Tungsten Crucible Is Used for High-Temperature Experiments
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 June 2025 15:03
As an important high-temperature refractory metal vessel, tungsten crucible is widely used in various high-temperature experiments, especially in the fields of materials science, metallurgical engineering, semiconductor manufacturing and nuclear energy technology.
Due to its extremely high melting point, good thermal stability, excellent mechanical strength and low vapor pressure, crucibles made of tungsten can remain structurally intact and chemically stable in extremely high temperature environments, making them one of the ideal materials for high-temperature laboratory vessels.
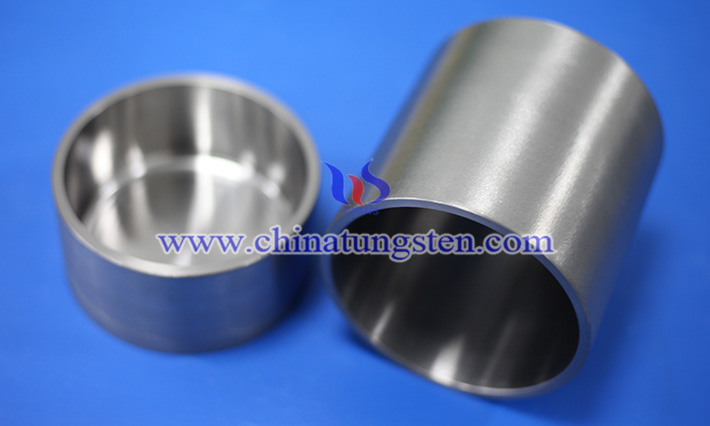
First of all, the most outstanding advantage of the W crucible is its ultra-high heat resistance. Compared to common laboratory vessel materials such as quartz, ceramics or platinum, tungsten not only does not soften easily at high temperatures, but can still withstand high mechanical stresses at temperatures close to the melting point. It can operate for a long time in temperatures in excess of 2500°C under vacuum or inert atmospheres (e.g. argon) and is suitable for extremely temperature-demanding experiments such as crystal growth, evaporative deposition, sintering reactions, metal melting, etc.
Secondly, the chemical stability of tungsten shows significant advantages at high temperatures. Tungsten is not easy to react with most chemical reagents at room temperature, but it is still necessary to pay attention to its reaction with oxygen, water vapor and some halogen gases at high temperatures, so it is often used with vacuum system or inert gas protection during experiments. In these controlled environments, it effectively avoids oxidative corrosion and ensures the purity and stability of the test.
In addition, the mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance of the W crucible are also excellent. It is not susceptible to thermal cracking or deformation during frequent heating and cooling cycles, making it particularly suitable for protocols that require repeated high-temperature treatments. In addition, the high density and low coefficient of thermal expansion of tungsten also help it maintain good structural stability at high temperatures.
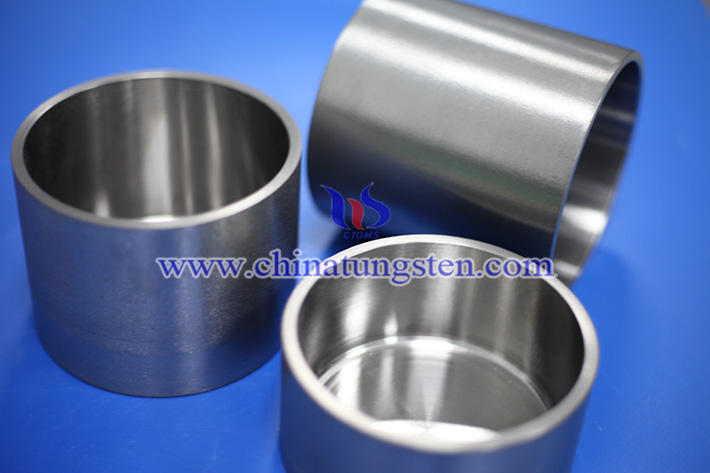

In practical applications, tungsten crucibles are often used to smelt metals with high melting points (such as niobium, tantalum, molybdenum) and their alloys, or to prepare high-purity oxides, carbides, nitrides and other functional materials. In semiconductor manufacturing, it is also commonly used in crystal growth furnaces to prepare single crystal materials such as sapphire, silicon, gallium nitride, etc., to ensure that the materials are not contaminated during high temperatures. In addition, it is used as a carrier for the study of fuel cladding materials in the study of nuclear energy materials due to its excellent radiation resistance and thermal stability.
However, there are certain limitations to its use, such as easy corrosion in oxidizing atmospheres and high processing difficulty, resulting in its high price. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly control the atmosphere and environment when using, and reasonably select the model in combination with the experimental requirements.
- Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- CTIA GROUP LTD: en.ctia.group
- Tungsten News & Price: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com