Synthesis of W-Cu Nanocomposite Using Ammonium Metatungstate by A Novel Solution Combustion
- Details
- Category: Tungsten Information
- Published on Tuesday, 27 July 2021 05:26
W–Cu composite combine high electrical and thermal conductivity of Cu and high arc corrosion resistance, hardness, and low thermal expansion coefficient of tungsten, and show excellent properties. Due to the distinct performance, W–Cu composites have found potential applications in electronic packaging, electric contact, aerospace, and some other high-tech areas. However, in some severe working environments, such as aerospace, micro electric manufacturing, etc, may face the issues of low relatively density and inhomogeneous microstructure.

In order to get over these issues and drawbacks, scientist had applied many strategies. Addition of Ni, Fe and some other elements into W-Cu powders as sintering aids, is a conventional and effective route to increase the sintered density. Unfortunately, these sintering materials might largely lower the electrical and thermal conductivity of the sintered W-Cu composites
To enhance the physical properties, W-Cu nanocomposite (W-30 wt%Cu) was synthesized using ammonium metatungstate (AMT) as raw material. The synthesis process of the W-Cu composite is as below:
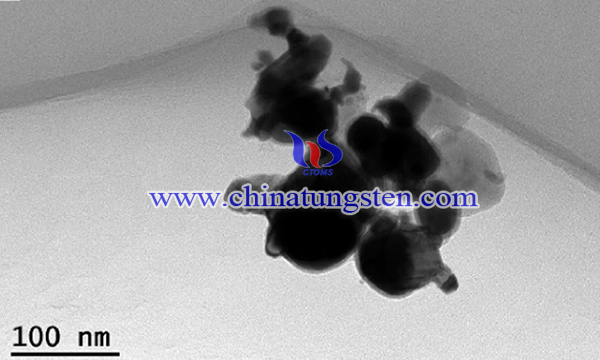
Firstly, ammonium metatungstate (AMT) was used to prepare solution with concentration of 0.01 mol/L. 0.24 mol/L ammonium nitrate and glycine (with molar ration of 1:1.5) were added into the solution. The mass ratio of copper to tungsten (Cu: W) in the solution was fixed at 3:7. The above mixed solution was heated to 250 °C on an electrical furnace in air for thermal process. During heating the water in the solution evaporates and a gelatinous mass forms. Upon further heating, the resultant mass swells suddenly, accompanied with the release of a lot of gases. The whole process of swelling and combustion of the gels indicates the non-explosive and self-propagating exothermic reaction, which takes in less than 1 min.
The combustion products were heated in high purity hydrogen gas with a flow rate of 200 ml min−1 to obtain the W-30Cu composite powders, at 700 °C. The resultant powders were uniaxially compacted at a pressure of 650 MPa into green pellets with size of Φ 20 × 3 mm. The green compacts then sintered in H2 atmosphere at 1200 °C for 2 h.
In conclusion, W-Cu nanocomposite with excellent physical properties was synthesized using ammonium metatungstate (AMT) as raw material. AMT and copper nitrate were applied as metallic ion sources. The W-Cu nanocomposite has an average particle size of 70 nm, and the sintered W-Cu samples posse homogeneous microstructure and good physical and mechanical properties. The relative density, microhardness and thermal conductivity reach 98.6%, 245.6HV and 223.55 W/(m·k), respectively.
- AMT Manufacturer & Supplier, Chinatungsten Online: ammonium-metatungstate.com
- Tungsten News & Prices of China Tungsten Industry Association: www.ctia.com.cn
- Molybdenum News & Price: news.molybdenum.com.cn
- Tel.: 86 592 5129696; Fax: 86 592 5129797; Email: sales@chinatungsten.com



 sales@chinatungsten.com
sales@chinatungsten.com