How to Make a Preparation of Tungsten Diiodide from Tungsten Hexacarbonyl?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 June 2023 22:18
There can be two methods of preparing tungsten diiodide using tungsten hexacarbonyl, the main difference between the two being in the choice of temperature.
The first preparation method selects tungsten hexacarbonyl and iodine crystals as reactants and sets a reaction temperature of 140°C after close mixing at room temperature, and the reaction of carbon monoxide gas release occurs in a Pyrex glass tube: W(CO)6+I2→WI2+CO. This method utilizes the principle that tungsten hexacarbonyl decomposes rapidly into tungsten and carbon monoxide at 140-150°C so that tungsten produced by decomposition can be fully reacted with the already sublimated iodine vapor to react fully. The reaction produces tungsten diiodide in the form of a black powder, which can be extracted chemically, but this method produces an intrinsically inhomogeneous reaction product, and there is a risk of explosion of the glass tube due to the gaseous pressure of carbon monoxide.

The second method is obtained by reacting iodine with tungsten hexacarbonyl at 600°C using nitrogen as a protective gas. This method uses the same reactants but has higher temperature requirements. The sublimation of the product tungsten diiodide to a gaseous state at this temperature not only reduces the chance of uneven content of the reaction product but also ensures that the reaction is carried out below the ignition point of carbon monoxide (650°C) to prevent subsequent separation of the gases from catching fire on contact with air.
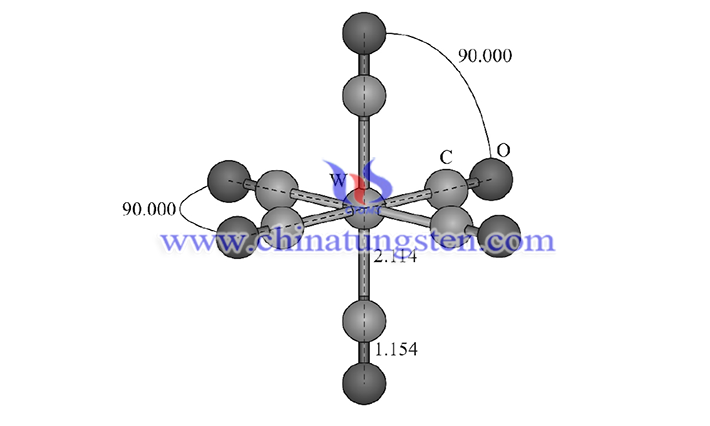
Tungsten hexacarbonyl (chemical formula: W(CO)6 is of high research value as an important reactant for the preparation of tungsten diiodide. It is a transition metal ion complex, insoluble in water, insoluble in ethanol, ether, and benzene, and soluble in fuming nitric acid, and its molecule has high symmetry. Similar to tungsten diiodide, tungsten hexacarbonyl can be used as a material or precursor in the materials industry by chemical vapor deposition process. Meanwhile, tungsten hexacarbonyl is also an important catalyst, which can not only prepare polyphenylacetylene with good fluorescence properties but also special compounds containing a bifluorene structure.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com