Tungsten Alloys with High Thermal Shock Resistance via Ammonium Paratungstate
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 06 April 2021 17:49
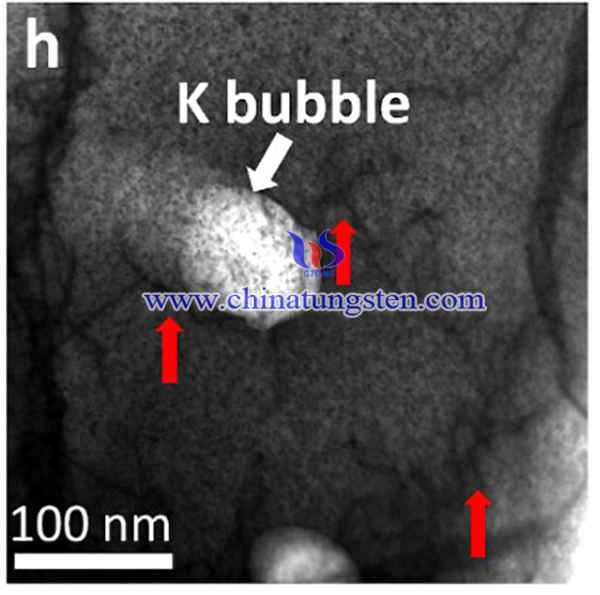
Tungsten (W) alloys has been applied in high temperature resistant materials for decades due to its amazing thermal resistance and toughness. W alloys have been applied in plasma-facing materials, solid target in spallation neutron source, electrical contacts, and fuel elements in rockets, etc. These applications have a requirement on higher mechanical properties and higher temperature stability.
W-Bivo4 Gas Sensing Material Using Ammonium Paratungstate
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 06 April 2021 17:33
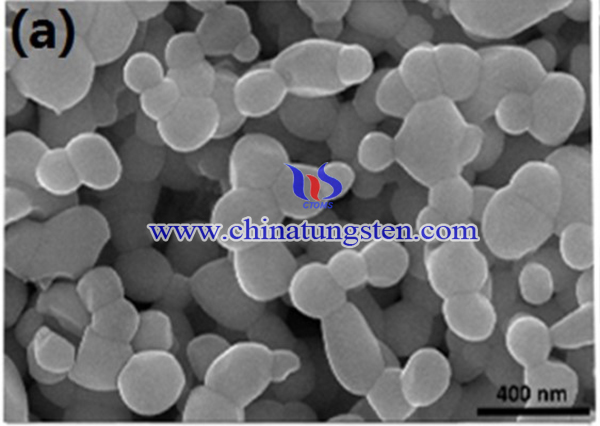

Trimethylamine is a hazardous volatile organic compound that originates from spoiled fishes and sea creatures and has negative effects on air quality and human health. The gas sensing materials based on metal oxide semiconductors have attracted considerable attention due to the advantages on high sensitivity, low-cost synthesis route and compatible with micro-electronic manufacturing technology.
Red Phosphors Fabricated via Ammonium Paratungstate by Sol-Gel Method
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 06 April 2021 17:19
White light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are considered as next generation lighting devices and gained promising attention because of their attractive advantages such as small size, long reliability, low energy consumption, high luminescent efficiency and eco-friendly nature over the conventional incandescent and fluorescent lamps. A technique which combines UV LED and tri-color (Red, Green, Blue) phosphors is a solution to achieve a better display. The combination produces bright white light with high color rendering index and low correlated color temperature. unfortunately, the performance of red phosphor is much weaker than the performance of blue and green phosphors.
Preparation of Tungsten Trioxide Solid Acids Using Ammonium Paratungstate as Tungsten Source
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 06 April 2021 16:42

Solid acid catalysts (SACs) have a widely and valuable industrial applications such as petroleum, biodiesel, and chemical industries. SACS are considered as the most important categories of catalysts that serve the petroleum industry. Thus, SACs promote environmentally benign heterogeneous catalysts that assist wide industrial applications.
Preparation Methods of Tungsten Alloy Ball
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 02 April 2021 14:40
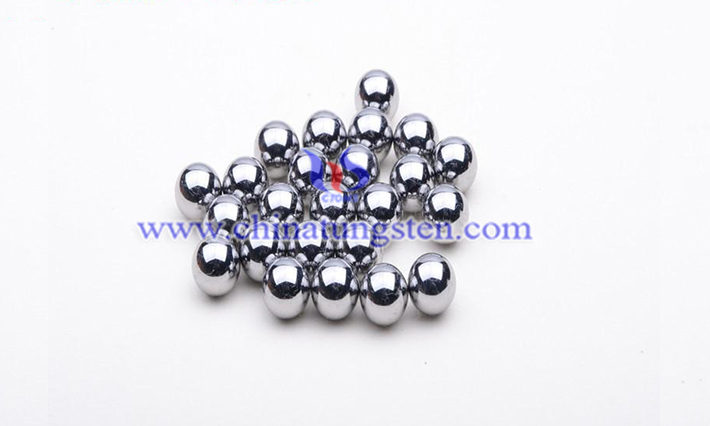

There are four preparation methods of tungsten alloy balls, namely compression molding, disc pelletizing, squeeze-cut rotation and injection molding.
Influencing Factors of Low Temperature Ductility of Tungsten Wire
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 01 April 2021 10:18
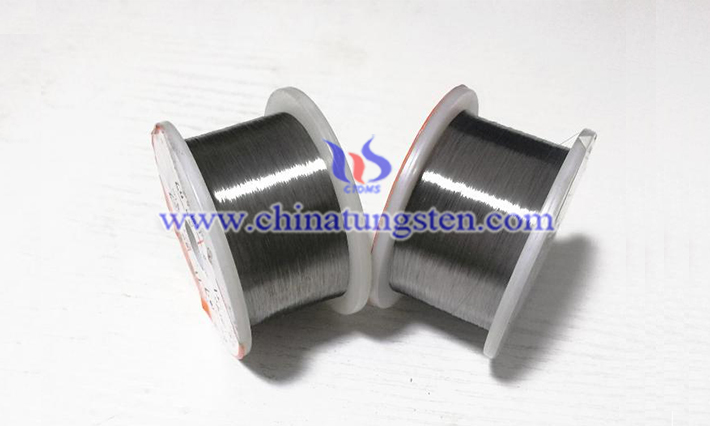

The low-temperature ductility of the tungsten wire is the main factor affecting the winding performance. The main influencing factors are the purity of raw materials, additives and the surface condition of the wire.
Application of Molybdenum in Medicine Field - Molybdenum Target
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 March 2021 09:55

Molybdenum (Mo) and molybdenum alloy materials have wide applications in the manufacturing industry, aerospace industry, steel smelting, petrochemical industry, medical devices, national defense construction and other industrial fields. In the field of medicine, the most widely known and closely relevant to our lives is molybdenum target.
The use of High Purity Molybdenum Sputtering Target in Liquid Crystal Display
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 30 March 2021 09:51
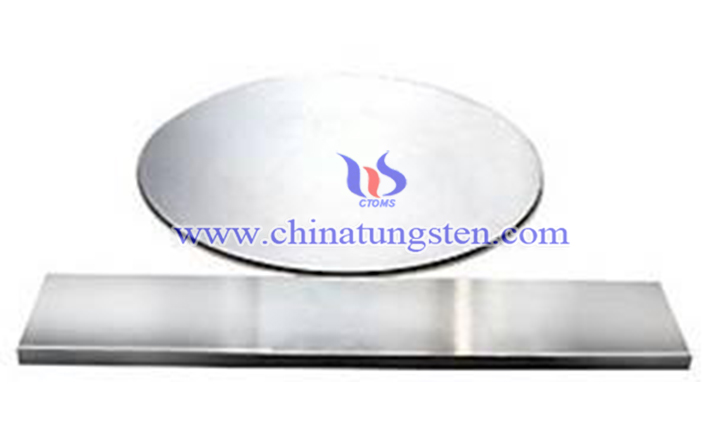
With the development of science and technology, molybdenum shows its advantages in many fields, which has changed human life in various aspects, one of the familiar applications is to manufacture liquid crystal display. Large-size high purity molybdenum sputtering target is the key raw material in the producing of LCD panel, and Mo is one of the preferred materials for sputtering target of LCD panel. This kind of target is used in the daily color TV, intelligent phone, tablet computer and some large household appliances, as well as the control screens of some military communication equipment and other electronic products.
Common Preparation Methods of Molybdenum Powder
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Friday, 26 March 2021 00:03

Molybdenum powder prepared by traditional technology is often used to be raw material of molybdenum sintered products, the common preparation methods include reduction method, fluidized bed reduction method, hydroxyl thermal decomposition method etc.
Preparation of Large-size Tungsten-Based Heavy Alloy
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 25 March 2021 23:07
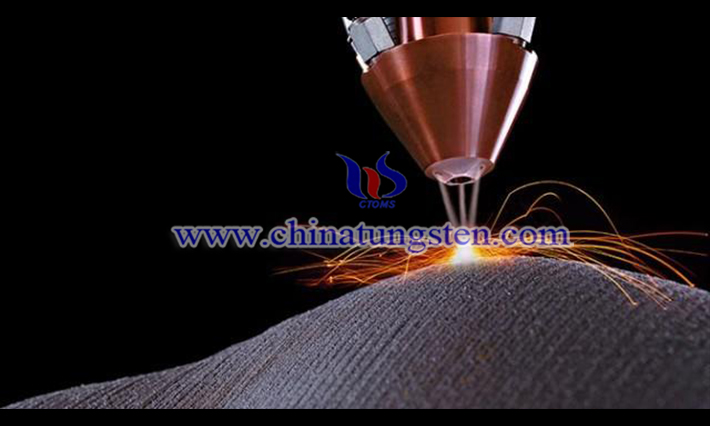

Large-size tungsten-based heavy alloy has a series of advantages including high density, low coefficient of thermal expansion, good oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance, etc. In fields of aerospace, electronic information and so on, large-size and high performance tungsten-based heavy alloy is in urgent need. Find the rule of internal structure of large-size tungsten based high specific gravity alloy during liquid phase sintering process to obtain high homogeneity, high performance and parts of large-size tungsten based high specific gravity alloy.



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com