Types of Injection Screw
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 06 October 2017 22:17
There are mainly three kinds of injection screw: progressive screw, sudden change screw and universal screw. The main difference between them is the difference in compression ratio.
Energy conversion and excitation degree of the three kinds of screw plasticizing materials are different, and the materials used between them are different.
Tapered screw: the compression section is longer, accounting for 50% of the total length of the screw. During plasticization, energy conversion is mild. And it usually used for plastics with poor thermal stability, such as PVC.
Mutant screw: compression section is relatively short, accounting for about 5%~15% of the total length of the screw. When plasticizing, the energy conversion is more intense. And it usually used for polyolefin, PA and other crystalline plastic.
General purpose screw: it is a universal screw with good adaptability, and can be used in many kinds of plastics processing.
Screw Parameters (shown below)
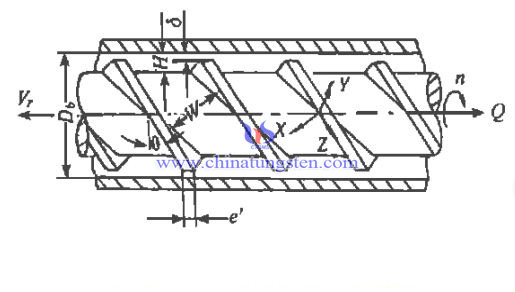
D - screw diameter. It directly affects the size of the plasticizing capacity, and affects the size of the theoretical injection volume.
L/D - draw ratio of screw. L is the effective length of the threaded part of the screw. It directly affects the thermal process of materials in the screw, and also affects the ability to absorb energy. If the L/D is too small, it directly affects the melting effect and melt quality of the material. If the L/D is too large, the torque will be increased and the energy consumption will increase.
L1 - length of feeding section. The length of L1 should ensure that the material has enough transportation space. Because when the L1 is too short, the material is too early to melt. It is also difficult to guarantee the delivery condition of the stable pressure and the plasticizing quality and the plasticizing ability of each section of the screw.
H1 - depth of screw groove in conveying section. When H1 is deep, it can hold more material. The feeding capacity and plasticizing capacity are increased, while the plasticizing effect of the material and the shear strength at the root of the screw are affected. Usually, H1≈(0.12~0.16)D.
L3 - length of measurement section. Taking longer L3 length helps to melt the fluctuation in the spiral groove, and has the function of stabilizing the pressure, so that the material can be discharged from the head of the screw with a uniform amount of material. Usually, L3=(4~5)D.
H3 - depth of metering groove. When H3 is small, then the spiral groove is shallow, improving the plasticizing effect of plastic melt and being conducive to homogenization of melt. But when H3 is too small, it will lead to high shear rate and excessive shear heat, which will lead to the degradation of molecular chains and influence the quality of melt. If the H3 is too large, the plasticizing effect of the screw back pressure will be reduced due to the pre-molding.
S - pitch. It affects the screw lift angle, thus affecting the conveying efficiency of the spiral groove, Screw lift angle φ=πDtgφ, usually D=S and φ=17°40′.
ε - reduction ratio. ε=H1/H3. It is he ratio between the depth of the screw groove and the depth H1 of the melting section is H3. When ε is large, the shear effect will increase, thus reducing the plasticizing capacity.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com