What Are the Chemical Properties of Tungsten Diiodide(I)?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 09 September 2023 17:41
- Written by Shuangfeng
- Hits: 1206
Tungsten diiodide (WI2) is an inorganic compound composed of the transition metal element tungsten and the halogen element iodine. It has many chemical properties, which will be described one by one below.
Read more: What Are the Chemical Properties of Tungsten Diiodide(I)?
Analysis of the Toxicity of Tungsten Diiodide
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 09 September 2023 17:36
- Written by Shuangfeng
- Hits: 1097

A small amount of tungsten diiodide has low theoretical toxicity and will not harm health.
What Gas Is in Tungsten Iodine Lamp?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 14 August 2023 01:19
- Written by Shuangfeng
- Hits: 957
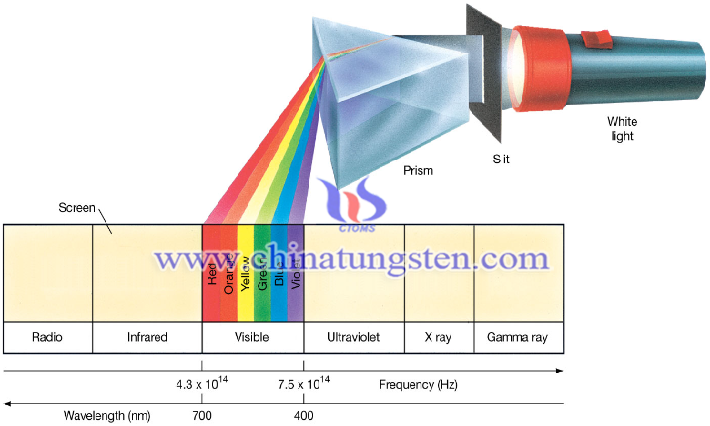
There are tungsten vapor, iodine vapor, tungsten iodide gas and inert gas in the iodine tungsten lamp.
What Are the Precautions for the Installation and Use of Iodine Tungsten Lamp?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 09 September 2023 17:30
- Written by Shuangfeng
- Hits: 902
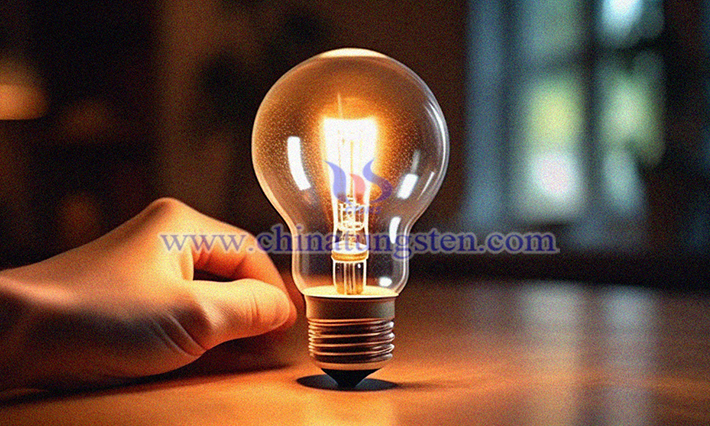

A tungsten iodide lamp is a kind of tungsten lamp filled with the halogen element iodine and belongs to a new generation of incandescent lamps In an iodine-tungsten lamp, the evaporation of iodine-tungsten circulating tungsten is effectively suppressed, and the problem of blackening glass shell is solved.Iodine tungsten lamp as a thermal radiation source has some potential safety hazards, so there are corresponding requirements and precautions for its installation and use.
Read more: What Are the Precautions for the Installation and Use of Iodine Tungsten Lamp?
Why Does the Tungsten Filament of a Tungsten Iodine Lamp Can Emit Light?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 11 August 2023 17:27
- Written by Shuangfeng
- Hits: 1168
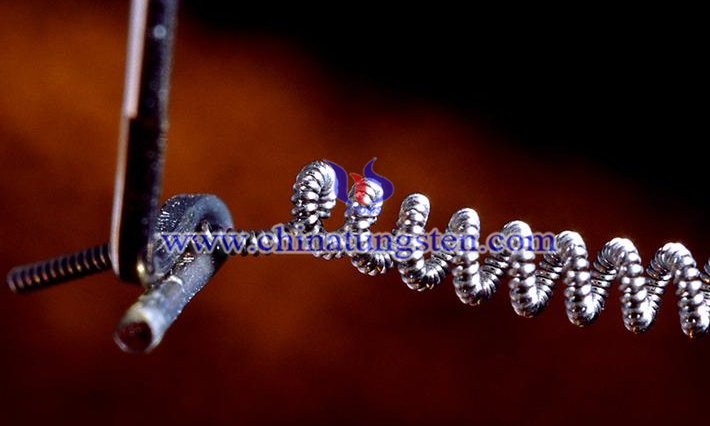

The tungsten filament of a tungsten iodine lamp is a conductor and can radiate visible light. A tungsten iodine lamp is a new type of electric light source, the main components are the internal tungsten filament and the external glass shell. Under the action of electric current, the spiral tungsten filament continuously gathers heat, making the temperature of the filament reach over 2000℃. Microscopically, the tungsten atom's electrons outside the nucleus are excited by heat to a high-energy state, to maintain stability and fall back to a low-energy state, the energy difference in the form of photons released, macroscopically visible luminescence phenomenon.
Read more: Why Does the Tungsten Filament of a Tungsten Iodine Lamp Can Emit Light?





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com