Global Rare Earth Production Increased by Nearly 4% in 2024
- Details
- Category: Rare Earth News
- Published on Thursday, 20 February 2025 19:35
Recently, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) released the global rare earth production and reserves in 2024, as well as the situation of the rare earth industry in the United States. The following is the relevant content compiled by China Tungsten Online.
Global rare earth reserves and production
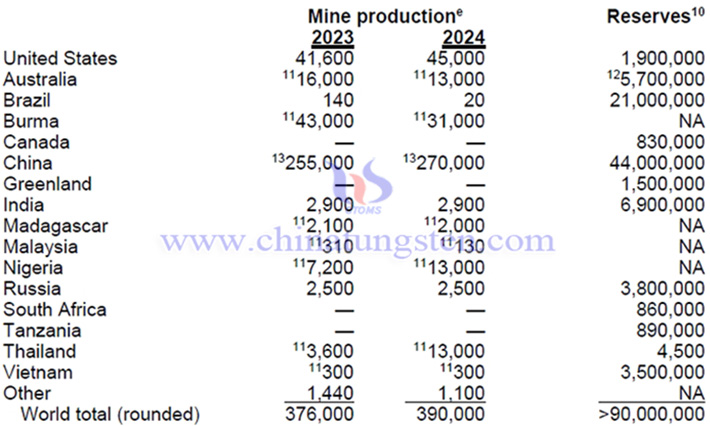
In 2024, the global rare earth reserves will be about 90 million tons, a year-on-year decrease of 18.18%. Among them, China has the highest rare earth reserves of 44 million tons, accounting for 48.89% of the global total reserves.
In 2024, the global rare earth production will be about 390,000 tons, a year-on-year increase of 3.72%. Among them, China has the highest rare earth production of 27 tons, accounting for 69.23% of the global total production.
Rare earths are relatively abundant in the Earth’s crust, but minable concentrations are less common than for most other mineral commodities. In North America, measured and indicated resources of rare earths were estimated to include 3.6 million tons in the United States and more than 14 million tons in Canada.
Situation of the rare earth industry in the United States
Rare earths were mined and processed domestically in 2024. An estimated 45,000 tons of REO in mineral concentrates were produced and were valued at $260 million. Bastnaesite (or bastnäsite), a rare-earth fluorocarbonate mineral, was mined as a primary product at a mine in Mountain Pass, CA. Monazite, a phosphate mineral, was stockpiled as a separated concentrate or included as an accessory mineral in heavy-mineral-sand concentrates in the southeastern United States. Mixed rare-earth compounds also were produced in the Western United States. The estimated value of rare-earth compounds and metals imported by the United States in 2024 was $170 million, an 11% decrease from $186 million in 2023. The estimated leading domestic end use of rare earths was catalysts. Significant amounts of rare earths are imported as permanent magnets embedded in finished goods. Other end uses were ceramics and glass, metallurgical applications and alloys, and polishing.
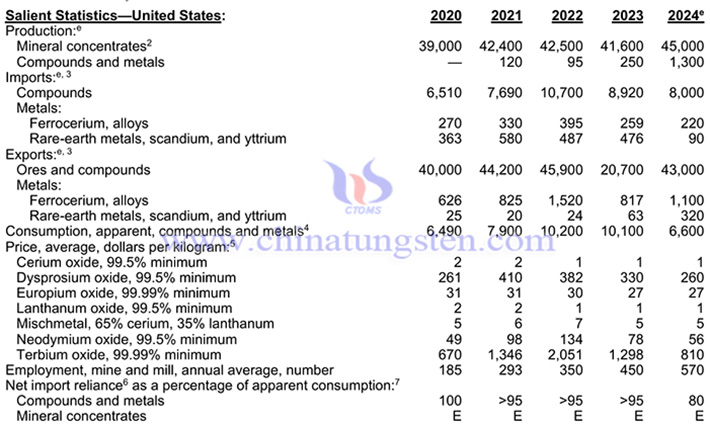
In 2024, the United States is expected to produce 45,000 tons of rare earth concentrates, an increase of 8.17% year-on-year; it is expected to produce 1,300 tons of rare earth compounds and metals, a year-on-year increase of 420%; it is expected to import 8,000 tons of rare earth compounds, a year-on-year decrease of 10.31%; it is expected to import 220 tons of ferrocerium and alloys, a year-on-year decrease of 15.06%; it is expected to import 90 tons of rare earth metals, scandium and yttrium, a year-on-year decrease of 81.09%; it is expected to export 43,000 tons of rare earth ores and compounds, a year-on-year increase of 107.73%; it is expected to export 1,100 tons of ferrocerium and alloys, a year-on-year increase of 34.64%; it is expected to export 320 tons of rare earth metals, scandium and yttrium, a year-on-year increase of 407.94%.
Import Sources (2020–23): Rare-earth compounds and metals: China, 70%; Malaysia, 13%; Japan, 6%; Estonia, 5%; and other, 6%. Compounds and metals imported from Estonia, Japan, and Malaysia were derived from mineral concentrates and chemical intermediates produced in Australia, China, and elsewhere.

source: USGS
- Rare Earth Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com