Research in Machining of Cobalt Alloys and CoCrMo Alloys—Ⅱ
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 16 October 2022 22:25
Time and cost constraints are necessary to reduce the manufacturing costs of Cobalt alloys and CoCrMo alloys. Some of these elements are obtained by mechanical machining and it is necessary to optimize the machining parameters for these products. Several researchers have conducted experimental studies on the machining of cobalt-based refractory materials in order to establish optimal cutting conditions for different cutting parameters. They have used several optimization techniques based on RSM methods, using sequential quadratic programming algorithms and Kriging interpolation to solve a constrained problem.
Bruschi et al. investigated the effect of cutting conditions on tool wear, surface integrity, and microstructure during the semi-finishing turning of CoCrMo alloys using PVD TiALN-coated carbide inserts under conventional lubrication conditions. They found that the feed rate was the largest parameter affecting the quality of the cut surface and tool wear. Higher feed rates had a greater effect on tool wear and surface quality, while reducing tool life. When high feed rates were used, adhesive wear and chipping were the main wear at the leading corners and flanks.
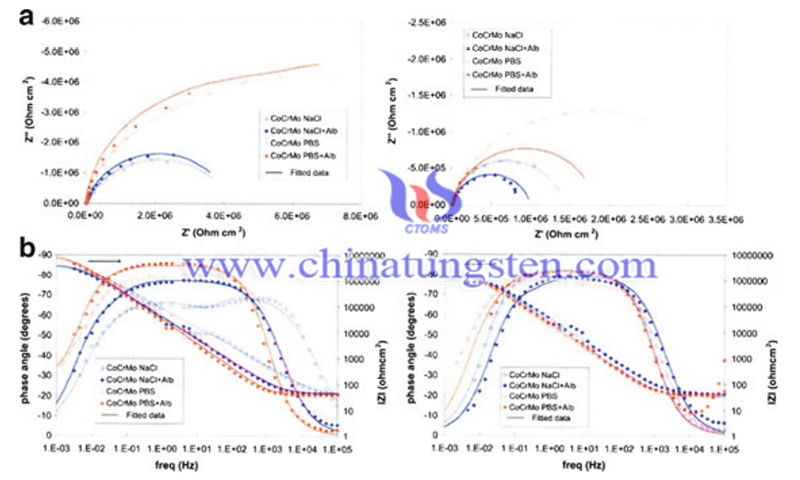
(Picture source: Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry No. 53)
Song et al. conducted another study to evaluate the best method of turning CoCrMo alloy using elliptical vibration cutting and plain cutting without tool vibration to assess the roughness and hardness of the finished surface, as well as tool wear. The results showed that elliptical vibration cutting performed better in reducing microcracking, tool wear, and machining hardening compared to normal cutting, resulting in better mirror finish results.
H. Shao et al. investigated the machinability of cobalt alloys using uncoated and coated carbide tools during dry turning with cutting conditions set at cutting speeds of 16, 27, and 43 m/min, feed rates of 0.20 and 0.25 mm/rev and depth of cut of 0.3 mm. their study showed that at lower cutting speeds, the main failure of coated tools mode is uniform flank wear. At relatively high cutting speeds and feed rates, adhesion, spreading, chipping, and chemical wear was observed. Coated tools outperformed uncoated tools in terms of tool life when machining stellite alloys.
Pedro Ferreira et al. studied the milling operations of Ti-6Al-4V and Co-28Cr-6Mo alloys to evaluate the effect of cutting speed on cutting temperature and cutting forces and to determine which material is the most difficult to machine. The results showed that for each cutting speed, the tangential and axial forces (Ft and Fa) were always higher for the Co-28Cr-6Mo alloy than for the Ti-6Al-4V alloy.
Bordin et al. present experimental results on surface integrity when turning CoCrMo alloys in dry machining for biomedical applications. The results demonstrate that cutting speed and feed rate are the main factors affecting surface integrity. An increase in feed rate tends to increase compressive stresses due to high strain rates while cutting speed has the opposite effect due to an increase in cutting temperature.
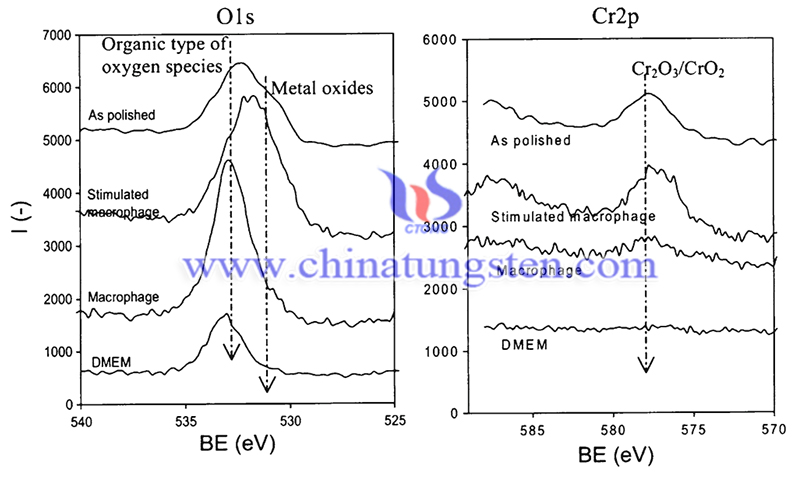
(Picture source: Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry No. 53)
Cited paper: Zaman H A, Sharif S, Kim D W, et al. Machinability of cobalt-based and cobalt chromium molybdenum alloys-a review[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2017, 11: 563-570.
| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com