Tungsten Carbide Brief Introduction
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 08 May 2017 19:58
There are three main compounds of binary tungsten-carbon system:
Tungsten monocarbide (WC)(shown as FIGUE.1), is the main constituent in most of the commercial cemented carbides, also commonly defined as tungsten carbide, is the only stable tungsten carbide at room temperature.
Ditungsten carbide (W2C), can be used as a hard material.
Nonstoichiometric tungsten carbide (WC1-x), is an cubic high-temperature modification, which undergoes a eutectoid decomposition at 2530-2535℃ into β(W2C)+δ(WC).At room temperature it can only be obtained by rapid quenching in liquid tin.

Tungsten carbide have such advantages as follow:
1.High melting point and boiling point, the melting point of tungsten carbide is 2870℃ and the boiling point is 6000℃ under atmospheric pressure。
2.High hardness, tungsten carbide is a common hard phase of cememted carbide.
3.High density, the density of tungsten carbide is 15.63g/cm3.
High thermal expansion coefficient, the thermal expansion coefficient of tungsten carbide is 6.9×10-6/K.
4.High elastic modulus, the elastic modulus of tungsten carbide is 5 times than steel's.
Tungsten carbide powder is synthesized by tungsten powder and carbon black in a high frequency induction furnace or Carbon tube furnace at high temperature with or without hydrogen gas. Under hydrogen atmosphere, the carbonation reaction happened between tungsten and methane which is synthesized by carbon and hydrogen, otherwise the reaction will happened directly between tungsten and carbide.
Tungsten carbide have such applications as follow:
1.It is a common hard phase in cememted carbide;
2.Tungsten carbide is used as a raw material of compound carbide;
3.Tungsten carbide can apply as catalyst in organic chemistry and electrochemistry as catalyst.
4.It used as surface strengthening material such as cast tungsten carbide and surface spraying material.
| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Purity of Tungsten Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 08 May 2017 19:51
Purity of the tungsten powder is of particular importance in powder metallurgy manufacturing of tungsten metal and alloy, since the purity of subsequent products are mainly influenced by raw materials. Typical upper limits of foreign element concentrations by chinese national standard(GB) in µg/g are follow:
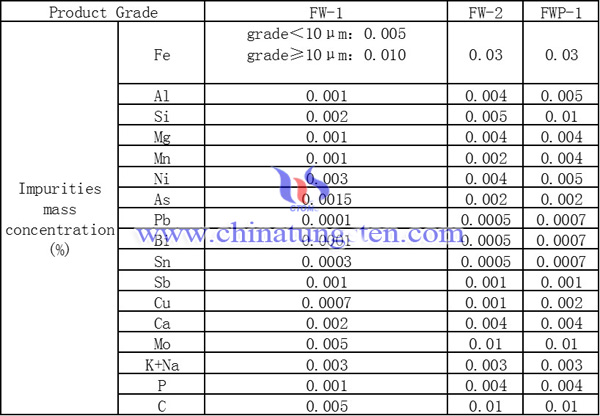
Since the remaining impurities after sintering significantly influencing the workability (grain boundary strenth, recrystallization temperature, grain size,etc.) and properties of the product, the impurities concentrations are strictly limitted in low level.
The purity of tungsten powder is mainly determined by the APT cleaness, since the maximum purity at the stage of APT crystallization in production process is more or less reached. Sources of contaminations after APT processing
mainly contacts with metallic tubes or boats in the furnaces. Consequently the foreign elements such as Fe, Ni, Cr and Co, are slightly increasing.
| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Tungsten Powder Production Process
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 08 May 2017 19:44
Tungsten powder is manufactured under strict quality control as raw materials of high density composites, diamond tools, metallizing paste, sintered parts of tungsten, etc. The manufature of tungsten powder is a key step in tungsten metal and alloy production, which significantly affect the properties of the subsequent products.
Production of tungsten powder is accomplished almost exclusively by the hydrogen reduction of tungsten oxides. The hydrogen reduction of tungsten halides and the carbon reduction of the tungsten oxides are presently not applied in industry on a large scale.
The common raw materials of tungsten powder reduction are tungsten trioxide and tungsten blue oxide(TBO), the latter has been the most widely used material since 1970s. Also, tungstic acid(H2WO4), tungsten yellow oxide and tungsten purple oxide are only used in selected metal grades.
The reduction of tungsten oxides by hydrogen is the essential reaction in tungsten powder production process,which equation and reaction process are shown as follow:
WOX+XH2=W+XH2O
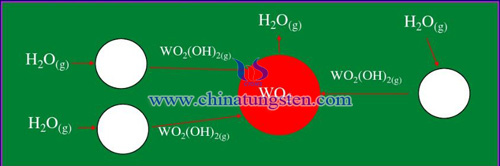
FIGURE1. Reduction process of tungsten oxide
The reduction can produce tungsten powder of grain size between 0.1 and 10μm starting from the same oxide precursor.
| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】 Tungsten Copper Electrode Types
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 08 May 2017 18:01

| Tungsten Copper Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-copper.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】Tungsten Carbide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 05 May 2017 19:13

| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】 Production Process of Thorium Tungsten Electrode
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 05 May 2017 18:07

| Tungsten Metals Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】What is Tungsten Carbide Ball
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 03 May 2017 17:55

| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】Tungsten Copper Electrode Applications
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 03 May 2017 17:50

| Tungsten Copper Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-copper.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
【Know Tungsten】What is Ammonium Paratungstate?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 03 May 2017 17:46

| APT Supplier: Chinatungsten Online ammonium-paratungstate.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Geometrical Properties of Tungsten Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 27 April 2017 16:24

| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com