Biocompatibility of Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 17 August 2022 23:14
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1292
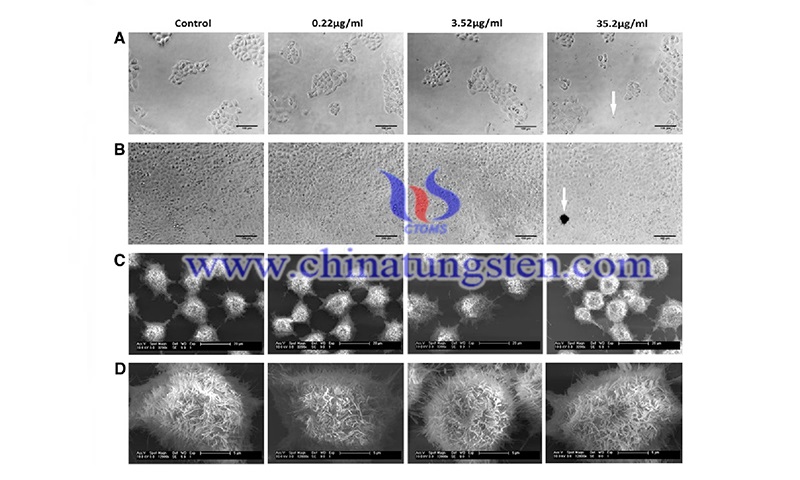
Biocompatibility of tungsten disulfide nanomaterials (WS2NM) such as tungsten disulfide inorganic nanotubes, and fullerene-like nanoparticles with salivary gland cells. There are currently no adequate methods to treat oral diseases due to impaired salivary gland function. The researchers investigated the biocompatibility of WS2 in salivary gland cells. In the study, multi-walled inorganic nanotubes (INT- WS2) and inorganic fullerene-like nanoparticles (IF WS2) were synthesized in a reactor that can be used at high temperatures.
Read more: Biocompatibility of Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials
WS2NM-Based Nanocarriers and Application in Tissue Engineering
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 16 August 2022 22:45
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1267
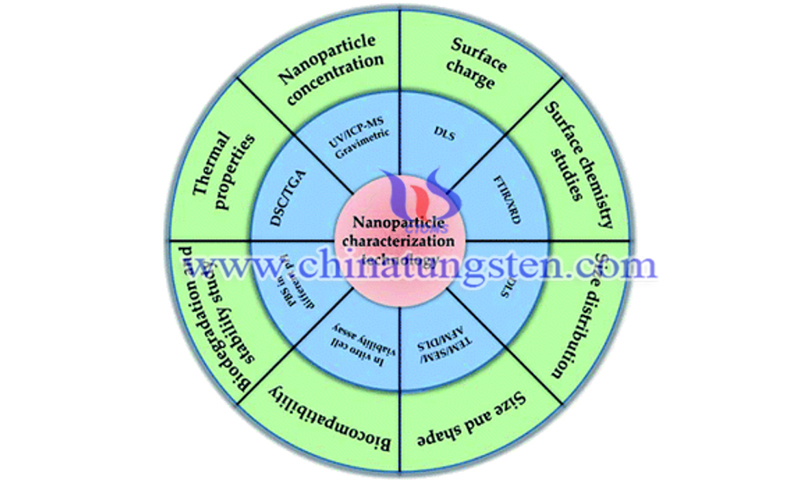
Recently, WS2NM-based nanocarriers have been developed in drug delivery systems, which also promote their application in tissue engineering. Due to the electrical properties of WS2, researchers have designed tungsten disulfide nanomaterials (WS2NM)-based electro-responsive drug delivery systems. Conventional drug delivery systems, such as oral and injectable, require higher concentrations of drugs to see therapeutic effects, and administering too much of the drug can lead to side effects in some patients.
Read more: WS2NM-Based Nanocarriers and Application in Tissue Engineering
Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials for Applications of Optical Biosensors
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 12 August 2022 18:46
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1325
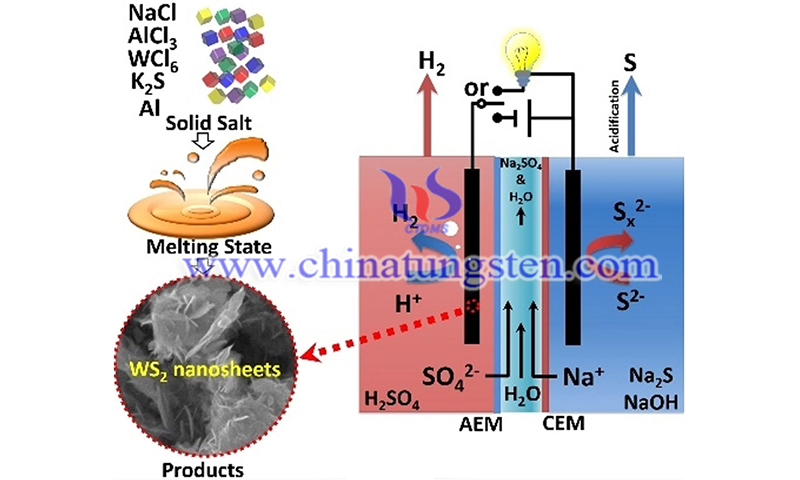
With the development of nanotechnology, tungsten disulfide nanomaterials (WS2NM) have been a new choice for optical biosensors. Researchers reported the use of a simple method to create a hybrid material consisting of WS2 nanosheets and hydroxylated MWCNTs (WS2/MWCNTs-OH). The substrate was screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCE), which has the advantage of requiring minimal cost and being disposable and energy efficient. Modification with WS2/MWCNTs-OH composites improved the rate of sensitive and selective behavior.
Read more: Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials for Applications of Optical Biosensors
Application of Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials in Bioimaging and Radiotherapy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 16 August 2022 22:41
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1249
The high atomic number and near-infrared absorption of tungsten disulfide quantum dots (WS2-QDs) (3 nm and 28 nm) of tungsten disulfide nanomaterials enable their synthesis as enhancers for X-ray computed tomography (CT)/photoacoustic imaging (PA), boosting their applications in bioimaging and radiotherapy.
Read more: Application of Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials in Bioimaging and Radiotherapy
Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials (WS2NM) for Biosensors – Ⅱ
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 11 August 2022 11:19
- Written by Caodan
- Hits: 1245
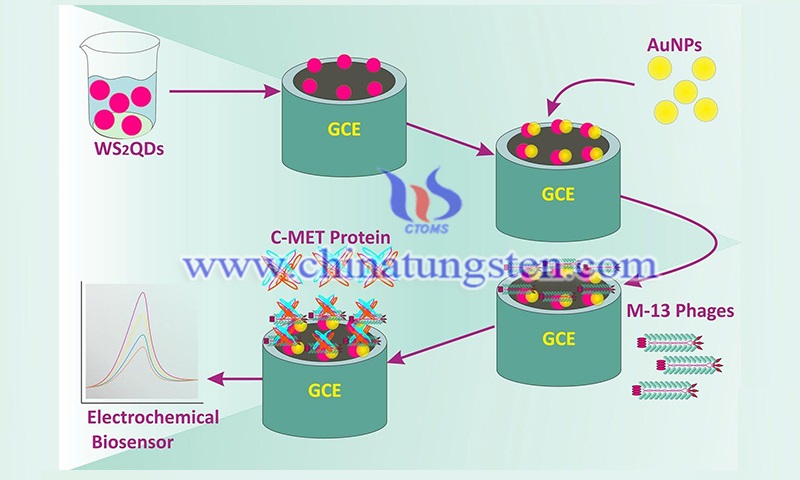
Tungsten disulfide nanomaterials can be successfully used in biosensors and nanomedicine, such as observation of DNA hybridization, enzymes, and proteins, as well as environmental contamination and medical diagnostics. For a long time, electrochemical biosensors, such as semiconductors and screen-printed electrodes, have been used for various applications in numerous fields.
Read more: Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials (WS2NM) for Biosensors – Ⅱ
More Articles...
- Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials (WS2NM) for Biosensors - Ⅰ
- Application of Tungsten Disulfide Nanomaterials (WS2NM) in Biosensors and Nanomedicine
- 100 Years of Doped Tungsten Wire Ⅳ- Scientific Background of Doped Tungsten Wires and Outlook
- 100 Years of Doped Tungsten Wire Ⅲ - The Invention of Hard Metals





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com