What Is the Type of Crystal Structure of Tungsten Diiodide?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 09 July 2023 01:12
The type of crystal structure of tungsten diiodide is an orthorhombic crystal system, space group Bbem (No. 64), with lattice parameters a = 1258 pm, b = 1259 pm, and c = 1584 pm, and is a crystal cell with hexahedra. Each hexahedron has a tungsten atom in the center surrounded by six iodine atoms, forming a tungsten-iodine octahedron. The tungsten and iodine atoms are located at positions (0,0,0) and (0.5,0.5,0.5), respectively. The crystal has a layered structure with each layer consisting of tungsten-iodine octahedra, with neighboring layers interacting with each other through weak van der Waals forces.
The crystal structure determines the material properties, and the physical phase change is an important parameter to examine the crystal structure change. When people study the properties of tungsten diiodide, they find that the physical phase change is closely related to the crystal structure of its orthorhombic crystal system.
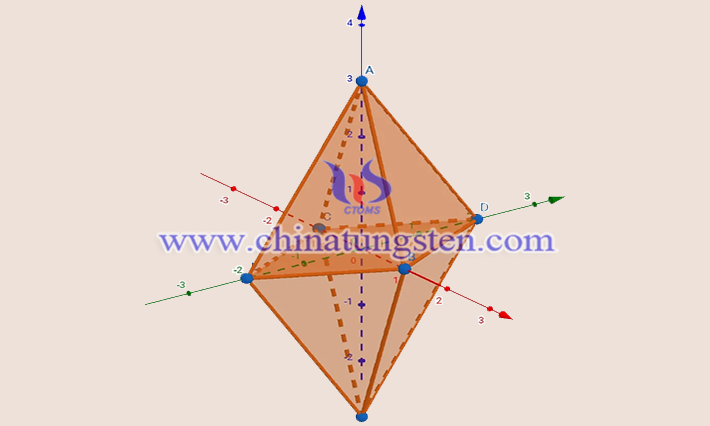
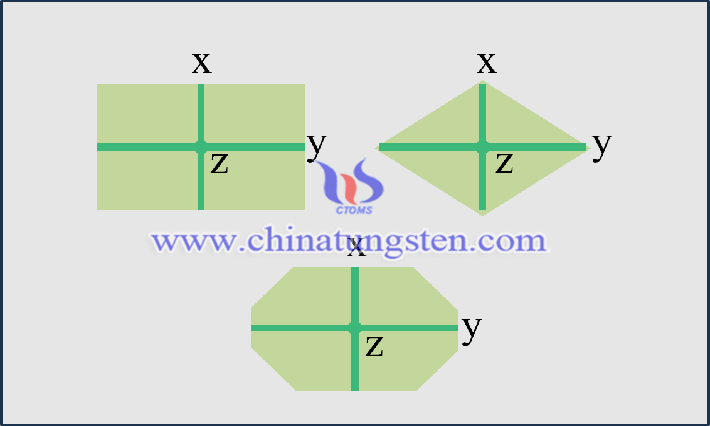
The orthorhombic crystal system, also known as the rhombohedral crystal system, has no higher axis of symmetry, i.e., the crystal system has no axis of symmetry around which the 360° rotations coincide more than three times. The three axes in a tungsten diiodide crystal are not at all equal in length, and their intersection angles are 90 degrees perpendicular to each other. Taking the cross-section of the crystal consisting of the x-axis and y-axis as an example, the plane formed by the two axes of a rhombohedral crystal system crystal can be either a rectangle, a rhombus, or a composite of the two.
The layers of tungsten diiodide crystals are stacked on top of each other relying on weak van der Waals forces. Due to the weak interaction force between the layers, it is easy to peel off the layers from each other under the action of external force. This feature allows tungsten diiodide to be decomposed and bonded within molecules in tungsten iodine lamps more efficiently and can largely extend the service life of the lamp. However, tungsten iodide lamps also have certain drawbacks, it has high power, and high heat generation, and the shell is relatively simple and easy to damage, not rainproof. According to "Safety Technical Code for Temporary Electricity Use at Construction Sites" and "Technical Code for Fire Safety at Construction Sites of Construction Projects", the use of tungsten iodine lamps is prohibited at construction sites, and it is more suitable for application in large-scale places that need strong light sources and dry environments.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com