Design Principle of Tungsten Wire in Glass Heating Equipment
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:27
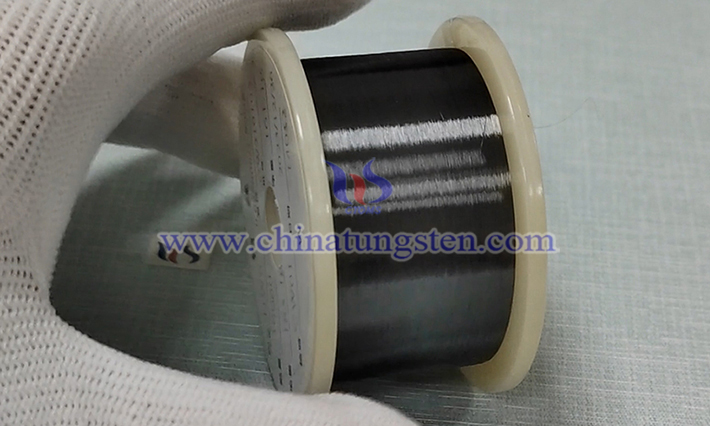
The core design of tungsten wire heating elements used in glass heating equipment (such as glass kilns, furnaces or vacuum coating equipment) is to use the extreme high temperature stability and efficient radiation heat transfer ability of tungsten metal to achieve uniform and rapid heating of glass in harsh environments. The following are its key design principles:
Advantages of Tungsten Wire in Heating Glass Process
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:25
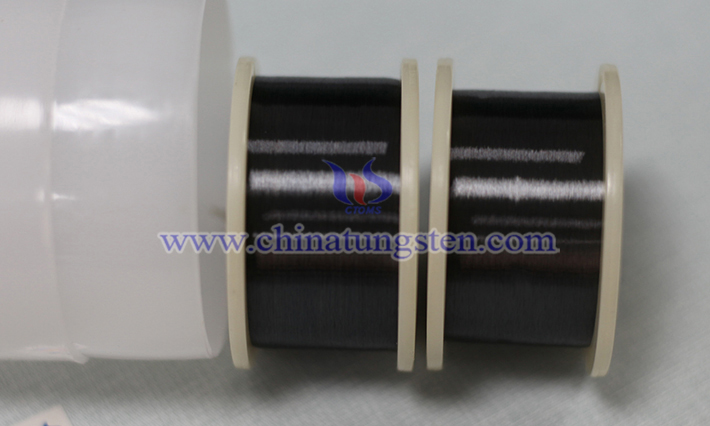

As a high-performance functional material, tungsten wire has shown multi-dimensional technological innovation value and application advantages in the field of heating glass process. Its unique physical and chemical properties not only break through the limitations of traditional heating technology, but also promote the evolution of glass products towards intelligence and efficiency.
Selection of Tungsten Wire in Glass Heating System
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:23
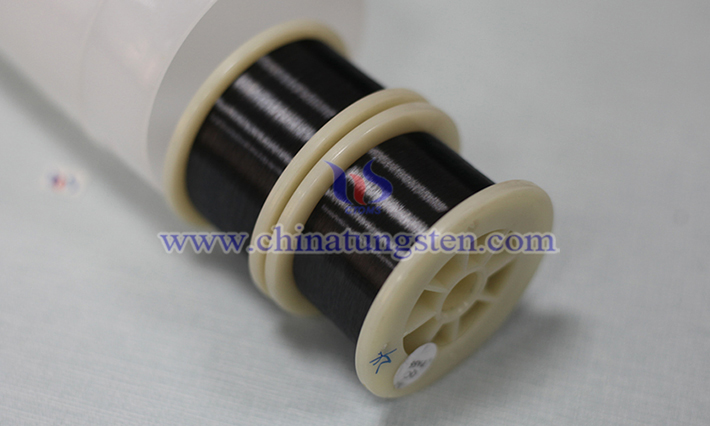
Tungsten wire has an extremely high melting point (about 3422℃) and is an ideal high temperature resistant material in glass heating system. Its resistivity is moderate, it can heat up quickly when heated, and it has good thermal stability and is not easy to deform or melt. Tungsten wire also has a low thermal expansion coefficient and can maintain structural stability at high temperatures. In addition, the chemical inertness of tungsten makes it difficult to react with glass or surrounding gases at high temperatures, extending its service life.
Tungsten Wire: The Temperature Guardian in Glass Heating Equipment
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:21
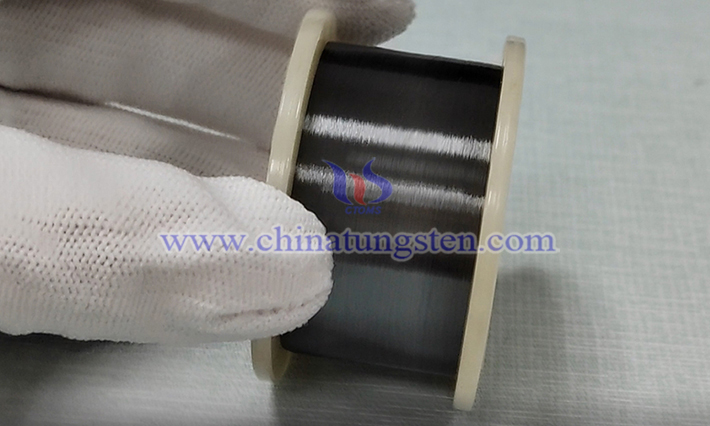
In processes such as glass melting, forming and sealing, heating equipment needs to operate stably at high temperatures far exceeding 1,000 degrees. When common alloy materials yield at high temperatures, tungsten wire becomes the key support in this extreme thermal field with its excellent physical properties.
Role of Tungsten Wire in Glass Heating Process
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:19

The role of tungsten wire in glass heating process is mainly reflected in efficient heating, stability and precise temperature control ability, and it is an important component to ensure the quality of glass products and process efficiency.
Cleaning of Tungsten Wire for Glass Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:17

Tungsten wire is often used in glass heating equipment due to its high melting point and heat resistance, but long-term use will affect performance due to oxidation, contamination or residue accumulation. Cleaning of tungsten wire for glass heating is an important step to ensure heating efficiency and extend service life.
Maintenance of Tungsten Wire for Glass Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:15
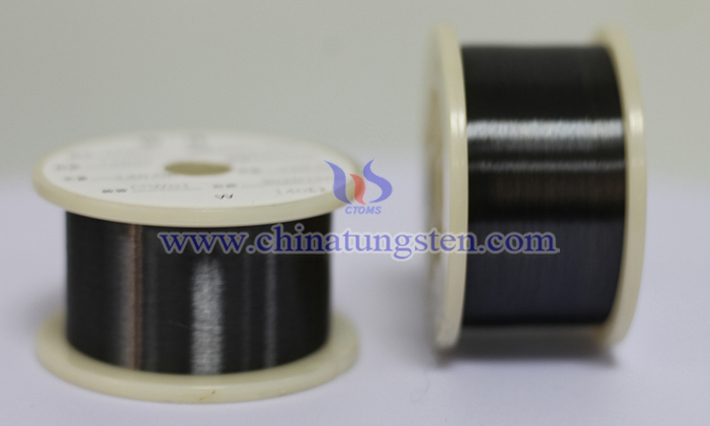
The maintenance of tungsten wire for glass heating is essential to extend its service life and ensure the heating effect. Tungsten wire is widely used in glass heating equipment due to its high melting point and excellent electrical conductivity, but it is easily damaged in high temperature and oxidizing environment, so scientific and reasonable maintenance methods are required.
Scope of Application of Tungsten Wire for Glass Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:13

Tungsten wire is often used in glass heating process due to its high melting point (about 3422°C), high strength and good thermal stability, especially in scenes requiring high temperature environment.
Storage of Tungsten Wire for Glass Heating
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 June 2025 19:09

The storage of tungsten wire for glass heating requires special attention to its physical and chemical properties to ensure that its performance is not damaged and its service life is extended.
What Is Tungsten Nail Sinker?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 25 June 2025 19:45
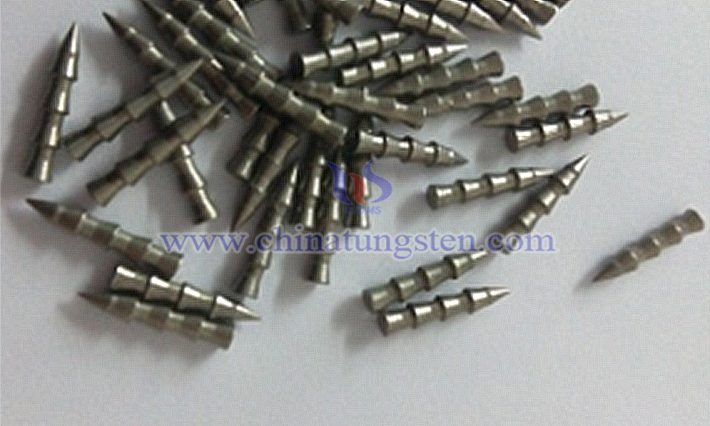

Tungsten nail sinker is a fishing tool crafted from metal tungsten as the primary material, processed into a slender needle-like shape, and categorized as a subset of "sinkers" in fishing accessories. Its core feature leverages tungsten’s high density (approximately 19.3 g/cm³), achieving significant weight in a small volume while optimizing hydrodynamic performance post-entry into water.


 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com