What Is the Standard Molar Enthalpy Change for the Reaction of Tungsten Diiodide?
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Sunday, 09 July 2023 13:04
The standard molar enthalpy change for the reaction of tungsten diiodide (WI2) is -70.61 kJ/mol. it is defined as the thermodynamic energy change between the reactants (i.e., W and I2) required for the formation of 1 mol of WI2 and its corresponding reaction product (i.e., the WI2 gas) under the standard condition. Specifically, the enthalpy of formation of the reaction of tungsten diiodide can be determined by determining the standard molar enthalpy of formation of tungsten, iodine, and tungsten diiodide, a value that can be obtained by experimental measurement.
A common method is to use calorimetry, using the standard molar enthalpy of formation of WI2 as an example, to measure the amount of heat released or absorbed during the reaction (i.e., the heat of reaction) by adding a known mass of WI2 solid to a hot vessel at a constant temperature and reacting it with a known amount of oxygen. The standard enthalpy of the reaction can then be used to calculate the standard molar enthalpy of the formation of WI2, a process that can be represented by the following equation:
W(s) + I2(g) ==WI2(g); ΔrHmθ =?
Among them, W(s) represents solid tungsten, I2(g) represents gaseous iodine, and WI2(g) represents gaseous tungsten diiodide.
The enthalpy of formation ΔrHmθ of a reaction can be calculated by applying the first law of thermodynamics, which is the law of conservation of energy. According to this law, the ΔrHmθ of a reaction is equal to the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants minus the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the products, i.e.
ΔrHmθ(WI2,g)= ΔfHmθ(WI2,g) -ΔfHmθ(I2,g)- ΔfHmθ(W,s)
ΔfHmθ represents the standard enthalpy of generation and the coefficients represent the number of moles of each substance in the products and reactants.
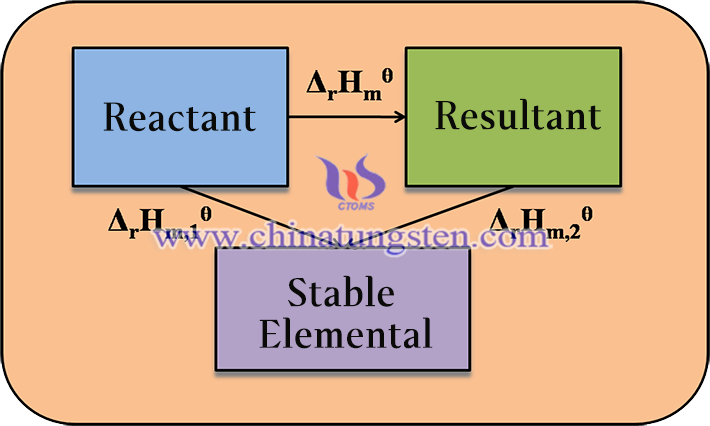
For this reaction, the reactants are tungsten and iodine and the product is tungsten diiodide. Their standard enthalpies of formation are as follows:
ΔfHmθ(W,s) = 0 kJ/mol
ΔfHmθ(I2,g) = 62.24 kJ/mol
ΔfHmθ(WI2,g) =-8.37 kJ/mol
Substituting these values into the above equation, the enthalpy of generation of tungsten diiodide can be calculated as:
ΔrHmθ(WI2,g)= ΔfHmθ(WI2,g) -ΔfHmθ(I2,g)- ΔfHmθ(W,s)
= [-8.37] - [0 + 62.24]
= -70.61 kJ/mol
Therefore, the heat released by the reaction of 1 mol of tungsten and 1 mol of iodine to form 1 mol of tungsten diiodide is 70.61 kJ/mol in the standard state.
- Tungsten Oxide Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.tungsten-oxide.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com