What Are the Main Applications of Tungsten Crucibles?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 29 April 2025 15:03
Tungsten crucibles are used in a wide range of applications due to their extremely high melting point, excellent high-temperature strength, good thermal conductivity and strong chemical inertness in vacuum or inert atmospheres.
1. Semiconductor single crystal growth
(1).Czochralski
During the growth of silicon single crystals, the crucible must withstand high temperatures of about 1400 °C and be in contact with molten silicon for long periods of time without chemical reactions. Due to its high-temperature strength and chemical stability, tungsten crucibles are the material of choice for melt-bearing in high-end crystal growth equipment.
(2). III–V semiconductors such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium nitride (GaN).
These materials have higher melting points and stricter purity requirements, often growing at temperatures above 1500 °C. W crucibles can provide a stable and high-purity melt environment, ensuring that the prepared single crystals have low dislocation density and high electrical consistency.
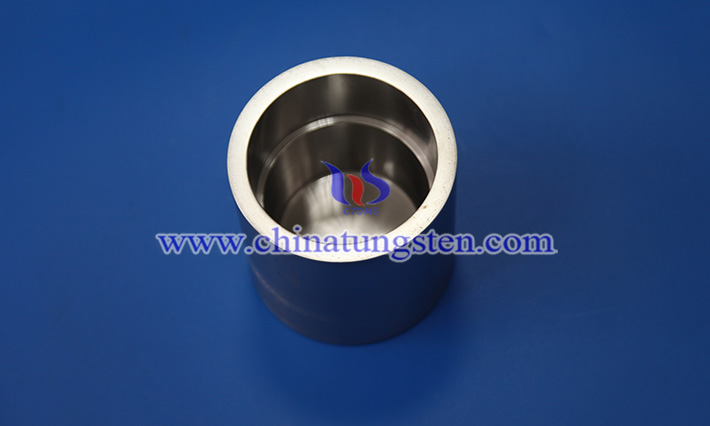
2. Smelting of superalloys and functional materials
(1). Cobalt-based and nickel-based superalloys
The superalloys used in critical components such as turbine blades and gas turbines of aero engines require vacuum arc or induction melting in vacuum or inert atmospheres up to 1500–1700 °C. W crucibles maintain dimensional stability and mechanical integrity under these extreme conditions.
(2). Tungsten alloy, rhenium alloy and rare and precious metals
The smelting process of alloys containing rare and precious metals such as tungsten, rhenium, platinum, and palladium has high temperature and harsh requirements for containers. Tungsten crucibles have good thermal insulation and excellent creep resistance, and can carry high melting points for long-term smelting.
(3). Oxide and carbide ceramic materials
Functional ceramics such as silicon carbide (SiC), silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), and zirconia (ZrO₂) can be used as liners or molds when sintered or molten at around 2000–2400 °C.
3. Nuclear industry and handling of radioactive materials
(1). Nuclear fuel preparation
In the high-temperature smelting and ingot casting process of uranium and thorium metals, W crucibles are used in the preparation of nuclear fuel blocks or targets due to their low neutron absorption cross section (about 2.7 b) and excellent radiation resistance.
(2). High-temperature treatment of radioactive waste
When converting high-level waste or waste into glass or ceramic solids, it is melted under a high-temperature vacuum or an inert atmosphere. The tungsten crucible can withstand long-term operation in high-temperature chemical environment, reducing the risk of secondary pollution.
4. Vacuum metallurgy and electron beam smelting
(1). Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
In EBM equipment, W crucibles are commonly used to carry metal powders or metal blocks, and electron beam is used for smelting and refining in a vacuum state. The crucible's resistance to high temperatures and evaporation ensures cleanliness and metal purity during the melting process.
(2). Vacuum heat treatment and hot isostatic pressing (HIP)
W crucibles are also often used as crucibles or inner sleeves in hot isostatic pressure ovens to support and seal powder preforms to ensure tissue densification at high temperatures and pressures.
5. Materials science research and high-temperature analysis
(1). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric (TG) tests
In high-temperature thermal analysis instruments, tungsten crucibles can be used to measure samples above 2000 °C to study material phase transformation, pyrolysis and oxidation behavior.

(2). High-throughput material R&D platform
In recent years, in the high-throughput melting and screening platforms built by scientific research institutions, W crucibles are often used for automated synthesis and snapshot performance testing of small-sized samples in parallel, so as to promote the rapid discovery of new materials.
6. Preparation of new energy and functional materials
(1). Thermoelectric materials
For the melting and crystallization of thermoelectric alloys or nanocomposites such as SiGe, PbTe, Bi₂Te₃, etc., W crucibles can provide a high-purity, high-temperature, and inert environment to ensure thermoelectric properties and material stability.
(2). Solar cell material
High-temperature melt treatment is required during the growth of single crystals or thin sheets of photovoltaic materials such as GaAs, CdTe, and CIGS. Tungsten crucible has become an important instrument in this field because of its cleanliness and stability.
- Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- CTIA GROUP LTD: en.ctia.group
- Tungsten News & Price: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com