Rare Earth Affected Tungsten Electrode Sintering Process - Temperature and Density
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Thursday, 26 May 2016 19:44
For powder sintering, the process is generally divided into three phases. The first phase is the initial sintering, called bonding stage. In this phase due to the temperature rise, the atomic amplitude of contact point between the particles is increase and there will have diffusion occurs, making particle contact change from point to the surface. And inner grains of particle are not change. Besides, the particle shape has little change and sintered blank is no shrinkage. What’s more sintered blank density changed little, but the strength and conductivity of it has increased significantly.
The second phase is sintering neck growth and produce sticky plastic flow stage. In this stage, the temperature is higher, so the migration rate of atoms phase junction surface is increase. And migration rate increase makes sintering neck to grow up and particle distance to reduce, forming the associated pore network. Besides, the grains in the particles grow up and grain boundaries moves over the pores. What’s more, the placed where grain boundary swept the pores disappear, so in this phase sintering blank has obvious shrinkage phenomenon and density and strength has significantly enhanced.
The third stage is closed pores spheroidization and shrinking stage. At this stage, most of the pores are completely divided, so closed-pore number has increased considerably and the shapes of pores tend to spherical and shrinking. Besides, at this stage, the entire sintered body continues to shrink. Closed-pore number has increased and shape tends to spherical achieved by pores disappearing and pores quantity reducing. What’s more, this stage can last for a long time.
The core process of sintering is the material migration. According to the migration patterns the powder sintering mechanism can be divide into there types which is diffusion mechanism, evaporation mechanism and condensation flow mechanism.
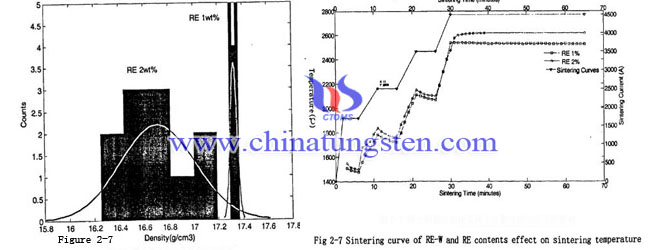
Analysis at the same sintering process, different rare earth content tungsten powder sintered, to understand the role of rare earth in tungsten powder sintering process and its influence on the tungsten electrode. The sintering curves and temperature change of different content rare earth tungsten billet shown in Figure 2-7. From the Figure 2-7 you can see at the same sintering current, rare earth content increase will lead to sintering temperature rises. And the reason is due to the rare earth and other impurities content increased, the electron scattering effect increased as well, causing the resistivity of the sintered tungsten bar increased. For constant current fusion sintering verification, the performance is the temperature also rises.
To test density of many tested sintered blank found the density is normal distribution, showing in Figure 2-8. From Figure 2-8 we can see two type tungsten powders which have different rare earth content in the same sintering process, the density has significantly different. Rare earth content with 1%, the tungsten powder after sintered has large density and has narrow distribution. The standard deviation is about 0.028. Tungsten powder with 2% rare earth content in the sintering process has lower density and has wide distribution. The standard deviation is about 0.303. Description in this process, tungsten electrode blank has strong sensitivity and production stability is difficult to control.
| Tungsten Metals Supplier: Chinatungsten Online www.tungsten.com.cn | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com