What Are the Uses of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:24
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 34
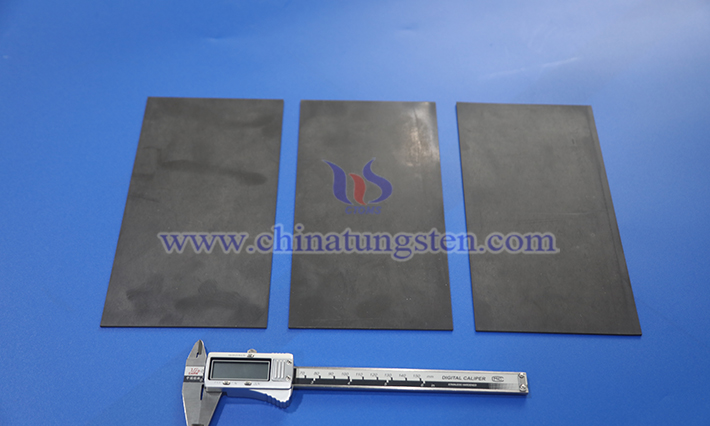
Tungsten resin, leveraging its high density, non-toxicity, radiation shielding capability, and processing flexibility, finds wide-ranging uses in medical, defense, industrial, civilian, and emerging technology fields.
What Are the Characteristics of Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:22
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 39
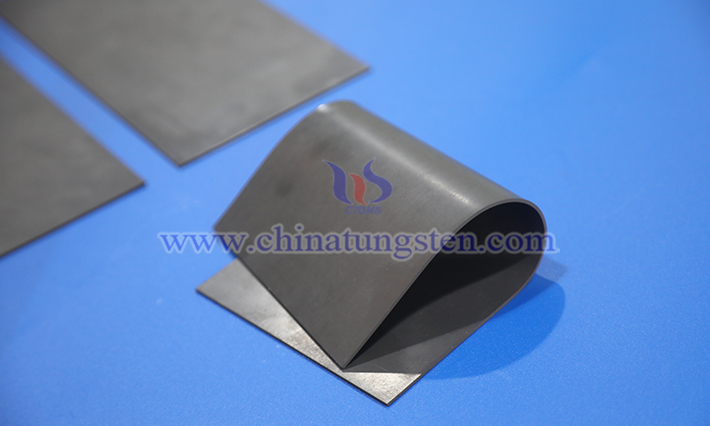
Tungsten resin is a composite material made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or polyethylene). It is widely used in defense, medical, industrial, and environmental fields, thanks to its unique physical, chemical, and processing characteristics.
What Is Tungsten Resin?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 September 2025 17:20
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 36
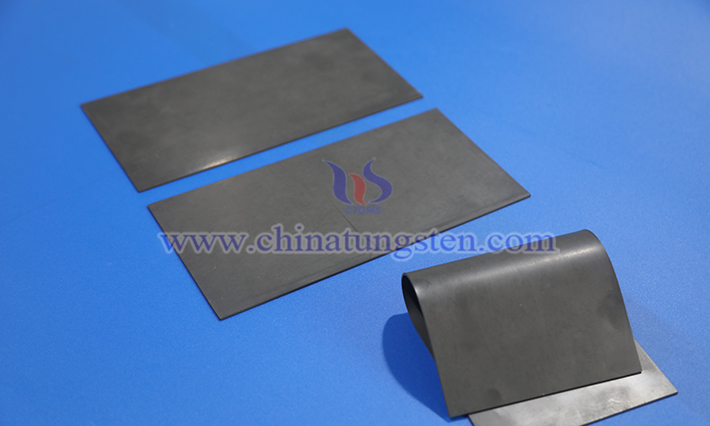
Tungsten resin, also known as tungsten polymer composite material or tungsten-filled resin, is a novel polymer composite material. It is primarily made by mixing high-purity tungsten powder with polymer resins (such as epoxy, polyurethane, or thermoplastic resins) in specific ratios and through specialized processes. This material combines the unique physical properties of tungsten (such as high density and radiation resistance) with the processing flexibility of resins, resulting in a non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and easily moldable material.
Application Fields of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:55
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 64
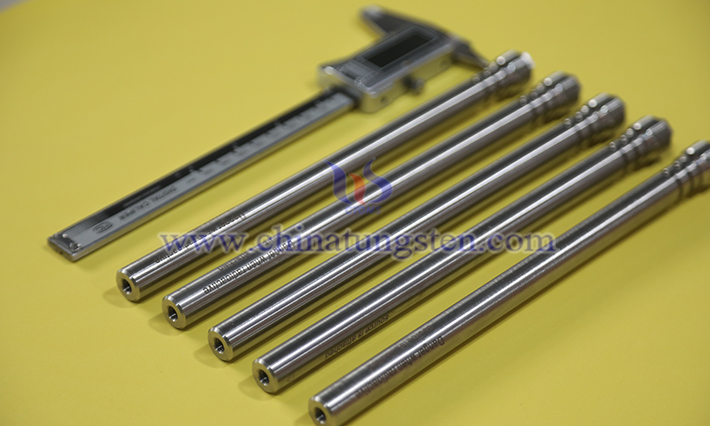

In contemporary industrial connection systems, tungsten alloy fasteners serve as high-performance connecting elements, playing a pivotal role and regarded as core components in materials engineering. Their exceptional performance stems from the inherent properties of tungsten and the optimization of other metal elements. Firstly, their high density ensures efficient weight distribution and connection stability within a limited volume.
Classification of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners (Part Three)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:49
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 63
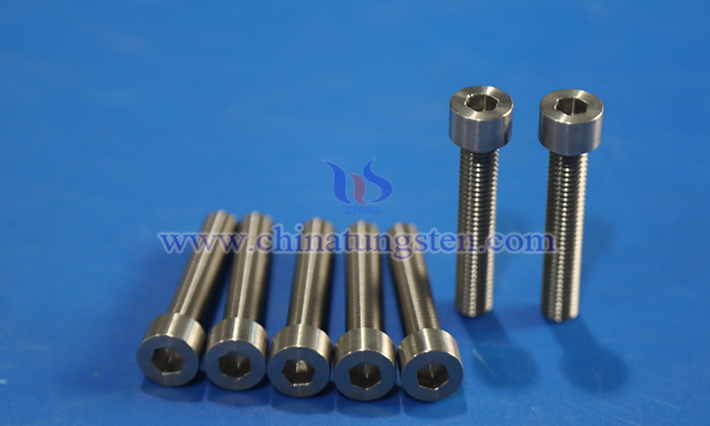

Tungsten alloy fasteners, with their high strength, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, play a crucial role in high-demand fields such as aerospace, nuclear industry, and precision machinery.
Classification of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners (Part Two)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:32
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 61
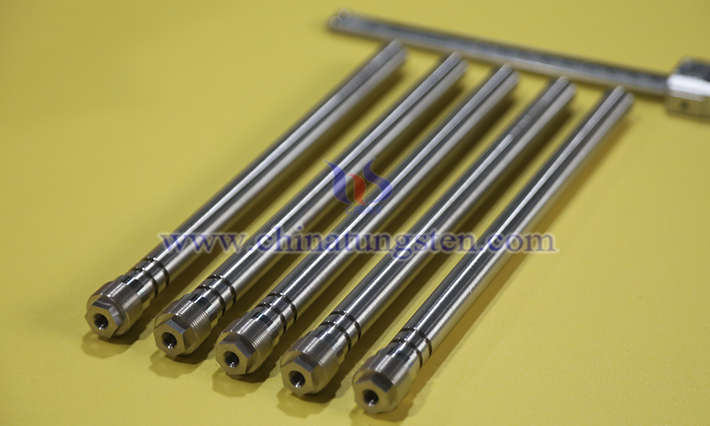

Tungsten alloy fasteners, owing to their excellent physicochemical properties, are designed as specialized connectors to meet the demands of specific working conditions. Based on functional requirements, the classification of these components falls into three major categories—high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and high precision—and each category has been optimized through special processes to adapt to extreme environments and high-reliability scenarios.
Classification of Tungsten Alloy Fasteners (Part One)
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 September 2025 15:28
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 58
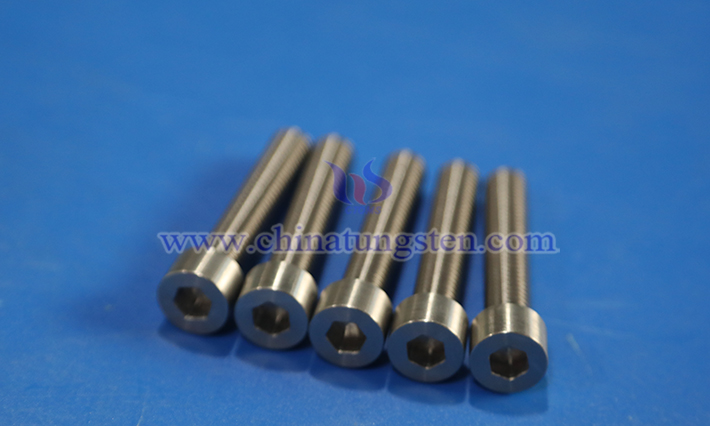

Tungsten alloy fasteners, with their perse structural designs, cater to complex connection requirements ranging from high-temperature furnaces to spacecraft. Screws offer flexible installation options, bolts and nuts meet high-strength fixation needs, and rivets provide robust assurance for non-detachable scenarios. Together, these types form the application ecosystem of tungsten alloy fasteners, supporting the reliability and efficiency of high-end manufacturing.
Performance Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Screws and Stainless Steel Screws
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 25 September 2025 14:47
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 69
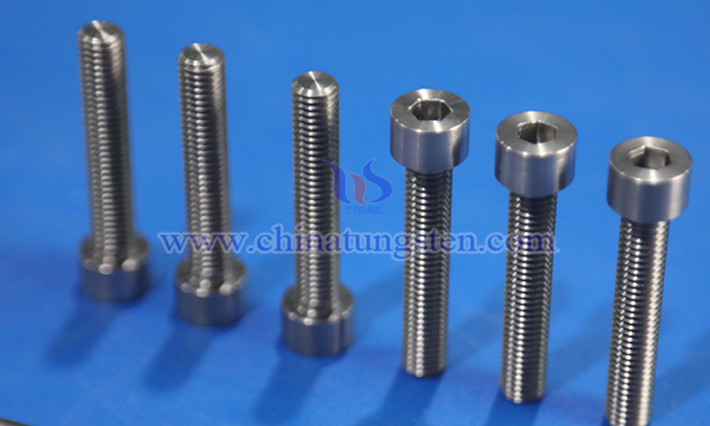

Tungsten alloy screws and stainless steel screws are two common screw materials, with the former renowned for its high hardness and high-temperature resistance, and the latter distinguished by its cost-effectiveness and versatility. The following text primarily discusses their performance comparison.
What Is Tungsten Alloy Threaded Rod?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 25 September 2025 14:43
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 72
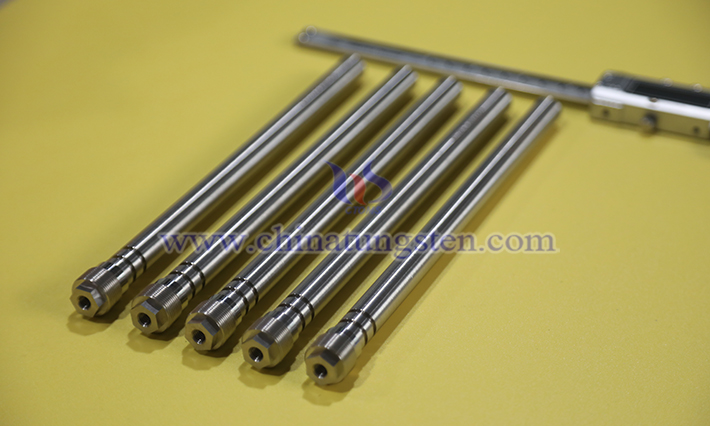

Tungsten alloy threaded rod is a high-performance mechanical connecting element featuring a continuous helical thread structure on its surface, primarily used to provide robust fixation and connection functions. As a refractory metal composite material, it uses tungsten powder as its main matrix, alloyed with nickel, iron, copper, or other elements (such as molybdenum or tantalum) through powder metallurgy processes. This not only imparts the high melting point and density of tungsten but also enhances toughness and machinability.
Performance Comparison of Tungsten Alloy Screws and Molybdenum Alloy Screws
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 24 September 2025 14:21
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 61
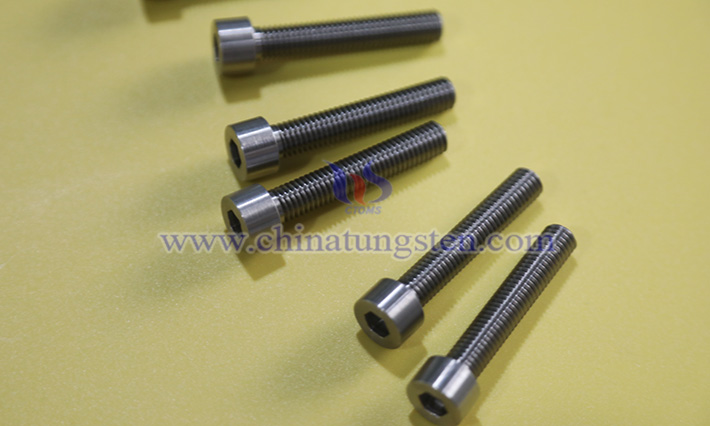

Tungsten alloy screws and molybdenum alloy screws, as two refractory metal-based materials, are widely used in high-temperature, high-strength, or specialized environment connection scenarios due to their unique physical and chemical properties. The following text primarily discusses the performance comparison between tungsten alloy screws and molybdenum alloy screws.




 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com