How to Score A Game of Tungsten Darts
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 18 August 2015 16:28
- Written by yingying
- Hits: 334
Scoring tungsten darts can seem overwhelming at first, but will make more sense once you understand the layout of the board. A round dartboard features 20 sections. The particular section a tungsten dart hits dictates what score you receive. The most common tungsten darts game is called 501, which involves bringing your score from 501 down to zero quicker than your opponent. A scorekeeper keeps track of points scored in each round and how many points you have remaining on a board that’s visible at all times.
The DartBoard
A dartboard is 17.75 inches in diameter and is separated into 20 different sections. Each of these sections is separated with thin metal wires. Around the far edges of the board are numbers, ranging from one to 20. Just inside the numbers is a thin section made of wire that’s referred to the double ring. There is another thin section made of wire further in toward the center of the circle that’s referred to as the triple ring. At the center of the board are the outer and inner bulls-eyes, different-sized circles created with the thin wire.
Scoring By the Numbers
Where your tungsten dart hits on the board influences what score you receive. Tungsten darts that land within the larger sections but not within the double, triple or bulls-eye sections, receive a score equal to that particular section’s number. For example, a tungsten dart landing in this larger area of a section assigned with a point value of 14 receives a score of 14. If the tungsten dart lands within the double section, it earns double points. If a dart lands within the triple section, it earns triple points. Tungsten darts that land within the outer bulls-eye receive 25 points and tungsten darts that land within the inner bulls-eye score 50 points. A tungsten dart that hits outside the wire or doesn’t stick into the board scores a zero.
Example: Playing 501
In the game of 501, both players begin with a score of 501. The goal is to get the score down to zero before your opponent. Each player throws three darts per round with the intention of scoring as many points as possible. For example, if you hit 25, 50 and 12, your score that round would be 87. The highest score possible in a round is 180, which is achieved by hitting the triple twenty with all three darts. After you’re finished with your round, your opponent gets to throw three darts. To win the game, not only do you need to bring your score down to exactly zero, but you have to hit your tungsten dart within the double section with your final tungsten dart. If you fail to hit a double or end up with a score below zero, your opponent gets to go and you have to wait for your next turn.
Keeping Track of Scores
A scorekeeper who is not participating in the game keeps track of the score. For 501, a scoreboard or sheet of paper is typically posted on a nearby wall. The scoreboard is split into two pairs of two columns, with each pair of columns assigned to a player. In each player’s left column, the scorekeeper keeps track of a player’s score for each round. The space in the right column is used to keep track of the countdown from 501. For example, if you scored 87 on your first round, the scorekeeper would write 87 at the top of the left column and 414 at the top of the right column. If you then scored 100 on your second round, the scorekeeper would write 100 just below 87 in the left column and then 313 just below 414 at the top of the right column.
Tungsten Dart Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - http://www.chinadart.com/
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Recycling of Tungsten Mining
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 18 August 2015 11:16
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 301
Recycling
Recycling is an important factor in the world’s tungsten supply. It is estimated that today some 30% is recycled, and the tungsten processing industry is able to treat almost every kind of tungsten-containing scrap and waste to recover tungsten and, if present, other valuable constituents.
Contaminated cemented carbide scrap, turnings, grindings and powder scrap are oxidized and chemically processed to APT in a way similar to that used for the processing of tungsten ores. If present, cobalt, tantalum and niobium are recovered in separate processing lines. Other tungsten containing scrap and residues might require a modified process.
Clean cemented carbide inserts and compacts are converted to powder by the zinc process (treatment with molten zinc which is dissolved in the cobalt phase and is then distilled off, leaving a spongy material which is easily crushed). This powder is added back to the manufacture of ready-to-press powder. By this process, not only tungsten carbide but also cobalt, tantalum carbide and other carbides are recycled.
Recycling of tungsten in high speed steel is high, and a typical melt contains 60 to 70% scrap, including internally generated scrap.
On the other hand, recycling in such applications as lamp filaments, welding electrodes and chemical uses is low.
Although tungsten seems to be relatively harmless to the environment, environmental concerns have led to an increasing recycling rate, especially when the material contains other metals in addition to the tungsten. Recycling is always more environmentally friendly and usually more economic than waste disposal.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Tungsten Mine Supply
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 18 August 2015 11:09
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 296
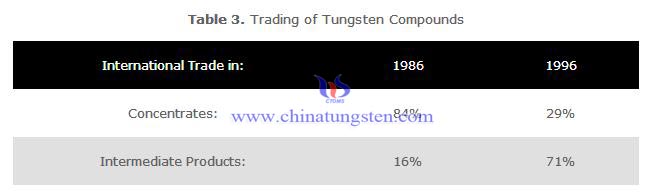
Over the last few years, sources of supply have changed dramatically. In 1986, the USSR was the world’s largest consumer but, by 1992, the reformed CIS was exporting tungsten and by 1996 was the world’s second largest supplier.
The other principal producing countries today are Austria, Bolivia, Peru and Portugal, whilst mines have closed in the last decade in Australia, Brazil, Canada, France, Japan, South Korea, Sweden, Thailand and the USA.
Not only have the sources of supply altered but so have the tungsten compounds traded, as fluctuating price differentials between concentrate and upgraded products and govermental restrictions played their part in the market.
Intermediate products include tungstates, tungsten oxides and hydroxides, W and WC powders, and ferrotungsten.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Tungsten Mining, Pricing and Processing
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 18 August 2015 11:13
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 326
Mining & Beneficiation
Tungsten is usually mined underground. Scheelite and/or wolframite is frequently located in rather narrow veins which are slightly inclined and often widen with the depth. Open pit mines exist but are rare.
Most tungsten ores contain less than 1.5% WO3 and ore dressing plants are always in close proximity to the mine.
The ore is first crushed and milled to liberate the tungsten mineral crystals.
Scheelite ore can be concentrated by gravimetric methods, often combined with froth flotation, whilst wolframite ore can be concentrated by gravity, sometimes in combination with magnetic separation.
Pricing
The average annual price of tungsten since 1950 has fluctuated between a nadir of US $10 per metric ton unit in 1963 and a peak of US $175 in 1977. During the last five years, trade in concentrates has diminished and the market has relied more and more upon the APT quotation as a price guide since APT is the product traded in the largest quantity. Prices are mainly based on the quotations published twice a week by London’s "Metal Bulletin", although other trade journals also publish quotations or indicative prices.
Processing Concentrates
Most tungsten concentrates are processed chemically to ammonium paratungstate (APT). Secondary raw materials like (oxidized) scrap and residues are another important feed for chemical tungsten processing.
Wolframite concentrates can also be smelted directly with charcoal or coke in an electric arc furnace to produce ferrotungsten (FeW) which is used as alloying material in steel production.
Pure scheelite concentrate may also be added directly to molten steel.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn
Tungsten Minerals and Deposits
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 18 August 2015 11:05
- Written by xinyi
- Hits: 329
Minerals
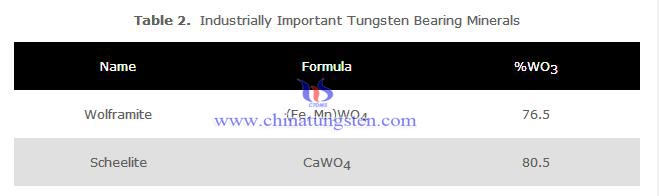
Tungsten occurs in the natural state only in the form of chemical compounds with other elements. Although more than twenty tungsten bearing minerals are known, only two of them are important for industrial use, namely wolframite and scheelite.
Pure scheelite has blue-white fluorescence in ultraviolet light, a property which is utilised in prospecting. Wolframite is a general term for iron and manganese tungstates where the iron/manganese ratio can vary. A mineral with more than 80% FeWO4 is called Ferberite and a mineral with more than 80% MnWO4 is called Hübnerite.
Deposits
All tungsten deposits are of magmatic or hydrothermal origin. During cooling of the magma, differential crystallization occurs, and scheelite and wolframite are often found in veins where the magma has penetrated cracks in the earth's crust. Most of the tungsten deposits are in younger mountain belts, i.e. the Alps, the Himalayas and the circum-Pacific belt.
The concentration of workable ores is usually between 0.3 and 1.0% WO3.
Tungsten Powder Manufacturer & Supplier: Chinatungsten Online - www.tungsten-powder.com
Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797
Email: sales@chinatungsten.com
Tungsten & Molybdenum Information Bank: http://i.chinatungsten.com
Tungsten News & Tungsten Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com
Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn





 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com