Debinding Process: Carbon Content Control
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 October 2017 23:36
Carbon content control has a great impact on the quality of tungsten carbide, which throughout the entire production process.
1, Significance of Carbon Content Control
The control of carbon content is an important link in the preparation of WC-Co tungsten carbide. Even minor fluctuations in carbon content will lead to significant changes in microstructure and properties of the alloy phases. The content of C in WC is generally 6.12%-.14%, and the C content in WC-Co cemented carbide is generally controlled at 5.63%-5.65%. In this range, WC-Co cemented carbide is composed of WC and Co phases.
If the carbon content is too high, the free carbon will be produced, and the low carbon content will lead to brittle phase. These third phases will lead to lower strength and hardness. Therefore, the carbon content should be strictly controlled during degreasing.
2, Control of Hydrogen Atmosphere During Degreasing
WC-Co injection blank is easy to produce decarburization in thermal debinding under H2 atmosphere, of which the reason is that there is always a small amount of H20 vapor present in the H2 atmosphere. When degreasing temperature is higher than 400-450℃, WC is easy to react with H20 vapor during debinding, producing W and CO or CO2, resulting in decarburization.
In severe cases, a very small amount of W is further converted into W02, leading to more serious decarburization. And it is difficult to remove the polymer in organic binder below 400℃. The figure below is the effect of H2 on carbon content.
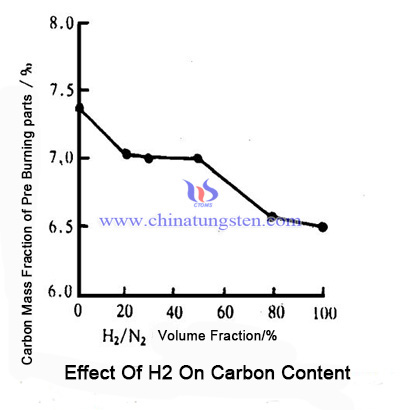
3, Effect of Degreasing Temperature on Carbon Content
When the degreasing temperature is higher than 450℃, the carbon content in the degreased blank will be low, and the decarburization will be serious. There is a large amount of free graphite in the skim blank.
With the prolonging of holding time, the total amount of C decreased. After holding for a certain period of time, the carbon content of the skim carbon is basically the same as that of the original mixed powder.
Compared with pure thermal debinding, the carbon content of the debinding blank is higher after solvent debinding and thermal debinding. The carbon content in the debinding process should be slightly higher than the theoretical carbon content in the actual degreasing process due to the decarburization of sintered skim billets during sintering.
- Tungsten Carbide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: tungsten-carbide.com.cn
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com