Sodium Tungstate Solution Activity Coefficient
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 13 January 2016 20:41
Concept of activity was put forward firstly by G.N.Lewis in 1907. It is quickly applied in electrochemistry to determine the activity coefficient of electrolytes in aqueous solution. Activity coefficient refers to the ratio of activity and the concentration. Due to the interaction between ions in the electrolyte solution, the total concentration of electrolyte can’t represent its effective concentration. An experience correction factor (activity coefficient) needs to be introduced to indicate the deviation of actual solution and ideal solution.
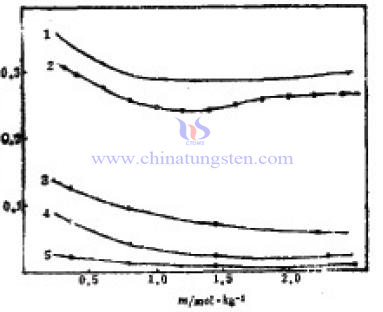 Due to the different measuring methods of sodium tungstate in the aqueous solution activity coefficient, the results have larger differences. This paper combining with inorganic salt aqueous solution thermodynamic properties, measures the activity coefficient of sodium tungstate in aqueous solution by the equal-pressure method. Experimental methods can be divided into following three points:
Due to the different measuring methods of sodium tungstate in the aqueous solution activity coefficient, the results have larger differences. This paper combining with inorganic salt aqueous solution thermodynamic properties, measures the activity coefficient of sodium tungstate in aqueous solution by the equal-pressure method. Experimental methods can be divided into following three points:
1. Take a certain amount of sodium tungstate, potassium chloride and sodium chloride to match into the appropriate concentration of solution and place them in the glass dryer.
2. Put the dryer on waterbath shake frame, swing 20 times per minute to build the balance. The balance time of the system varies with different concentrations.
3. After balance, weigh sample dish and calculate the concentration of the solution balanced from the change of solution. The solution with appropriate attenuation, repeat the above operation to dilute the concentration of 0.3mol.kg-1.
In 1981, Goldberg and others reported the activity coefficient calculated value of sodium tungstate solution within 0.001-2.25mol.kg-1 concentration. Value In each of the corresponding concentrations is higher than the experiment between 0.03 and 0.04. Deviation is normal. Curve 1 and 2 in figure also show that the activity coefficient changing with the concentration consistently. When concentration increases, the activity coefficient decreases. When the concentration reaches 1.4mol.kg-1, activity coefficient begins to increase again. But the change range is same with the high temperature and both are relatively small. The curve 3, 4 and 5 in the graph are the results of the high temperature. Seeing from curve, the higher the temperature is, the smaller the activity coefficient value is. As temperatures rising, strong interactions occur in the ions of the solution. This effect will strengthen with the increase of concentration.
| Sodium Tungstate Supplier: Chinatungsten sodium-tungstate.com | Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797;Email:sales@chinatungsten.com |
| Tungsten News & Prices, 3G Version: http://3g.chinatungsten.com | Molybdenum News & Molybdenum Price: http://news.molybdenum.com.cn |



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com