Latest Research for Non-volatile Memory Device Uses WO3
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Wednesday, 07 September 2016 15:48
Not long ago, James M. Tour of Rice University group by anodic treatment to obtain a flexible nano-porous (NP) WO3-xRRAM at room temperature. The Task Force found that the flexibility of NP WO3-x RRAM exhibits bipolar switching property and high Ion/Ioff ratio (approximately 105); at the same time, this device has a stable holding time (more than 5×105s) and excellent pole uniformity between the elements; besides, in the conditions of flat or the maximum bending, the degrees of resistance to bending are more than 103 cycles. Research indicates, the flexible resistive memory (RRAM) has a great prospect in the future non-volatile memory device, this time the discovery of ACS nano flexible WO3-x non-volatile memory device becomes the latest research of tungsten trioxide (WO3) in non-volatile memory device, and expanding the application fields of WO3.
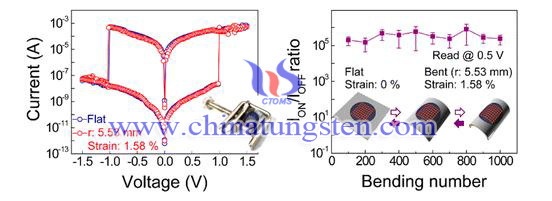
In addition, in 2015, Professor Xie Yi, USTC has made new progress on the high-performance of flexible non-volatile memory device, synthesized excellent storage property based on WO3•H2O thin nano-sheets and assembled into Cu/WO3•H2O/ITO-PET flexible non-volatile memory device. Further, the group also proposed novel mechanism of resistance change memory which is contributing to the further research and development of mechanism of resistive non-volatile memory.
Further reading: Non-volatile memory, nonvolatile memory, NVM or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retrieve stored information even after having been power cycled (turned off and back on). Examples of non-volatile memory include read-only memory, flash memory, ferroelectric RAM (F-RAM), most types of magnetic computer storage devices (e.g. hard disk drives, floppy disks, and magnetic tape), optical discs, and early computer storage methods such as paper tape and punched cards. Non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage, or long-term persistent storage. The most widely used form of primary storage today is a volatile form of random access memory (RAM), which means that when the computer is shut down, anything contained in RAM is lost. However, most forms of non-volatile memory have limitations that make them unsuitable for use as primary storage. Typically, non-volatile memory costs more, provides lower performance, or has worse write endurance than volatile random access memory. Non-volatile data storage can be categorized in electrically addressed systems (read-only memory) and mechanically addressed systems (hard disks, optical disc, magnetic tape, holographic memory, and such). Electrically addressed systems are expensive, but fast, whereas mechanically addressed systems have a low price per bit, but are slow. Non-volatile memory may one day eliminate the need for comparatively slow forms of secondary storage systems, which include hard disks.
| Tungsten Oxide Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten-oxide.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com