Tungsten Alloy Radiation Shielding For Radioactive Decay
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 May 2016 19:14
- Written by minghui
- Hits: 325
 Radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays and conversion electrons. A decay, or loss of energy from the nucleus, results when an atom with one type of nucleus, called the parent radionuclide (or parent radioisotope), transforms into an atom with a nucleus in a different state, or with a nucleus containing a different number of protons and neutrons. The product is called the daughter nuclide. In some decays, the parent and the daughter nuclides are different chemical elements, and thus the decay process results in the creation of an atom of a different element.
Radioactive decay, also known as nuclear decay or radioactivity, is the process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays and conversion electrons. A decay, or loss of energy from the nucleus, results when an atom with one type of nucleus, called the parent radionuclide (or parent radioisotope), transforms into an atom with a nucleus in a different state, or with a nucleus containing a different number of protons and neutrons. The product is called the daughter nuclide. In some decays, the parent and the daughter nuclides are different chemical elements, and thus the decay process results in the creation of an atom of a different element.
No matter be which kind of decay, radioactive rays will be generated. Exposure of large dose or exposure of a certain dose for a long-term both will cause harm to human body. Such as γ-rays can penetrate human skin and get into human body, to interact with cells in vivo, thus eroding complex organic molecules (such as proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes). These molecules once destroyed, the normal chemical processes in the human body will get disturbed, and cell death will be increased in severe cases. Other radiation also can penetrate the human skin to cause radiation damage. When radiation enters the body, it will destroy the molecular structure of the genetic material DNA, leading to congenital malformations or leukemia, and it will also damage the reproductive system, central nervous system and endocrine system and cause cataracts, cancer, and a number of radiation sickness.
Tungsten alloy radiation shielding can be used to shield the radioactive rays produced by the process of radioactive decay. Tungsten alloy radiation shielding for radioactive decay is made up of tungsten heavy alloy with high density. Since the shielding property of a material is closely related to its density. The higher the density is, the better the shielding performance is. Therefore Tungsten alloy radiation shielding for radioactive decay has excellent shielding property, so that can absorb and shield the radioactive rays produced by the process of radioactive decay in a high degree, protecting humans from radiation damage. The density of lead is lower than tungsten alloy, so comparing to the same weight of lead shielding, tungsten alloy radiation shielding is smaller and thinner. In addition, tungsten alloy radiation shielding for radioactive decay is non-toxic and environmentally friendly shielding material.
| Tungsten Alloy Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-alloy.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
WO3 Prepares Non-Supported Desulfurization Catalyst - Urea Melting Reaction Method
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 May 2016 17:17
- Written by chunyan
- Hits: 273
 Urea melting reaction method is mixing the precursor metal components and urea, reacted in a molten state urea to remove excess urea to obtain the catalyst particle with nano-pores and high specific surface area. The example that using urea melting reaction method and taking tungsten trioxide as raw material to prepare non-supported desulfurization catalyst is as following:
Urea melting reaction method is mixing the precursor metal components and urea, reacted in a molten state urea to remove excess urea to obtain the catalyst particle with nano-pores and high specific surface area. The example that using urea melting reaction method and taking tungsten trioxide as raw material to prepare non-supported desulfurization catalyst is as following:| Tungsten Oxide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-oxide.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burrs Description (2/2)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 May 2016 16:52
- Written by xiaobin
- Hits: 257
Compared with developed country, there are several problems in tungsten carbide rotary burrs of our country: 1. The defect of materials (includes the purity of raw material, the machining parameters control, etc.,); 2. The most used tungsten carbide rotary burr is not integral, which uses tungsten carbide as head, bearing steel as shank and fabricated rotary burr by welding. So it will have problems in welding firmness; 3. The precision and operability of CNC machining equipment; 4. The angle, shape and tolerances of the edge and insufficient concentricity.
In order to further improve the cutting properties and extend the service life of tungsten carbide rotary burr, we analyze it from the mechanism of cutting and forming. Generally, Carbide rotary burrs edge back is composed of straight or curved: the straight edge is easy to be processing, but the strength of the edge is lower; the intensity and difficulty of processing polyline edge back has a certain increase; although curve edge has a difficulty in processing, it can ensure that the strength at any point of the cross-section is substantially equal. Therefore, we need to find out a kind of edge that based on the strength and also easy to be fabricated.
Besides, the spacing between two edges also plays a important role in the process. If the spacing is too large, the corresponding cutting and machining efficiency decreases; if the spacing is too small, it can not ensure the scrap removing, which will have an effect on edge blocking and the efficiency of tungsten carbide rotary burr. The overall milling process can be divided into three steps: the initial wear stage, normal wear stage and rapid wear stage. On each of the different stages through reasonable cutter angle (rake angle, relief angle, the main angle, relief angle and blade angle) choice, you can reduce the wear of the cutting force and cutting heat brought in the same under the cutting conditions, cutting into full play, enhance overall efficiency and precision. Overall, improvements and material from the rotary file rotary file blade teeth should have high hardness, high strength, high wear resistance, good impact resistance and high temperature conditions can still ensure good cutting performance, but also to facilitate the processing of the material; The tolerances on the edge to be precise enough to meet the requirements of surface roughness.
| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Non-Supported Hydrodesulfurization Catalyst Material--WO3
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 May 2016 17:15
- Written by chunyan
- Hits: 258
 With the declining oil quality and industrial emissions standards becoming critical, the issue to develop ultra-clean fuel is increasingly difficult, and very necessary. Vary the reaction conditions (such as raising the temperature and pressure of the reaction, reducing airspeed, etc.) can achieve the goal of deep hydrodesulfurization process, however, they will result in the loading cost increased, product quality and the amount of processing oil reduced, also the other issues, therefore, the development of new deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst is imperative.
With the declining oil quality and industrial emissions standards becoming critical, the issue to develop ultra-clean fuel is increasingly difficult, and very necessary. Vary the reaction conditions (such as raising the temperature and pressure of the reaction, reducing airspeed, etc.) can achieve the goal of deep hydrodesulfurization process, however, they will result in the loading cost increased, product quality and the amount of processing oil reduced, also the other issues, therefore, the development of new deep hydrodesulfurization catalyst is imperative.| Tungsten Oxide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-oxide.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |
Tungsten Carbide Rotary Burrs Description (1/2)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 May 2016 16:50
- Written by xiaobin
- Hits: 251
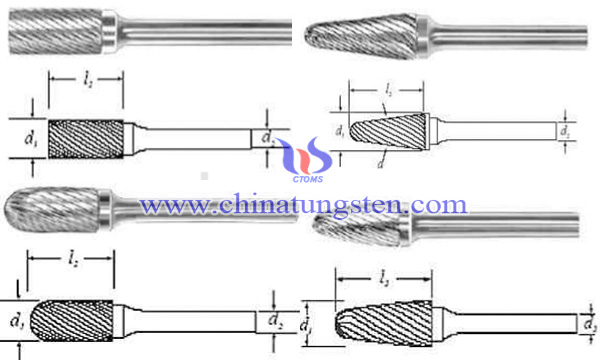
Tungsten carbide rotary burrs consist of the hard phase WC and the binder phase Co, which is also known as tungsten carbide assorted cutter or high-speed molding cutter and so on. It is mainly cooperated with high-speed electric grinder and pneumatic tools. Due to its processing hardness can reach more than HRA 85, it can be widely applicable to the most of materials, such as common cast iron, steel, copper, aluminum, marble, alloy steel, carbon steel and other metal or non-metal materials. The principle is that tungsten carbide rotary burr clamped on high-speed rotary tool, which achieves the cutting performance by the pressure and feed rate controlling.
Since tungsten carbide rotary burr has excellent cutting properties and long life span, it has a broad application prospect, such as finishing for metal mold cavity; castings, forgings, welding components the existence of flash, burrs, weld cleaning; A variety of mechanical parts chamfering, machining grooves and keyways; pipeline, flow channel, the inner surface of the hole parts cleaning and grinding; the sculpture of A variety of metal or non-metallic materials, etc.
According to the shape of head, tungsten carbide rotary burr can be divided into cylinder (A), cylindrical-shaped (C), round arch (F), spherical (D), round-shaped torch (H), 90° conical (K), 60° conical (J), 38° conical (M), arc-shaped disk (T), inverted conical (N), tapered round (L), tapered tip (M), drum-shaped (B), ellipse (E), curved arrow-shaped (G), tapered flat-shaped (S), half arc-shaped (W) and so on. And the common grades used in tungsten carbide rotary burrs are YG6, YG8 and YG10x, which has excellent impact toughness, wear resistance and is suitable for cold heading, cold punch, cold mold fabricating.
| Tungsten Carbide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online tungsten-carbide.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News&Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com