Phosphotungstic Acid-Organometallic Framework Catalytic Material
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 29 June 2019 22:18
Biomass can be regarded as a promising alternative energy source for petroleum. The key to convert biomass into important energy materials and basic platform compounds is to convert cellulose, an important component of biomass, into glucose by directional hydrolysis.
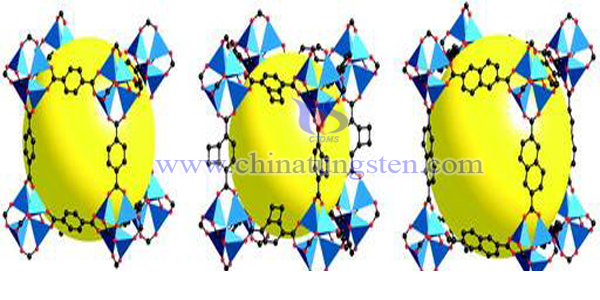
Some researchers have found a phosphotungstic acid-metal organic framework catalytic material which can be used to catalyze cellulose hydrolysis. Its characteristics are as follows: phosphotungstic acid is immobilized in the pore structure of the metal organic framework material with both alkaline and strong electronegative groups, and the metal organic framework is fixed by the restriction of pore size and the double binding action between the alkaline group of the active functional group and phosphotungstic acid. Phosphotungstic acid. The preparation method of the material includes the following steps:
The solvents, organic ligands, metal sources and phosphotungstic acid were mixed and stirred evenly. The solids were heated from room temperature to 110 ~220 ℃, kept at 110 ~220 ℃ for 8~36 h, centrifugally separated after cooling. The settled solids were washed with N, N-dimethylformamide at room temperature, then filtered and washed repeatedly until the filtrate was clear and transparent. After washing, the filtered solids were vacuum dried for 10~16 h at 60 ~80 ℃. That is to say, the phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton multifunctional material is obtained.
Phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton was used to catalyze cellulose hydrolysis: 0.02g starch, 0.1g phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton multi-functional material and 10mL distilled water were added into 25 mL COD digestion tube in turn. The magnetic rotor was put into the reactor at 120 ℃ for 5 h. The reaction process was stirred continuously. After the reaction was completed, centrifugal separation was carried out, and the upper clarifier was starch hydrolysate, and the settling solid was catalyzed. A mixture of chemicals and unreacted starch. After the reaction, the catalyst was washed repeatedly with distilled water for three times. After centrifugal separation, the solid was deposited in the centrifugal tube and dried in vacuum for 10 hours at 60 ℃. The solid powder obtained was the recovered catalyst. The hydrolysis of starch was repeated with the recovered catalyst for five times, and the yield of glucose was kept at 18.93%-19.98%.
Compared with ordinary catalysts, phosphotungstic acid, the active component of phosphotungstic acid in phosphotungstic acid-metal organic framework catalytic materials, directly participates in the synthesis of metal organic framework. The electrostatic interaction between basic groups and phosphotungstic acid can ensure the immobilization efficiency of phosphotungstic acid, simplify the operation steps of immobilization of phosphotungstic acid, make phosphotungstic acid uniformly distributed on the carrier and reduce the loss of phosphotungstic acid in the hydrolysis reaction. The catalyst can be recycled for many times, and the catalytic activity has not decreased significantly.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com