Sintering - Plastic Flow
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 22 February 2018 22:39
In the process of sintering, there are many kinds of material migration mechanisms, such as viscous deformation, diffusion, plastic deformation and so on. Some scholars believe that the formation and growth of the sintered neck can be regarded as the result of the plastic deformation of the metal powder under the action of surface tension.
Plastic flow theory is the result of high temperature micro creep theory applied in sintering process. The high temperature creep of metal is the process of micro deformation under constant low stress. Under the effect of surface stress (about 0.2-0.3MPa), slow flow of the powder is similar to that of the micro creep. The difference is that the surface tension decreases gradually with the sintering process, so the sintering speed gradually slows down.
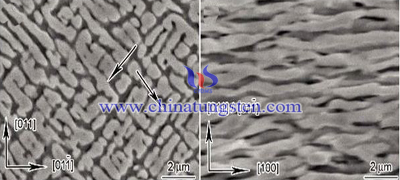
LeNir and Ansel believed that in the early stages of the sintering, the surface tension was large, and the plastic flow could be achieved by dislocation movement, a dislocation mechanism similar to that of creep. In the later period of sintering, the expansion of the flow is similar to the diffusion creep under low stress. The diffusion creep is realized by the self-diffusion of vacancy, and the creep velocity is proportional to the stress. Creep under high stress occurred by dislocation slip or climb.
According to the relationship between the diffusion creep and the vacancy diffusion under stress, the relationship between the viscosity coefficient of the plastic flow resistance and the self-diffusion coefficient D is obtained as follows.
1/η=Dδ3/(kTl2)(1)
Where
η-- Coefficient of viscosity,
D-- Self-Diffusion coefficient,
k-- Boltzmann constant,
δ-- Lattice constant,
T-- System temperature.
Assuming that the two ball is sintered, the size of the sinter neck region is equal to the volume of the lens shaped part that runs through the two balls. The diffusion equation of the plastic flow mechanism is as follows:
x9/a4.5=At(2)
Where
x-- Radius of the sintered neck,
a-- Radius of powder particle,
B—Coefficient,
t-- Sintering time.
In the process of sintering, the 9 squares of the radius X in contact with the neck is proportional to the sintering time t. Plastic flow is suitable for the early stage of powder sintering.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com