Chemical Methods for WS2 Film Preparation
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Wednesday, 14 September 2022 00:41
Two common methods for preparing tungsten disulfide (WS2) films by chemical methods are chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and hydrothermal growth of single-crystal tungsten disulfide from aqueous solutions under high temperature and pressure conditions. CVD is the most common method used to prepare tungsten disulfide. The CVD method involves a reaction process in which a gaseous precursor reacts chemically on a solid surface to produce a solid deposit.
Preparation of tungsten disulfide by CVD can be achieved using either a one-step or a two-step method. The one-step method involves direct heating of the sulfur and tungsten sources in a CVD furnace followed by controlled carrier gas flow and then deposition of WS2 films on the target substrate. A commonly used tungsten source is WO3, where the reaction 2WO3 + 7 S → WS2 + 3 SO2 occurs.
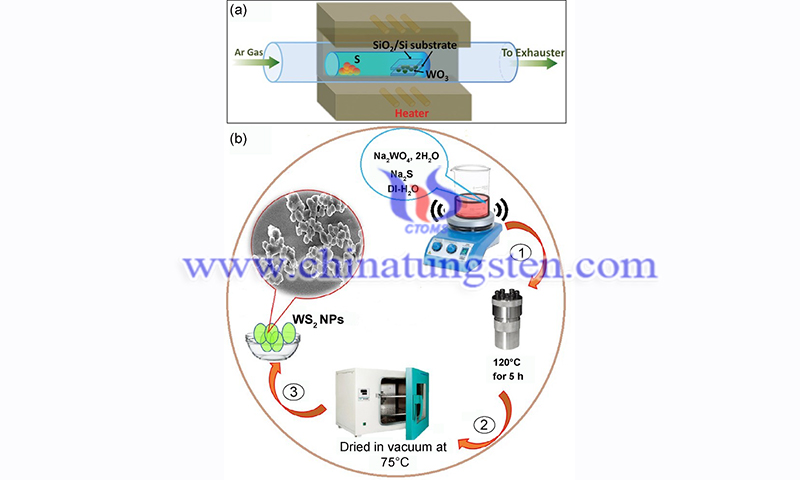
The most commonly used substrates are silicon, copper, and quartz glass. The two-step method consists of depositing a thin film of tungsten or tungsten compound on the target substrate, followed by sulfidation in a CVD furnace to synthesize the tungsten disulfide film. Typically, the deposition is performed by electron beam evaporation or magnetron sputtering on the substrate.
For example, Carlo et al. prepared W films by magnetron sputtering and then sulfurized them. Their experimental results showed that the number of layers can be highly controlled by controlling the initial deposition thickness of W films, and tungsten disulfide films can be prepared on a large area using this method. CVD can precisely control the thickness and size of WS2 films by controlling the variation of temperature and carrier gas flow rate.
High-quality tungsten disulfide films with good optical and electrical properties can be synthesized using CVD. In addition, the two-step method enables the preparation of large-scale films, thus overcoming the drawbacks of the one-step method. However, this method still has disadvantages, such as the need for high substrate temperatures and relatively expensive equipment.
The hydrothermal method is a typical wet chemical synthesis method. For the preparation of WS2 films, the following representative procedure can be used. First, 10 mmol of Na2WO4, 2H2O, and 10 mmol of Na2S are dissolved in 50 ml of deionized water and stirred continuously for 30 min to form a clear solution. The solution was then transferred to a hydrothermal reactor for 5 h at 220℃.
(Photo source: Rosanna Mastria et al/Nature)
Finally, the tungsten disulfide particles were collected after vacuum drying at 75◦ C. This method has been widely used for the preparation of two-dimensional nanomaterials, especially WS2 particles. The advantages of the hydrothermal method are high purity, high crystallinity of the formed particles, and easy control of the operating parameters. However, the thickness of the film cannot be controlled when used in the device and the reaction process is not obvious.
Cited Article: Ding J, Feng A, Li X, et al. Properties, preparation, and application of tungsten disulfide: A review [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2021, 54(17): 173002.
- Tungsten Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: www.chinatungsten.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com