Beijing Institute of Technology 3D Printing Molybdenum Ion Thruster Components
- Details
- Category: Tungsten's News
- Published on Friday, 26 July 2019 13:45
Researchers in Beijing Institute of Technology are exploring better ways to identify ionic optics by adding materials to make molybdenum components. Their results have recently been published in the paper “3D Printed molybdenum for grids and keeper electrodes in ion thruster”.
The main components of ion thruster are ion optics and protector. Optics plays an important role in the geometry of the engine. However, their erosion limits the life of ion thrusters. The purpose of the protector is to protect the hollow cathode from "ion bombardment" and turn on the cathode discharge. Metals and carbon materials are usually used to make the necessary electrodes. Molybdenum is a metal material commonly used in ion optics and conservative manufacturing.
Among carbon-based materials with near zero thermal expansion coefficients (CTE) and lower sputtering yield than molybdenum, graphite has become a conventional choice because of its low cost and high understanding of its manufacturing methods, although pyrolytic graphite and carbon-carbon composites have been used for many times in ion optical systems mounted on important thrusters, the researchers said.
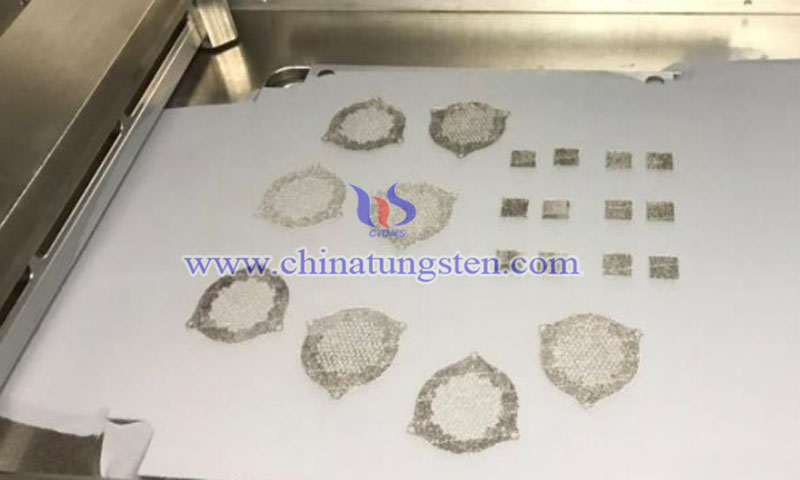
In order to simplify the manufacture of ion optics system, a study was carried out by Beijing University of Technology, focusing mainly on the 3D printing of molybdenum on the parts of electric propeller. It is successful and still in the development stage. So far, several healthy electrodes have been produced. The researchers chose selective laser melting (SLM) for the project, mainly because of its ability to print metals and, of course, because of the level of accuracy it can provide, especially in aerospace. The commonly used metal materials are titanium, aluminum and stainless steel.
The research project of Beijing Polytechnic University has created several 3D printed ion optics components previously used in titanium to further study the concept of ion optics in the fabrication of additives. Another study measured energy density, involving: laser power; laser scanning speed; hatch spacing; layer thickness.
"The results show that the mechanical and thermal properties of SLM molybdenum are similar to those of solid metals when the energy density applied in the preparation process is close to the maximum energy density, thus producing refractories, i.e. about 300 Jmm-3. This fact is related to the porosity produced, which decreases with the increase of energy density. The researchers concluded. The sputtering corrosion behavior of selective laser melting materials has not been evaluated yet, but it must be studied before the components manufactured by the additives can meet the practical application of electric propulsion.

| Molybdenum Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.molybdenum.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com