide blades
Bigger nozzle diameter means larger impact area and more impact force to the limestone, which helps to reduce the mechanical force on the blade and lessen the wear of it. Fig. 5 summarizes the effect of nozzle diameter on the wear rates of the cemented carbide blades under the water pressure of 30 MPa. It is showed that wear rates decrease with the increasing of the nozzle diameter of the drill bit.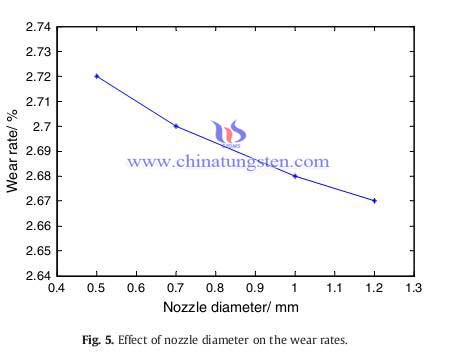
Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - http://www.tungsten-carbide.com.cn
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email:sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Vacuum Smelting Process for Producing Ferrotungsten-Description IX
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 08 September 2015 09:45
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 265
The heating of the pelletized charge to within the desired temperature range is achieved at a rate as quickly as possible without incurring fracture or rupture of the pellets due to the rapid gasification of any moisture and other volatile constituents therein including the binder constituent, thereby producing pellets of a porous nature which become progressively more porous as the vacuum smelting reaction proceeds until a temperature is attained at which some sintering and densification of the pellets occurs. When iron oxide is employed in the pelletized feed stock as the source of the iron-bearing material, the reduction of iron oxide takes place commencing at a temperature of about 1800° F. and is accompanied by a liberation of carbon monoxide gas. A reduction of the tungsten oxide constituent takes place commencing at a temperature of about 1800° F. and the reaction itself is carried out for a period of time sufficient to effect a substantially complete reduction of the tungsten oxide constituent and of any iron oxide present to the metallic state. As metallic tungsten is produced during the course of the vacuum smelting reaction, the initial iron constituent present or the metallic iron produced by the reduction of the iron oxide constituent becomes alloyed with the tungsten, producing a nonsegregated substantially dense pellet of ferrotungsten alloy. Upon completion of the vacuum smelting operation, the pelletized charge is permitted to cool to a temperature below about 300° F. whereafter the dense ferrotungsten alloy product can be extracted and exposed to air such as by back-filling the vacuum smelting furnace and the product recovered.
In order to further illustrate the process comprising the present invention, the following examples are provided. It will be understood that the examples hereinafter set forth are provided for illustrative purposes and are not intended to be limiting of the invention as herein described and as defined in the subjoined claims.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Cemented Carbide Blades Wear Characteristics In Drilling Limestone Ⅳ
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 07 September 2015 18:53
- Written by zhihua
- Hits: 292
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effect of water jet pressure on the wear rates of the cemented carbide blades
Fig. 4 shows the wear rates of cemented carbide blades under different water jet pressure (the used diameter of the water jet nozzle is 1.2 mm). It is shown that the wear rate is quite high (nearly 10%) without the help of water jet, but the wear rates decrease sharply when the water jet joins in. The wear rates decrease when the jet pressure increases. Nevertheless, the wear rate decrease slowly when the jet pressure is over 10 MPa.
The wear rates are affected by the mechanical stress and temperature of the blades, and the water jet is helpful to reduce the mechanical stress and temperature. The more impact stress the water
jet gives to the rock, the less mechanical stress is on the blades. The maximum impact stress of the water jet on the rock (Pi) is given by the Eq. Pi=v*ρ1*c1*ρ2*c2/(ρ1*c1+ρ2c2)
where v is the jet velocity of the liquid and ρ1, ρ2 and c1, c2 are the densities and the shock velocities in the liquid and the solid. According to the equation, the impact stress will increase with the jet velocity. The relationship between jet pressure and velocity could be estimated by the expression, where P is jet pressure. So the impact stress will increase with the jet pressure: bigger jet pressure means lower mechanical stress on the blade.
Higher jet pressure could also increase the thermal exchange efficiency to reduce the working temperature. Heat transfer takes place when the water jet flows through the surface of blade, with a cooling effect. This cooling process can approximately be regarded as the process of convective heat transfer outside flat plate. The surface heat transfer coefficient of the blade will be, where h is the heat transfer coefficient of the surface, λ is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of water, l is the flow length on the blade, ξ is the kinematic viscosity of water, μ is the dynamic viscosity of water, Cp is the specific heat capacity of water. The power of heat exchanging is given by Eq. where Φ is the power of heat exchanging, TH is the temperature of blade, TL is the temperature of water, S is the area of flow on the blade.
In a word, the cooling effect is proportional to the square root of jet speed v, and according to Eq. (3) , it is also proportional to the forth root of jet pressure P.
Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - http://www.tungsten-carbide.com.cn
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email:sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Vacuum Smelting Process for Producing Ferrotungsten-Description VIII
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 08 September 2015 09:43
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 273
During the vacuum smelting operation, other constituents which are also volatilized and removed from the pelletized feed stock to effect a purification of the resultant ferrotungsten alloy residue include: silica, iron and iron compounds, calcium compounds, manganese and manganese compounds, aluminum compounds, lead compounds and other oxygen-containing compounds, as well as other conventional impurities normally found in ore deposits containing tungsten. The substantial reduction in the content of such contaminating constituents renders the resultant ferrotungsten alloy briquettes eminently suitable in many instances for direct use as metallurgical alloying agents in steel-making operations and the like without any further purification. A typical composition of ferrotungsten alloys, including permissible amounts of various contaminating constituents in accordance with ASTM specifications are as follows:
______________________________________
Tungsten 72.0 - 82.0% Carbon 0.60 max. Phosphorous 0.060 max. Sulfur 0.060 max. Silicon 1.00 max. Manganese 0.75 max. Copper 0.10 max. Arsenic 0.10 max. Antimoney 0.080 max. Tin 0.10 max. Total arsenic, antimony and tin 0.20 max. Iron Balance
______________________________________
The ferrotungsten pellets produced can be suitably packaged in steel containers providing premeasured quantities of the ferrotungsten alloy, and in that form can be utilized in steel-making and foundry operations.
The temperature of the pelletized feed stock during the vacuum smelting operation may range from as low as about 2500° F. to as high as about 3100° F. and preferably is controlled within a range of from about 2700° F. to about 2900° F. Temperatures below about 2500° F. are commercially unsatisfactory due to the slow rate of reduction of the tungsten oxide constituent, while on the other hand, temperatures above about 3100° F. are undesirable because of excessive costs of refractories required in the vacuum smelting furnace. The vacuum smelting operation is carried out at pressures less than about 0.5 Torr and preferably at pressures less than about 0.05 Torr (50 microns) to as low as about 0.001 Torr (1 micron) and even lower, depending upon the limitations of the vacuum equipment employed. Particularly satisfactory results are achieved when the pelletized charge is heated at a temperature ranging from about 2800° F. to about 3100° F. employing a vacuum ranging from about 0.05 Torr to about 0.001 Torr.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Cemented Carbide Blades Wear Characteristics In Drilling LimestoneⅢ
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 07 September 2015 18:33
- Written by zhihua
- Hits: 244
2. Materials and experimental procedures
2.1. Materials
The blade material of drill bit is WC/Co cemented carbide YG6 (6%Co, 94%WC), whose mechanical properties are listed in Table 1. The installation of the blade and water jet nozzle are shown in Fig. 1. The sizes of the blades are listed in Table 2.
Limestone (taken from Songzao Mine in southwest China) is drilled as hard rock material in the experiment. The properties of the limestone are listed in Table 3, and the SEM micrograph of it is shown in Fig. 2
2.2. Experimental procedures
The experiments were performed at room temperature. The drill rig kept the drilling speed at 120 mm/min and rolling speed at 70 rounds/min for 30 min in the experiments, which aimed to investigate the influence of different water jet parameters (jet pressure, nozzle diameter) on the wear characteristics of the cemented carbide blades(m0):R=mx/m0
The weight of blades was measured with a balance (minimum 0.01 mg) made by Mettler Toledo. For the determination of wear mechanisms, the wear surfaces were analyzed by scanning electron
microscope made by TESCAN
Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - http://www.tungsten-carbide.com.cn
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email:sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com