IBM and Daimler Team to Improve Lithium Battery Safety
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Thursday, 16 January 2020 17:11
Lithium battery safety has always been a major concern for EV owners. Therefore, IBM and Daimler are set to improve cell safety. According to information, the current annual rate of new energy vehicle combustion accidents is about 0.9 to 1.2 per 10,000. Although this figure is lower than 2 to 4 per 10,000 fuel vehicles, it cannot be underestimated. Among these accidents, the rate of ternary lithium batteries accounted for the highest, reaching 89%. Domestic and foreign vehicle and battery suppliers are also intensifying research and development on battery safety.
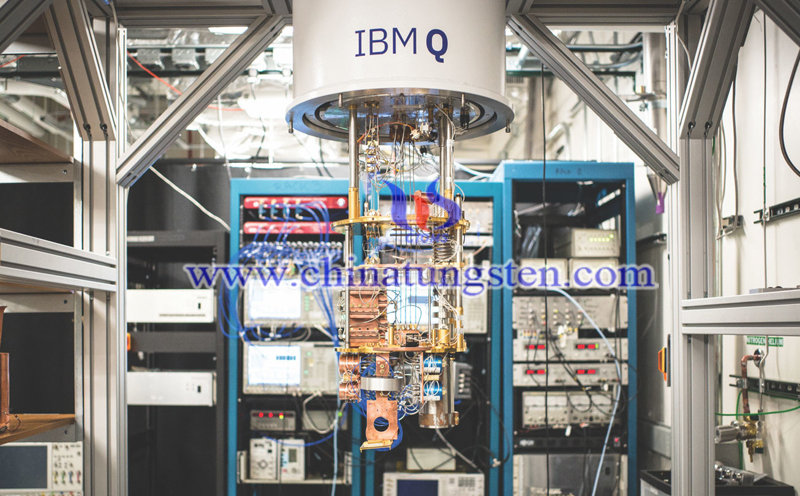

Recently, researchers from IBM and Daimler AG collaborated on quantum computing to model the dipole moment of three lithium-containing molecules, which brings people one step closer the next-generation lithium sulfur (Li-S) batteries.
A quantum computer is a type of physical device that performs high-speed mathematical and logical operations, stores, and processes quantum information per the laws of quantum mechanics. Researchers develop lithium-sulfur batteries by using a quantum computer to model the magnetic dipole moment of lithium molecules in lithium batteries. It is reported that lithium-sulfur battery would be more powerful, longer lasting and cheaper than today’s widely used lithium battery.
Simulation of molecules is a tough task, and accurate modeling is essential for discovering new materials. Daimler researchers hope that quantum computers will help them design next-generation lithium-sulfur batteries, because they have the potential to compute and precisely simulate their fundamental behavior. To ensure the accurate calculations on the hardware, researchers also use IBM quantum simulators to perform calculations on a traditional computer.
Current supercomputers can only simulate very simple molecules. For complex issues such as improving battery charging and battery life, traditional computers are not able to maintain accuracy on a smaller scale. Researchers usually observe and model in experiments, and test the theory.
In September 2017, the IBM research team published related papers of studying simulation of hydrogen, lithium hydride (LiH), and beryllium hydride (BeH2). The particular encoding from orbitals to qubits studied in this work can be used to simplify simulations of even larger molecule. This is not the first time that IBM has cooperated with Daimler Group on battery. Previously, the company had cooperated with Daimler Group, Japanese battery electrolyte supplier Central Glass Company and battery manufacturer Sidus to extract minerals from seawater and replace the costly cobalt for lithium battery manufacturing.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com