What Is the Tungsten Elemental Valence in Tungsten Diiodide?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 28 June 2023 17:15
In tungsten diiodide, the tungsten element has a valence of +2, and the iodine element has a valence of -1. Therefore, the quantity ratio of iodine to tungsten in tungsten diiodide is 2:1, which is determined according to the principle of electroneutrality.
The principle of electric neutrality refers to the system of compounds composed of many kinds of atoms, the number of electrons gained by some atoms must be equal to the number of electrons lost by other atoms to maintain the electric neutrality of the system. The valence electron configuration of the tungsten atom in tungsten diiodide is 5d46s2, with 6 electrons in the outermost layer, which loses 2 electrons in the chemical combination with iodine and gains 2 electrons from iodine to maintain the electrical neutrality and stability of the compound.
For transition metal elements, tungsten does not excite all the outer electrons to participate in the chemical reaction when it becomes the central atom of tungsten diiodide. As of now, we can obtain stable compounds of tungsten and iodine only in the form of tungsten diiodide, tungsten triiodide, and tetraiodide, but not in the form of tungsten hexaiodide. The consideration is not only the radius of the iodine atoms but also the fact that tungsten does not fill all the valence electrons around it when it combines with iodine to participate in the reaction in the hybridization orbital.
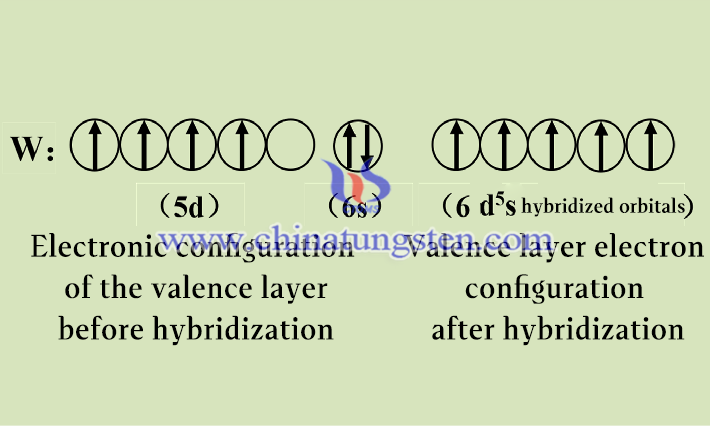
Although the series of compounds between tungsten and iodine do not allow all valence electrons to enter the hybridization orbitals, electronegative elements (e.g., fluorine, oxygen, chlorine) can excite the tungsten atom at the highest valence, i.e., the +6 valence. When the tungsten atom forms the highest valence molecule, the 5d and 6s electron orbitals with similar energies are superimposed on each other and recombined, where the valence electron orbital 6s is filled and 5d is unfilled. According to the quantum effect and the energy level formula E=n²h²/8ml², the atomic orbitals 5d and 6s of the valence electrons of each tungsten atom are first linearly combined, i.e., 5d and 6s are hybridized to form six d5s hybridized orbitals, and the six valence electrons are filled in the six hybridized orbitals respectively after hybridization.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com