Rare Earth Enrichment Mechanism of Deep-Sea Sediments
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Wednesday, 24 March 2021 23:02
Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (hereinafter referred to as Guangzhou Marine Laboratory) research revealed the rare earth enrichment mechanism of deep-sea sediments and its influencing factors. The related study was recently published online in Minerals.
The research team found that rare earth-rich deposits are a new type of rare earth-rich phosphate type after a lot of studies. The statistical results show that most of the phosphorus (P) in the sediments is in the form of rare earth-rich phosphates, except for 2.8% of the samples. The change of P is very important for the influence of rare earth elements (REEs) content and mode.
The study carried out multiple linear regression analysis on 6088 samples and obtained quantitative results of phosphate composition and REE enrichment. The contribution of phosphate components to the enrichment increases with the increase of P content. When the content of P2O5 exceeds 1.5%, the contribution to REEs exceeds 89.1%. Elemental correlation analysis combined with mineralogical research results show that the main elements of the phosphate component include P, Ca, Sr, REY, Sc, U, Th, etc., and the chemical composition is relatively stable.
Studies have found that the phosphate component in deep-sea sediments is one to two orders of magnitude higher than the REE content of marine phosphate rock and terrestrial phosphate rock. It exists in the form of biological apatite, authigenic apatite, etc., which is important to my country’s maritime power.
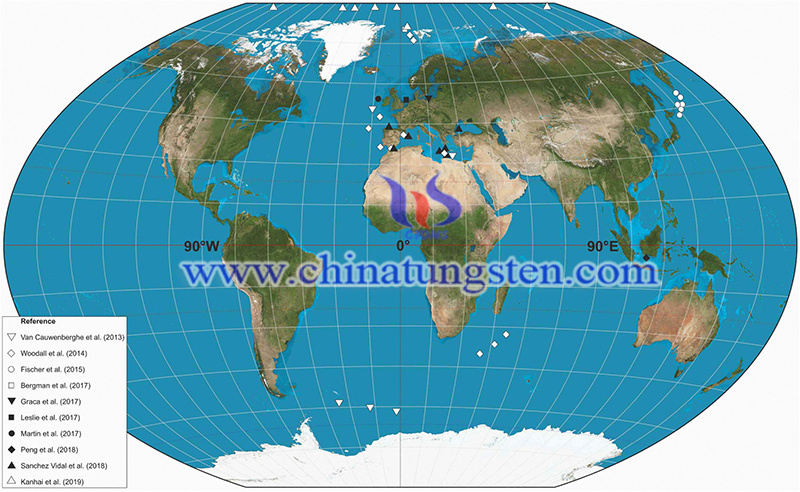
The study also counted the REE content and its temporal and spatial distribution of surface samples from the 177 sediments columnar sample station in the global seas and extracted the deposition rate, surface sea chlorophyll, bottom seawater oxygen concentration, and seabed large animal biological parameters at relevant sites. Studies have shown that the key factors for the enrichment of REEs include low deposition rate, on the one hand, which is conducive to the accumulation of phosphate components in the unit volume of sediment, but also conducive to the replenishment of REEs in the bottom seawater.
The high REE content of the bottom seawater provides a high background value of rare earth content for the enrichment of REE by the phosphate component of the seabed. The non-carbonate deposition environment avoids the formation of rare earth-poor phosphates by replacing carbonate with phosphate.
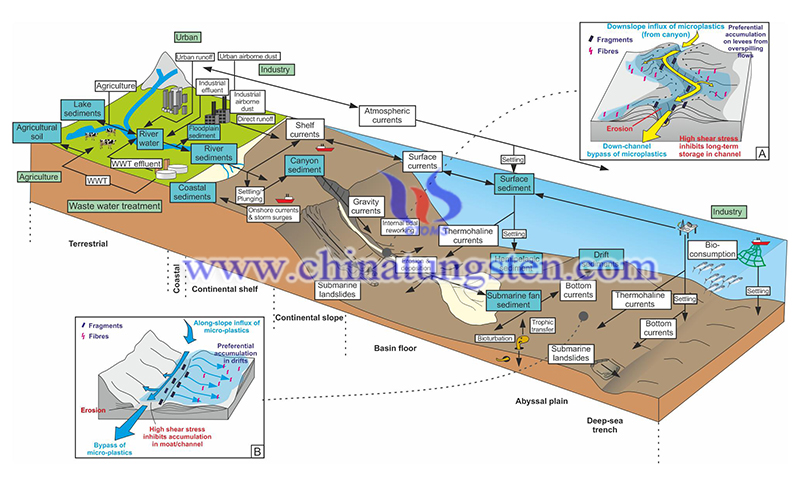
Besides, the sorting effect of the bottom current on the sediments further accumulates rare-earth-rich phosphates to form rare-earth-rich deposits. After the early diagenesis process of biogeochemistry, adsorption, desorption, transformation, and migration, the enrichment of rare earth by the phosphate component has been completed near the seawater/sediment interface. In the process of REE enrichment in deep-sea sediments, the accumulation of phosphorus plays a foundation role, and the formation of rare earth-rich phosphate is the key factor.
- Rare Earth Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com