Properties of Titanium/Tungsten/Graphene Oxide Thin Films
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Monday, 20 June 2022 23:09
Recent research discusses the optical and self-cleaning properties of composite films titanium/tungsten/graphene oxide thin films. The article, published in Surface and Interface, develops a discussion of the optical properties of photocatalytic titanium dioxide - tungsten trioxide - reduced graphene oxide (TiO2-WO3-rGO) (TWG) and TiO2 films and the feasibility of using these films for different applications, particularly as self-cleaning coatings (SCC).
In recent years, SCCs gained considerable interest in several applications in solar energy conversion systems, the automotive industry, and the construction sector. In addition to its self-cleaning properties, the multifunctional self-cleaning coating also exhibits antimicrobial activity and anti-fouling, anti-fogging, and anti-frost properties.
(Image Credit: Maria Covei/Surfaces and Interfaces)
SCCs on PV modules reduce fouling and lead to an increase in power output by significantly preventing efficiency losses in PV modules during the first 15 years of operation. However, these coatings degrade over time due to exposure to weathering, which requires reapplication of the coating on the modules.
A good SCC must have high photodegradation efficiency of organic pollutants and superhydrophobicity or superhydrophilicity to wash off the by-products of the photocatalytic process. These requirements can be controlled by the morphology and structure of the photocatalyst (PC).
Common PCs, such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and silica, are not suitable as SCCs due to their large band gap values requiring ultraviolet (UV) activation. Researchers investigated the optical properties of TiO2 films with thicknesses of 450, 300 and 150 nm, which were deposited by chemical vapor deposition methods.
These films show a maximum transmission value of 78.2% at 100 nm thickness and up to 78% visible light transmission is observed at 150 nm thickness. The absorption coefficient increases with decreasing thickness, while the refractive index increases with increasing film thickness. However, a high band gap value of 3.69 eV was observed in the 150 nm thickness of the film. The band gap of the films decreases only when the thickness is increased to 450 nm.

(Image Credit: Dmitry Kalinovsky/Shutterstock.com)
Composites with carbon-derived fillers, such as reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and metal oxide matrices, can be activated by visible light (VIS) and are also effective PC materials due to the increased surface area of the carbon fillers.
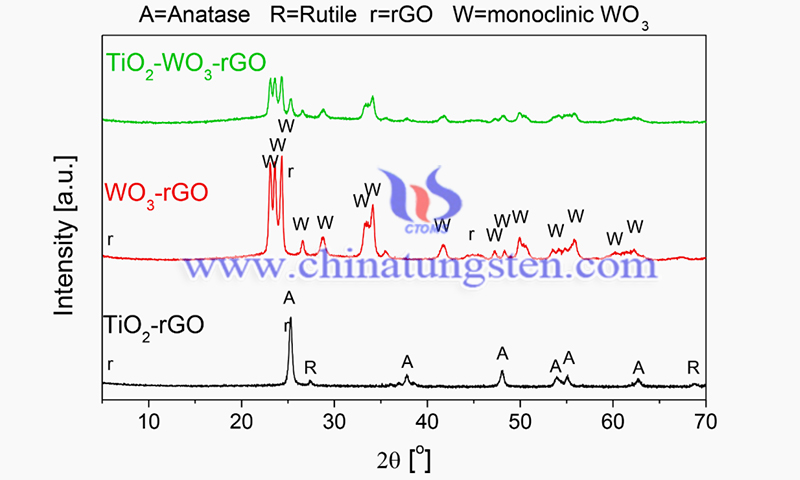
An enhanced electron storage material was obtained by adding rGO to TiO2-WO3 composites by a one-step hydrothermal method. Photocatalysts that can effectively degrade 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid were synthesized by scattering gold-doped TiO2-WO3 nanoparticles (NPs) on rGO.
The researchers synthesized composite titanium/tungsten/graphene oxide thin films and evaluated their feasibility as self-cleaning coatings with good photoactivity, controlled optical properties, and good wetting properties under UV-Vis radiation. The researchers used a low-temperature, versatile, and low-cost deposition method for coating large areas with composite films of titanium, tungsten, and graphene oxide powders.
The composite titanium/tungsten/graphene oxide thin films deposited by single batch deposition method can be effectively used as self-cleaning coatings compared to common photocatalyst films such as TiO2-based films.
The study titled “Photocatalytic composite thin films with controlled optical properties based on TiO2, WO3 and rGO” has been published in Surfaces and Interfaces 31 (2022) 102075. The study was carried out by Maria Covei, Dana Perniu, Cristina Bogatu, Anca Duta, Ion Visa at Transilvania University of Brasov.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com