Tungsten Crucibles Are Used in the Preparation of Semiconductor Materials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 09 June 2025 15:05
With the rapid development of semiconductor technology, the requirements for material purity, structural stability and preparation process are increasing. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties, tungsten crucible occupies an extremely important position in the preparation of semiconductor materials, especially in key processes such as high-temperature crystal growth, smelting, and vapor deposition.
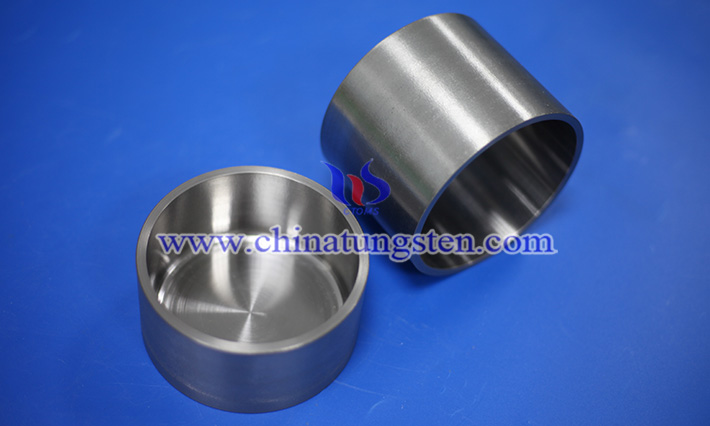
Tungsten is a metal with an ultra-high melting point of up to 3410°C, second only to tantalum and rhenium among all metals. This allows the W crucible to maintain stable structure and non-deformation characteristics at extremely high temperatures, making it ideal for the preparation of semiconductor materials such as monocrystalline silicon, gallium nitride (GaN), silicon carbide (SiC) and other materials with high melting points. For example, in the physical vapor deposition (PVD) of gallium nitride or the high-temperature sublimation growth of silicon carbide, long-term processing at temperatures above 2000°C is often required, where only high-temperature metals such as tungsten can be used as container materials.
Another key advantage of tungsten crucibles is their excellent chemical stability. In reducing or neutral atmospheres (such as hydrogen and argon), tungsten will not easily react with other elements even in a high-temperature environment, which can effectively avoid contamination of semiconductor raw materials by reaction products and maintain high purity of materials. In the semiconductor industry, any impurities can affect the electronic properties of a device, so its low reactivity and very low vapor pressure are key to ensuring product quality.
W crucibles are commonly used for zone melting or recrystallization of monocrystalline silicon. In the zone melting process, the silicon rod is partially melted by electromagnetic heating and the melting zone is moved slowly to gradually purify the impurities. It acts as an auxiliary container to keep the structure intact and prevent the spread of impurities. In addition, W crucibles are also used in the preparation of certain special alloyed semiconductors (such as Si-Ge alloys, GaAs, etc.) to meet the challenges of high-temperature melting and high active ingredients.
In the Czochralski crystal pulling method (CZ method) of sapphire (Al₂O₃) single crystals, molybdenum crucibles are commonly used, but when the temperature is higher or the atmosphere is more demanding, W crucibles are also used as an alternative material. Especially in the field of advanced power electronics and third-generation semiconductor manufacturing, tungsten crucibles provide a reliable guarantee for high-temperature and long-term operation.
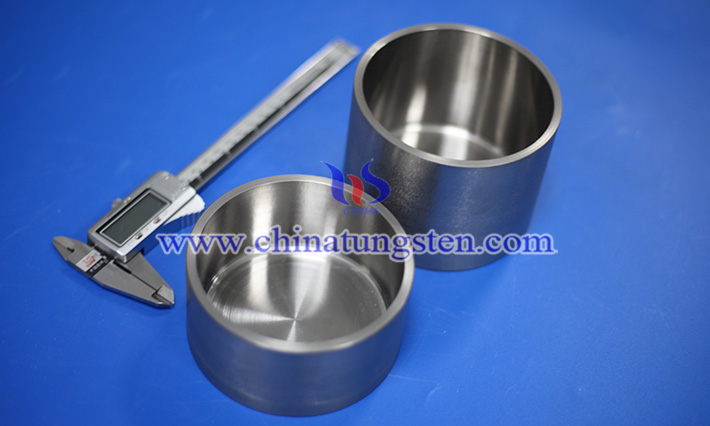

The use of W crucibles is also accompanied by its high density, good mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, which allows it to withstand repeated thermal stress and machining. Although tungsten material itself is relatively hard and difficult to process, with the development of precision manufacturing technology, the quality and size control ability of tungsten crucible is becoming more and more perfect, which can meet the strict standards of the semiconductor industry.
It should be noted that tungsten is easily oxidized to form tungsten oxide (WO₃) in an oxidizing atmosphere, especially in air above 400°C. Therefore, it must be used with vacuum system or inert gas protection to prevent the surface oxidation of tungsten from causing structural brittleness or performance degradation. In addition, the price of W crucibles is high, and their recycling and maintenance methods have also become an important part of cost control.
- Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- CTIA GROUP LTD: en.ctia.group
- Tungsten News & Price: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com