Nanosized Tungsten Powder Prepared from Ammonium Paratungstate
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 31 December 2020 17:46
Tungsten is used in the production of numerous end use items. It is widely used for high temperature applications such as filaments in light bulbs, cathodes in high power lamps, and rocket nozzles in space crafts. Tungsten is also used in the manufacture of superalloys and catalysts. In addition, its considerable applications in industry as a refractory metal owing to its outstanding hardness and wear resistance in the form of tungsten carbide are well known.
As the powder properties significantly affect the subsequent operations, such as pressing and sintering. Nanoscaled tungsten powder promises to yield very hard, strong, and wear resistant materials via the press-sinter route.A thermal plasma process was applied to produce nanosized tungsten powder using ammonium paratungstate (APT) as the starting material.
The experimental procedures are as follow:
Nanosized tungsten powder was synthesized in a thermal plasma reactor, in which ammonium paratungstate (99.9%) was used as the precursor and hydrogen (99.9%, H2) was used as the reducing agent.
The synthesized tungsten powder and submicron tungsten powder were each mixed with 2 wt.% of wax. The wax was used to decrease friction between the particles as well as between the powder and the press die in the subsequent compaction process. In order to prepare nanosized tungsten powder, the submicron tungsten powder mixed with 2 wt.% of wax was milled using a High Energy-Dual Planetary Mill (HE-DPM) for 6 h. The ratio of WC balls to powder was 10:1 by weight and heptane was used as the milling media. The tungsten powders were cold-pressed by the use of Carver Laboratory Press under 5 tons (∼242 MPa) holding for 1 min using a WC–Co die of 16.2 mm diameter. Then, the green compacts were sintered under flowing H2 atmosphere at 1400 °C for different holding times of 1, 30 and 60 min, in which the ramping rate of tube furnace to increase the temperature up to 1400 °C was 10 °C/min and the cooling rate to room temperature was also 10 °C/min.
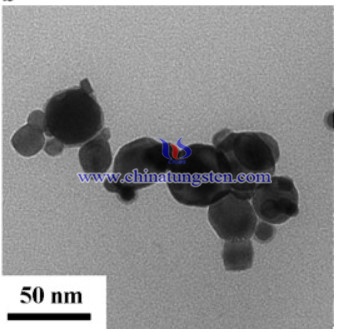
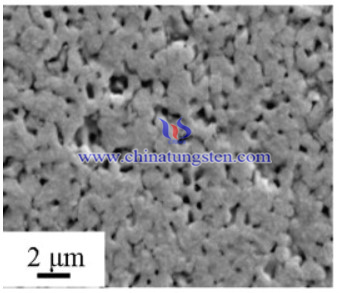
The produced tungsten powders were analyzed by XRD (Siemens, D5000) and its morphology was examined by TEM (FEI, Tecnai30). The tungsten powders and sintered compacts were analyzed using analytical scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Topcon sm-300). The grain size of produced W powder was calculated from the XRD pattern by applying the Scherrer equation or the Stokes and Wilson equation.
In conclusion, In the present work, nanosized W powder with an average particle size of 25 nm was synthesized by a thermal plasma process using ammonium paratungstate (APT) as the precursor. Comparing with submicron W powder (0.5 μm average size) and nanosized W powder (23 nm average size) produced from the latter by high energy milling. The hardness of the compact of the plasma-synthesized powder (315 VHN) sintered at 1400 °C was higher than that of submicron-sized powder (193 VHN) and was similar to that of the milled powder (309 VHN). The plasma-synthesized powder, however, yielded a compact with much lower tendency to form cracks than the milled powder.
- APT Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: ammonium-paratungstate.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com