Brief Introduction of Molybdenum Disilicide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 18 August 2021 14:08
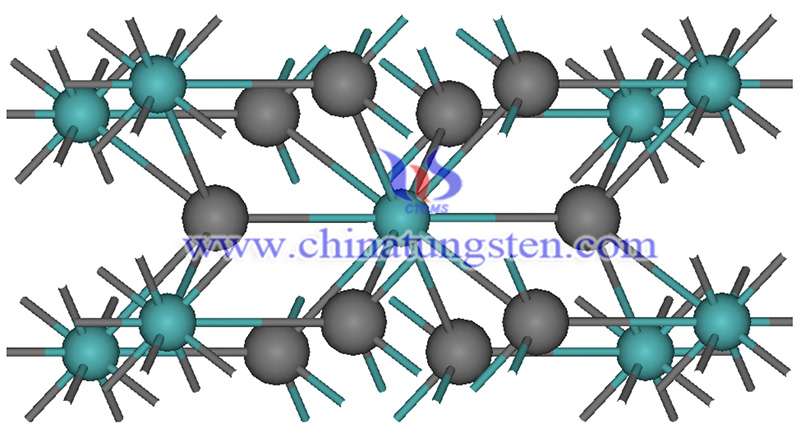
Molybdenum disilicide is an inorganic compound, which is a gray metallic solid, with the chemical formula of MoSi2. It is soluble in nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid while insoluble in most acids. The radii of the two kinds of atoms differ from each other, the electronegativity is relatively close, and they host similar properties to ceramics and metals.
MoSi2 is conductive. In order to prevent further oxidation, a passivation layer of silicon dioxide can be formed on the surface at high temperatures. It is mainly used in the fields of high-temperature anti-oxidation coating materials, electric heating elements, structural materials, integrated electrode membranes, composite materials, structural ceramic connecting materials, and wear-resistant materials, and so on.
![]()
MoSi2 is the mesophase with the highest silicon content in the Mo-Si binary alloy system. It is a Dalton intermetallic compound with a fixed composition.
It is a high-temperature resistant material with excellent performance and with the dual characteristics of ceramics and metal. At the same time, it owns excellent high temperature oxidation resistance. The oxidation temperature is as high as 1600℃, equivalent to silicon carbide with medium density (6.24g/cm3) and low thermal expansion coefficient (8.1×10-6K-1).
Molybdenum disilicide is metallic, soft and plastic above 1000℃. Below the brittle-to-ductile transition temperature (1000°C), it holds good electrical and thermal conductivity and has ceramic-like high hardness and brittleness. MoSi is mainly used as integrated circuits, heating elements, high-temperature anti-oxidation coatings, and high-temperature structural materials.
U-shaped MoSi2 heating rod is the most widely applied specification in the heating element of MoSi2 heating rod. In electric heating equipment, the components are vertically suspended and installed through the support chuck to avoid adding mechanical stress to the heating end of the component, or it is easy to cause the component to break.
The MoSi2 heating rod works for a long time at high temperature, the surface of the film gradually evaporates, and the heating rod undergoes thermodynamic phase equilibrium from the inside to the surface. When the concentration gradient of surface silicon is not enough to form the lowest silicide phase, oxidation and volatilization of free molybdenum will occur, forming a quartz glass protective film on the new molybdenum silicide interface.
In this manner, volatilization and film formation continue, and the composition continues to decrease, until the local minimum cross-section is overloaded and burned. This is the main failure mode of the silicon molybdenum disilicide heating rod in the continuous kiln.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com