Effect of Tungstate on Nitrate Reduction by Pyrobaculum aerophilum
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 05 April 2022 19:06
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1168
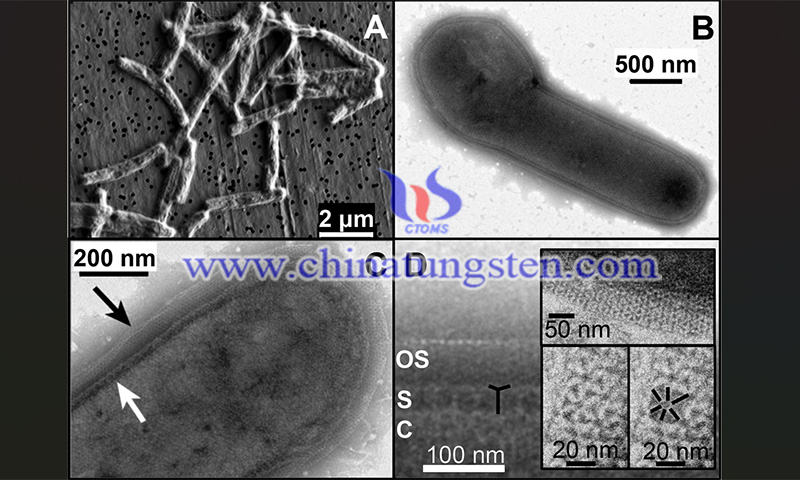
Researchers at the University of California have conducted a study on the effect of tungstate on nitrate reduction in Pyrobaculum aerophilum, a hyperthermophilic archaeon that can respire both at low levels of oxygen and anaerobically with nitrate as the electron acceptor. Under anaerobic growth conditions, nitrate is reduced to molecular nitrogen via the denitrification pathway.
Read more: Effect of Tungstate on Nitrate Reduction by Pyrobaculum aerophilum
Molybdenum Oxide Nanoparticle Aggregates Grown by Chemical Vapor Transport
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 05 April 2022 18:59
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1333
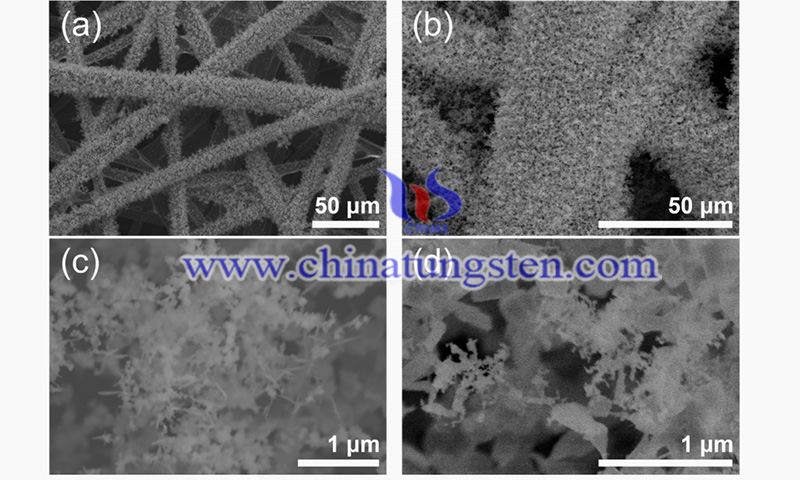
A study conducted by researchers at Daegu Catholic University in South Korea introduces advanced methods that combine chemical vapor transport (CVT) with quenching effects to create molybdenum oxide nanoparticle aggregates arrays consisting of fine nanoparticles (NPs) in a layered structure, grown vertically on individual carbon fibers of a carbon fiber paper (CFP) substrate.
Read more: Molybdenum Oxide Nanoparticle Aggregates Grown by Chemical Vapor Transport
Electron Flow Versus Magnetic Flux in Monolayer Molybdenum Disulfide Quantum Dot
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 April 2022 19:52
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1420
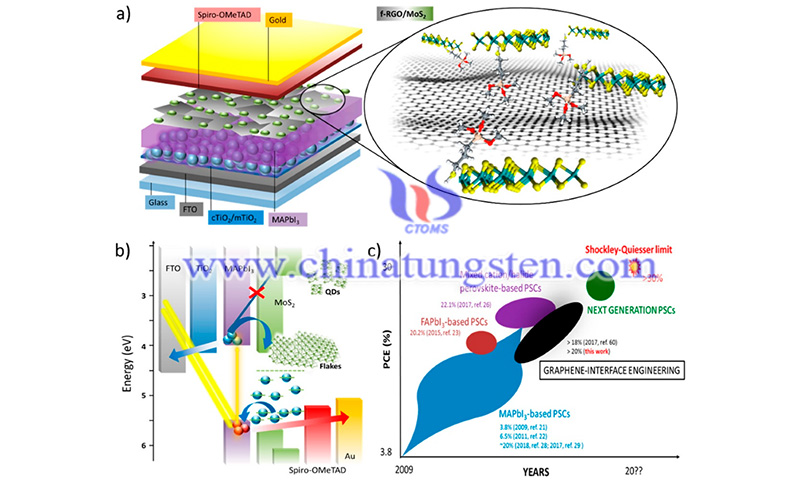
Researchers from Morocco have investigated the Dirac electron scattering problem in quantum dots of monolayer molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) quantum dots subject to magnetic flux. Analytical expressions for the eigenstates, scattering coefficients, scattering efficiency, and radial component of the reflected electron flow were developed by solving the Dirac equation.
Read more: Electron Flow Versus Magnetic Flux in Monolayer Molybdenum Disulfide Quantum Dot
Molybdenum-Based Sodium Ion Batteries Development
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 04 April 2022 16:33
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1367

A recent study carried out by Yu Jiang et al at Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Thin Films, Soochow University, Suzhou, China has investigated the Molybdenum-based materials for sodium ion batteries (SIBs). SIBs are considered to be one of the most promising candidates for energy storage required for renewable energy sources. The main difficulty is finding a suitable anode material, and molybdenum-based materials are expected to solve this problem.
Read more: Molybdenum-Based Sodium Ion Batteries Development
Molybdenum Doped Bilayer Photoanode Nanotubes Enhance Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Saturday, 02 April 2022 19:49
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1343
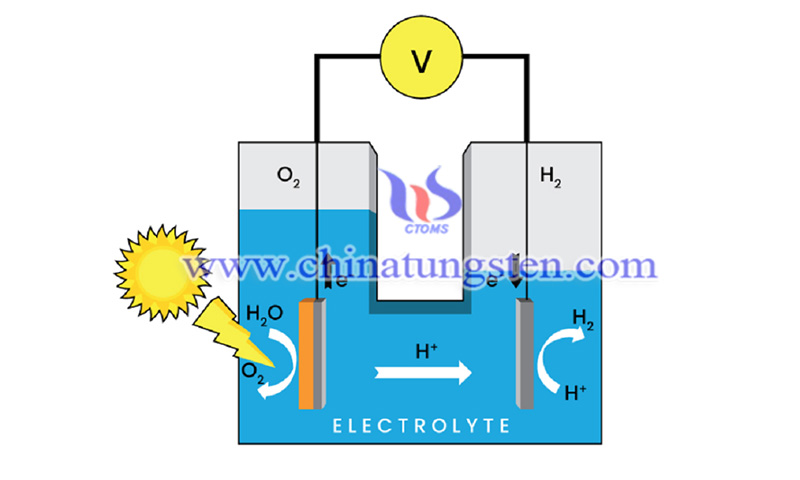
Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh recently enhanced the photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting capability of bilayer photoanode nanotubes through simple but effective molybdenum (Mo) doping method.





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com