Global Molybdenum Production Increased by Nearly 5% in 2024
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Thursday, 20 February 2025 19:39
Recently, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) released the global molybdenum production and reserves in 2024, as well as the situation of the U.S. molybdenum industry. The following is the relevant content compiled by China Tungsten Online.
Global Molybdenum Reserves and Production in 2024
In 2024, the estimated average U.S. molybdic oxide price decreased by 13% compared with that in 2023. Estimated U.S. total imports for consumption of molybdenum decreased slightly compared with those in 2023. Estimated U.S. total exports decreased by 5% compared with those in 2023. Estimated apparent consumption in 2023 increased by 11% compared with that in 2023. In 2024, a Canadian company announced plans to restart its idled Idaho molybdenum mine in the second half of 2027 as well as a progressive rampup to full capacity production at its molybdenum-processing facility in Pennsylvania. Estimated global molybdenum production in 2024 increased by 6% compared with that in 2023. In descending order of production, China, Peru, Chile, the United States, and Mexico provided 90% of total global production. Of the five major producers, only China and the United States produced molybdenum from both primary molybdenum mines and byproduct copper mines; the other countries produced molybdenum as a byproduct from copper mines. Declining ore grades at porphyry copper mines continued to affect molybdenum production. Several large porphyry copper mines are expected to reach end-of-life in the mid-2030s which will further affect future molybdenum supply. Molybdenum was expected to continue to have strong demand in global power generation and infrastructure projects as countries continue to prioritize clean energy to address climate change.
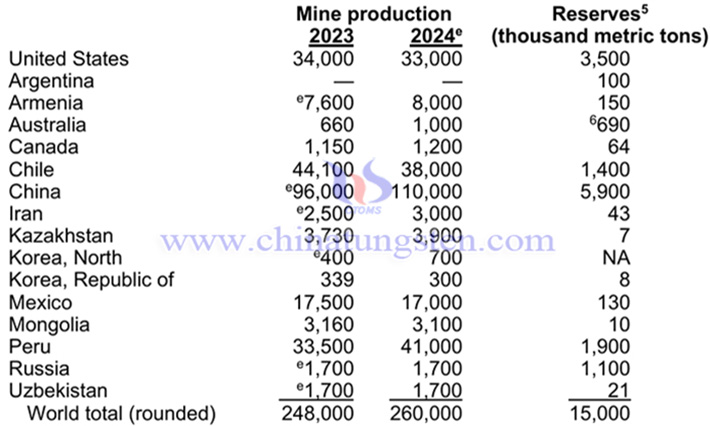
In 2024, the global molybdenum reserves will be about 15,000 kilotons, which is the same as the previous year. Among them, China has the highest molybdenum reserves of 5,900 kilotons, accounting for 39.33% of the global total reserves.
In 2024, the global molybdenum production will be about 260,000 tons, a year-on-year increase of 4.84%. Among them, China has the highest molybdenum production of 110,000 tons, a year-on-year increase of 14.58%, accounting for 42.31% of the global total production.
Identified resources of molybdenum in the United States are about 5.4 million tons and, in the rest of the world, about 20 million tons. Molybdenum occurs as the principal metal sulfide in large low-grade porphyry molybdenum deposits and as an associated metal sulfide in low-grade porphyry copper deposits. Resources of molybdenum are adequate to supply world needs for the foreseeable future.
There is little substitution for molybdenum in its major application in steels and cast irons. In fact, because of the availability and versatility of molybdenum, industry has sought to develop new materials that benefit from its alloying properties. Potential substitutes include boron, chromium, niobium (columbium), and vanadium in alloy steels; tungsten in tool steels; graphite, tantalum, and tungsten for refractory materials in high-temperature electric furnaces; and cadmium-red, chrome-orange, and organic-orange pigments for molybdenum orange.
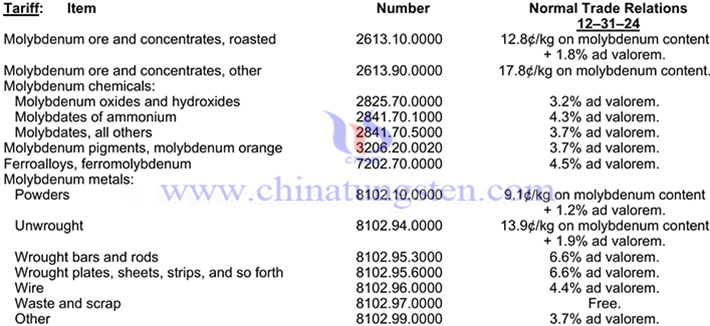
The situation of the molybdenum industry in the United States in 2024
Total estimated U.S. mine production of molybdenum concentrate decreased by 3% to 33,000 tons of molybdenum content in 2024 compared with 34,000 tons in 2023. Molybdenum concentrate production at primary molybdenum mines continued at two operations in Colorado, and molybdenum concentrate production from mines where molybdenum was a byproduct continued at seven operations (four in Arizona and one each in Montana, Nevada, and Utah). Three roasting plants converted molybdenum concentrate to molybdic oxide, from which intermediate products, such as ferromolybdenum, metal powder, and various chemicals, were produced. Molybdenum is a refractory metallic element used principally as an alloying agent in cast iron, steel, and superalloys and is also used in numerous chemical applications, including catalysts, lubricants, and pigments.

In 2024, the United States is expected to produce 33,000 tons of molybdenum concentrate, a year-on-year decrease of 2.94%; it is expected to import 16,000 tons of molybdenum ore and its concentrate, a year-on-year decrease of 1.23%; it is expected to import 13,000 tons of molybdenum primary products, a year-on-year decrease of 3.70%; it is expected to export 45,000 tons of molybdenum ore and its concentrate, a year-on-year decrease of 8.16%; it is expected to export 5,500 tons of molybdenum primary products, a year-on-year increase of 30.02%.
Import Sources (2020–23): Ferromolybdenum: Chile, 77%; Republic of Korea, 19%; United Kingdom, 3%; and other, 1%. Molybdenum ore and concentrates: Peru, 64%; Mexico, 18%; Chile, 12%; Canada, 5%; and other, 1%. Total: Peru, 35%; Chile, 34%; Mexico, 10%; Republic of Korea, 6%; and other, 15%.
source: USGS
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129595/5129696 Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices: Chinatungsten Online news.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com