Tungsten-Containing Compound Plays A Unique Role in Converting Cellulose to Ethanol
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Thursday, 11 July 2019 09:40
Tungsten-containing compound plays a unique role in converting cellulose into ethanol because of its special function in catalyzing the cleavage of cellulose carbon-carbon bonds. This major discovery was recently discovered by Dalian Institute of Chemicals Physics of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Recently, the researcher Aiqin Wang and the academician Tao Zhang of the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics made new progress in the research of biomass catalytic conversion and developed a multifunctional Mo/Pt/WOx catalyst, a tungsten-containing compound to convert cellulose "one-pot" into ethanol for the first time. Related work has been published on Joule.
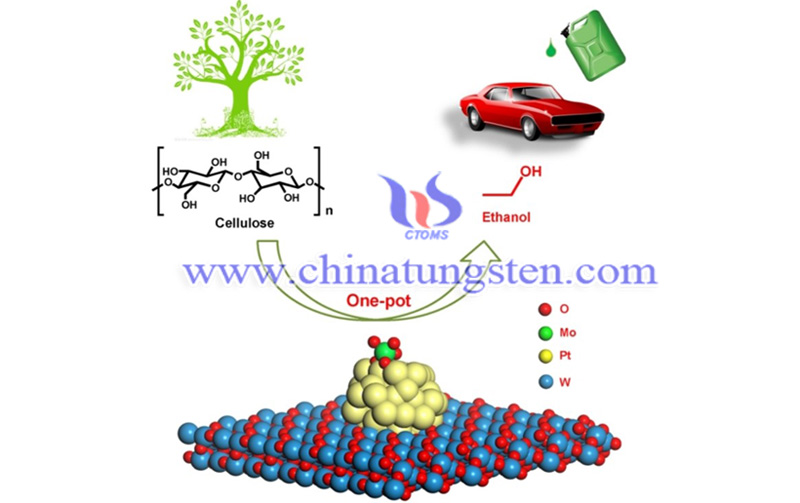
As the most abundant biomass resource in nature, cellulose is abundantly derived from agricultural and forestry waste and its inedible characteristics make it an ideal renewable carbon resource for the production of fuels and chemicals. Cellulose ethanol is one of the most important biofuels. Mixing it with gasoline in a certain proportion can form a new generation of clean and environmentally friendly vehicle fuels. The fuels can reduce emissions of automobile exhaust such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. However, up to now, the usage of bio-fermentation technology to produce cellulosic ethanol still faces various technical and economic challenges. To this end, it is of great significance to explore the non-biotransformation method to produce cellulosic ethanol.
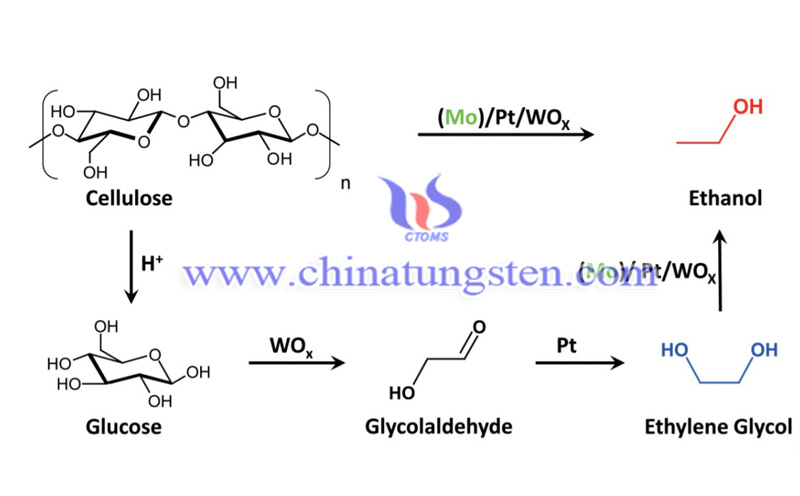
The research team has been working on the selective cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds and carbon-oxygen bonds in biomass to prepare important small-molecule alcohols. They discovered the first catalytic conversion reaction of cellulose hydrogenolysis to ethylene glycol, and the unique role of tungsten-containing compounds in catalyzing the selective cleavage of cellulose carbon-carbon bonds, and proposed a two-step process in which cellulose can be produced by first oxidative esterification and rehydrogenation reduction.
In this work, the team developed a new Mo/Pt/WOx multi-functional catalyst based on the previous work, which can be used to couple the hydrogenolysis of cellulose to ethylene glycol and ethylene glycol to ethanol. The process of directly producing ethanol in a "one-pot" of cellulose, the ethanol yield of the reaction reached 43.2%. At the same time, the catalyst also exhibits excellent stability and resistance to carbon monoxide poisoning, making it a potential for future practical applications.
The above research work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences' Strategic Pilot Science and Technology Project. The research on the use of tungsten-containing compound in converting cellulose to ethanol will keep on going, making cellulosic ethanol biofuels get better promoted in daily life.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com