Materials and Properties of Tungsten Cemented Carbide Balls
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 10 September 2025 17:29
- Written by Zhenghua
- Hits: 55
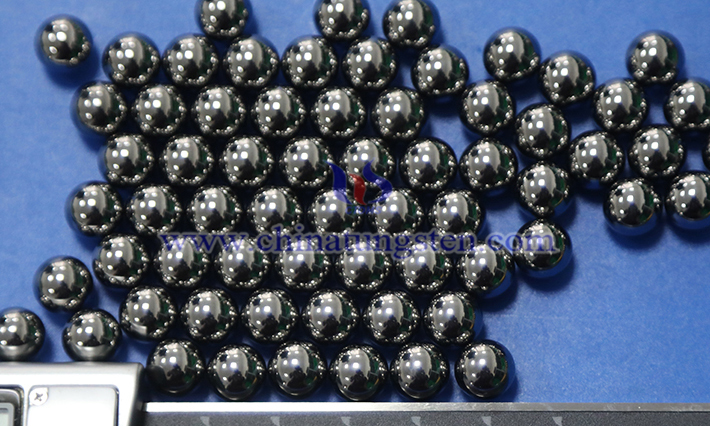

Tungsten cemented carbide balls are primarily made of tungsten carbide (WC) and a binder (such as cobalt (Co) or nickel (Ni)) through a powder metallurgy process. They exhibit high hardness, high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and good compressive strength. The following is a detailed analysis of their materials and properties:
Read more: Materials and Properties of Tungsten Cemented Carbide Balls
Characteristics of Tungsten Cemented Carbide Balls
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 10 September 2025 17:27
- Written by Zhenghua
- Hits: 52
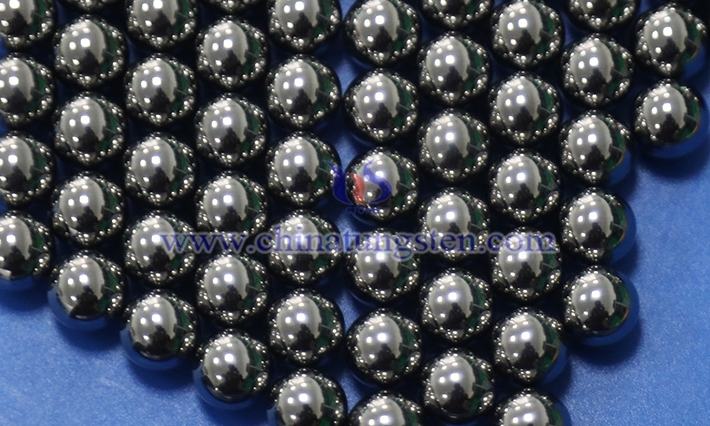

Tungsten cemented carbide balls, due to their outstanding performance, are widely used in industrial applications such as precision bearings, valves, abrasive media, and metering instruments. Their high hardness and wear resistance make them outstanding in harsh environments.
Read more: Characteristics of Tungsten Cemented Carbide Balls
Applications of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Target Material Fields
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 09 September 2025 15:40
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 63
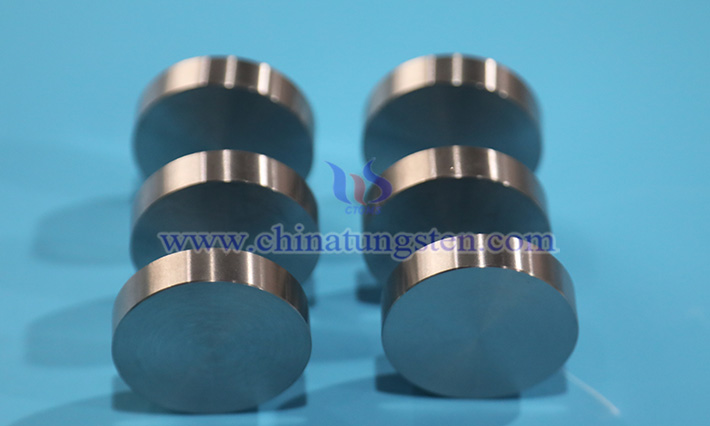

Tungsten alloy discs, with their high density, excellent high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, have wide-ranging applications in the target material field, particularly excelling in advanced manufacturing techniques such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), sputtering coating, and ion beam deposition. As a high-performance target material, tungsten alloy discs play a critical role in industries such as semiconductors, solar cells, display panels, and optical coatings.
Read more: Applications of Tungsten Alloy Discs in Target Material Fields
What Are Tungsten Cemented Carbide Balls?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 10 September 2025 17:24
- Written by Zhenghua
- Hits: 49
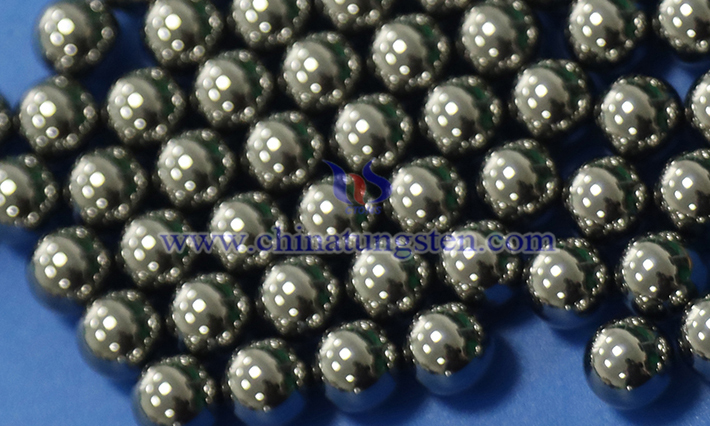

Tungsten cemented carbide balls are spherical components primarily made from tungsten carbide and a metal binder (such as cobalt) using a powder metallurgy process. They exhibit extremely high hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Their unique properties have led to their widespread use in industries such as industry, manufacturing, and precision instruments.
What Is Tungsten Alloy?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 09 September 2025 15:37
- Written by Xiaoting
- Hits: 56
The primary component of tungsten alloy is tungsten (W), typically enhanced with elements such as nickel (Ni), iron (Fe), and copper (Cu) to optimize performance. Tungsten boasts a density of 19.35 g/cm³, significantly higher than common materials like steel (approximately 7.8 g/cm³) or aluminum (approximately 2.7 g/cm³). This high density allows tungsten alloy to provide substantial weight in a smaller volume, meeting the stringent space requirements of counterweight designs.





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com